Abstract
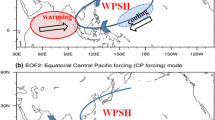
Investigating the relationships among different factors impacting the East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) is urgent for improving its predictability. In the present study, two factors, the Tibetan Plateau (TP) atmospheric thermal forcing and the Indian Ocean sea surface temperature basin mode (IOBM), are selected to compare their relative contributions to the interannual variability of the EASM. Both statistical methods and numerical experiments are used to separate and compare their respective influences under realistic circumstances. The results indicate that the IOBM mainly drives an anticyclonic anomaly over the northwestern Pacific in the lower troposphere, which is consistent with the dominant mode of the EASM circulation system. Meanwhile, influences from the TP thermal forcing are primarily on the anticyclonic anomaly over the TP in the upper troposphere, together with the enhanced southwesterly over southern China and a northerly anomaly over northern China in the lower troposphere. Moreover, the TP thermal forcing seems to play a more important role than the IOBM in affecting the main rainfall belt of the EASM, which extends from the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River to Japan. Such a rainfall pattern anomaly is directly related to the anomalous northerly over northern China and the resultant stronger moisture convergence over the main rainfall belt region when a strong TP thermal forcing occurs. In addition, the IOBM can increase the precipitation over the southeastern TP during its positive phase and hence enhance the in situ atmospheric heat source to a certain degree.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler RF, Huffman GJ, Chang A et al (2003) The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979-present). J Hydrometeorol 4:1147–1167
Chang CP, Zhang Y, Li T (2000) Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific SSTs. Part I: roles of the subtropical ridge. J Clim 13:4310–4325
Clough SA, Shephard MW, Mlawer EJ, Delamere JS, Iacono MJ, Cady-Pereira K, Boukabara S, Brown PD (2005) Atmospheric radiative transfer modeling: a summary of the AER codes. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transf 91:233–244
Dee DP, Uppala SM, Simmons AJ et al (2011) The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137:553–597
Ding Y, Chan JC (2005) The East Asian summer monsoon: an overview. Meteorol Atmos Phys 89:117–142
Duan AM, Wu GX (2005) Role of the Tibetan Plateau thermal forcing in the summer climate patterns over subtropical Asia. Clim Dyn 24:793–807
Duan AM, Wu GX (2008) Weakening trend in the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan plateau during recent decades. Part I: observations. J Clim 21:3149–3164
Duan AM, Wang MR, Lei YH, Cui YF (2013) Trends in summer rainfall over China associated with the Tibetan Plateau sensible heat source during 1980–2008. J Clim 26:261–275
Ebita A, Kobayashi S, Ota Y et al (2011) The Japanese 55-year reanalysis “JRA-55”: an interim report. SOLA 7:149–152
Edwards JM, Slingo A (1996) Studies with a flexible new radiation code. 1. Choosing a configuration for a large-scale model. Q J R Meteorol Soc 122:689–719
Feng L, Zhou T (2012) Water vapor transport for summer precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: multidata set analysis. J Geophys Res 117:D20114. doi:10.1029/2011JD017012
Fu CB, Teng XL (1988) Summer climate anomalies of China in association with ENSO phenomenon. Sci Atmos Sin special issue for 60th anniversary of IAP, pp 125–137
Gong DY, Ho CH (2003) Arctic oscillation signals in the East Asian summer monsoon. J Geophys Res 108(D2):4066. doi:10.1029/2002JD002193
Gong Y, Ji L (1998a) The numerical experiment of the medium-range change of the subtropical high I: the influence of the heat source over Tibetan Plateau. J Trop Meteorol 14(2):106–112
Gong Y, Ji L (1998b) The numerical experiment of the medium-range change of the subtropical high II: the influence of the heat source over tropical western Pacific. J Trop Meteorol 14(3):201–207
Gong DY, Yang J, Kim SJ, Gao Y, Guo D, Zhou T, Hu M (2011) Spring Arctic oscillation-East Asian summer monsoon connection through circulation changes over the western North Pacific. Clim Dyn 37:2199–2216
Harris LM, Lin SJ (2014) Global-to-regional nested grid climate simulations in the GFDL high resolution atmospheric model. J Clim 27(13):4890–4910
Holtslag AAM, Boville BA (1993) Local versus nonlocal boundary-layer diffusion in a Global Climate Model. J Clim 6:1825–1842
Hsu HH, Liu X (2003) Relationship between the Tibetan Plateau heating and East Asian summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 30(20):2066. doi:10.1029/2003GL017909
Huang R (1985) The influence of the heat source anomaly over Tibetan Plateau on the northern hemispheric circulation. Acta Meteorol Sin 43(2):208–220
Huang SS, Yang XQ, Jiang QR, Tang MM, Wang ZM, Xie Q, Zhu YC (1995) The effects of the polar sea ice on climate. J Meteorol Sci 15(4):46–56 (in Chinese)
Jian M, Luo H, Qiao Y (2004) On the relationships between the summer rainfall in China and the atmospheric heat sources over the Eastern Tibetan Plateau and the Western Pacific warm pool. J Tropical Meteorol 20(4):355–364
Kanamitsu M, Ebisuzaki W, Woollen J, Yang S, Hnilo JJ, Fiorino M, Potter GL (2002) NCEP–DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83:1631–1643
Li CF, Yanai M (1996) The onset and interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon in relation to land–sea thermal contrast. J Clim 9:358–375
Li G, Duan T, Gong Y (2000) The bulk transfer coefficients and surface fluxes on the western Tibetan Plateau. Chin Sci Bull 45:1221–1226
Liu YM, Wu GX, Ren RC (2004) Relationship between the subtropical anticyclone and diabatic heating. J Clim 17:682–698
Luo H, Chen R (1995) The impact of the anomalous heat sources over the Eastern Tibetan Plateau on the circulation over East Asia in summer half year. Sci Meteorol Sin 15(4):94–102
Nan S, Li J (2003) The relationship between the summer precipitation in the Yangtze River valley and the boreal spring Southern Hemisphere annular mode. Geophys Res Lett 30(24):2266. doi:10.1029/2003GL018381
Nan SL, Li JP, Yuan XJ, Zhao P (2009) Boreal spring Southern Hemisphere annular mode, Indian Ocean sea surface temperature, and East Asian summer monsoon. J Geophys Res 114:D02103. doi:10.1029/2008JD010045
Nordeng TE (1994) Extended versions of the convective parameterization scheme at ECMWF and their impact on the mean and transient activity of the model in the tropics. Research Department Technical Memorandum No. 206, ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading, UK
Palmer TN, Shutts GJ, Swinbank R (1986) Alleviation of a systematic westerly bias in general-circulation and numerical weather prediction models through an orographic gravity-wave drag parameterization. Q J R Meteor Soc 112:1001–1039
Rayner NA, Parker DE, Horton EB, Folland CK, Alexander LV, Rowell DP, Kent EC, Kaplan A (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res 108(D14):4407. doi:10.1029/2002JD002670
Saji NH, Yamagata T (2003) Possible impacts of Indian Ocean dipole mode events on global climate. Clim Res 25(2):151–169
Song F, Zhou T (2014) Interannual variability of East Asian summer monsoon Simulated by CMIP3 and CMIP5 AGCMs: skill dependence on Indian Ocean-Western Pacific anticyclone teleconnection. J Clim 27:1679–1697
Sun Z (2011) Improving transmission calculations for the Edwards–Slingo radiation scheme using a correlated-k distribution method. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137:2138–2148. doi:10.1002/qj.880
Tiedtke M (1989) A comprehensive mass flux scheme for cumulus parameterization in large-scale models. Mon Weather Rev 117:1779–1800
Wang B, Wu RG, Fu XH (2000) Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J Clim 13:1517–1536
Wang B, Bao Q, Hoskins B, Wu GX, Liu YM (2008a) Tibetan plateau warming and precipitation changes in East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 35:L14702. doi:10.1029/2008GL034330
Wang B, Wu ZW, Li JP, Liu J, Chang CP, Ding YH, Wu GX (2008b) How to measure the strength of the East Asian summer monsoon. J Clim 21:4449–4463
Wang B, Liu J, Yang J, Zhou T, Wu Z (2009a) Distinct principal modes of early and late summer rainfall anomalies in East Asia. J Clim 22:3864–3875
Wang B, Lee JY, Kang IS et al (2009b) Advance and prospectus of seasonal prediction: assessment of the APCC/CliPAS 14-model ensemble retrospective seasonal prediction (1980–2004). Clim Dyn 33:93–117
Wang B, Xiang B, Lee JY (2013) Subtropical high predictability establishes a promising way for monsoon and tropical storm predictions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:2718–2722
Wang Z, Duan A, Wu G (2014) Time-lagged impact of spring sensible heat over the Tibetan Plateau on the summer rainfall anomaly in East China: case studies using the WRF model. Clim Dyn 42:2885–2898
Weng H, Ashok K, Behera S, Rao S, Yamagata T (2007) Impacts of recent El Niño Modoki on dry/wet conditions in the Pacific rim during boreal summer. Clim Dyn 29:113–129
Wu RG, Kirtman BP (2007) Observed relationship of spring and summer East Asian rainfall with winter and spring Eurasian snow. J Clim 20:1285–1304
Wu TW, Qian ZA (2003) The relation between the Tibetan winter snow and the Asian summer monsoon and rainfall: an observational investigation. J Clim 16:2038–2051
Wu G, Liu H, Zhao Y, Li W (1996) A nine-layer atmospheric general circulation model and its performance. Adv Atmos Sci 13(1):1–18
Wu B, Zhou TJ, Li T (2009a) Seasonally evolving dominant interannual variability modes of East Asian climate. J Clim 22:2992–3005
Wu BY, Zhang RH, Wang B, D’Arrigo R (2009b) On the association between spring Arctic sea ice concentration and Chinese summer rainfall. Geophys Res Lett 36:L09501. doi:10.1029/2009GL037299
Wu Z, Wang B, Li J, Jin FF (2009c) An empirical seasonal prediction model of the East Asian summer monsoon using ENSO and NAO. J Geophys Res 114:D18120
Wu B, Li T, Zhou TJ (2010) Relative contributions of the Indian Ocean and Local SST anomalies to the maintenance of the Western North Pacific anomalous anticyclone during the El Niño decaying summer. J Clim 23:2974–2986
Wu GX, Liu YM, He B, Bao Q, Duan AM, Jin FF (2012) Thermal controls on the Asian summer monsoon. Sci Rep 2:404. doi:10.1038/srep00404
Xiang B, Wang B, Yu W, Xu S (2013) How can anomalous western North Pacific Subtropical High intensify in late summer? Geophys Res Lett 40:2349–2354
Xie SP, Hu KM, Hafner J, Tokinaga H, Du Y, Huang G, Sampe T (2009) Indian ocean capacitor effect on Indo-Western Pacific Climate during the summer following El Niño. J Clim 22:730–747
Yanai M, Wu GX (2006) Effects of the Tibetan Plateau. In: Wang B (ed) The Asian monsoon. Springer Praxis, Chichester, pp 513–549
Yang S, Lau KM (1998) Influences of sea surface temperature and ground wetness on Asian summer monsoon. J Clim 11:3230–3246
Yang S, Lau KM (2006) Interannual variability of the Asian monsoon. In: Wang B (ed) The Asian monsoon. Springer Praxis, Chichester, pp 259–293
Yang JL, Liu QY, Xie SP, Liu ZY, Wu LX (2007) Impact of the Indian Ocean SST basin mode on the Asian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 34:L02708. doi:10.1029/2006GL028571
Yasutomi N, Hamada A, Yatagai A (2011) Development of a long-term daily gridded temperature dataset and its application to rain/snow discrimination of daily precipitation. Glob Environ Res 15(2):165–172
Ye B, Yang D, Ding Y, Han T, Koike T (2004) A bias-corrected precipitation climatology for China. J Hydrometeorol 5:1147–1160
Yeh TC, Gao YX (1979) Meteorology of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau. Science Press, Beijing
Yu HY, Bao Q, Zhou LJ (2014) Sensitivity of precipitation in aqua-planet experiments with an AGCM. Atmos Ocean Sci Lett 7:1–6
Zar J (1998) Biostatistical analysis, 4th edn. Pearson Education, Boston
Zhao P, Chen LX (2001) Interannual variability of atmospheric heat source/sink over the Qinghai–Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau and its relation to circulation. Adv Atmos Sci 18:106–116
Zhao P, Zhang X, Zhou X, Ikeda M, Yin Y (2004) The sea ice extent anomaly in the North Pacific and its impact on the East Asian summer monsoon rainfall. J Clim 17:3434–3447
Zhao P, Zhou ZJ, Liu JP (2007) Variability of Tibetan spring snow and its associations with the hemispheric extratropical circulation and East Asian summer monsoon rainfall: an observational investigation. J Clim 20:3942–3955
Zhou L, Liu Y, Bao Q (2012) Computational performance of the high-resolution atmospheric model FAMIL. Atmos Ocean Sci Lett 5:355–359
Zhou XJ, Zhao P, Chen JM, Chen LX, Li WL (2009) Impacts of thermodynamic processes over the Tibetan Plateau on the Northern Hemispheric climate. Earth Sci 39:1473–1486. doi:10.1007/s11430-009-0194-9
Zhou L, Bao Q, Liu Y, Wu G, Wang WC, Wang X, He B, Yu H, Li J (2015) Global energy and water balance: characteristics from finite-volume atmospheric model of the IAP/LASG (FAMIL1). J Adv Model Earth Syst. doi:10.1002/2014MS000349
Zhu Y (2009) The Antarctic oscillation-East Asian summer monsoon connections in NCEP-1 and ERA-40. Adv Atmos Sci 26:707–716
Zhu Z, Li T, He J (2014) Out-of-phase relationship between boreal spring and summer decadal rainfall changes in southern China. J Clim 27:1083–1099
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Yimin Liu for providing constructive suggestions regarding experimental design, and thank two anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments. This work was supported jointly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 91337216 and 41175070) and the Special Fund for Public Welfare Industry (meteorology) administered by the Chinese Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant No. GYHY201406001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Duan, A. Relative contributions of the Tibetan Plateau thermal forcing and the Indian Ocean Sea surface temperature basin mode to the interannual variability of the East Asian summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 45, 2697–2711 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2503-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2503-7