Abstract
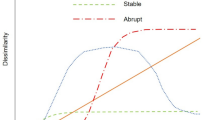
The Chew Bahir Drilling Project (CBDP) aims to test possible linkages between climate and evolution in Africa through the analysis of sediment cores that have recorded environmental changes in the Chew Bahir basin. In this statistical project we consider the Chew Bahir palaeolake to be a dynamical system consisting of interactions between its different components, such as the waterbody, the sediment beneath lake, and the organisms living within and around the lake. Recurrence is a common feature of such dynamical systems, with recurring patterns in the state of the system reflecting typical influences. Identifying and defining these influences contributes significantly to our understanding of the dynamics of the system. Different recurring changes in precipitation, evaporation, and wind speed in the Chew Bahir basin could result in similar (but not identical) conditions in the lake (e.g., depth and area of the lake, alkalinity and salinity of the lake water, species assemblages in the water body, and diagenesis in the sediments). Recurrence plots (RPs) are graphic displays of such recurring states within a system. Measures of complexity were subsequently introduced to complement the visual inspection of recurrence plots, and provide quantitative descriptions for use in recurrence quantification analysis (RQA). We present and discuss herein results from an RQA on the environmental record from six short (< 17 m) sediment cores collected during the CBDP, spanning the last 45 kyrs. The different types of variability and transitions in these records were classified to improve our understanding of the response of the biosphere to climate change, and especially the response of humans in the area.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrose SH (1998) Late Pleistocene human population bottlenecks, volcanic winter, and the differentiation of modern humans. J Hum Evol 35:115–118. https://doi.org/10.1006/jhev.1998.0219
Berke MA, Johnson TC, Werne JP, Livingstone DA, Grice K, Schouten S, Sinninghe Damsté JS (2014) Characterization of the last deglacial transition in tropical East Africa: insights from Lake Albert. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 409:1–8
Brandt SA, Fisher EC, Hildebrand EA, Vogelsang R, Ambrose SH, Lesur J, Wang H (2012) Early MIS 3 occupation of Mochena Borago Rockshelter, Southwest Ethiopian highlands: implications for Late Pleistocene archaeology, paleoenvironments and modern human dispersals. Quatern Int 274:38–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2012.03.047
Brooks N (2006) Cultural responses to aridity in the Middle Holocene and increased social complexity. Quatern Int 151:29–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2006.01.013
Brown ET, Johnson TC, Scholz CA, Cohen AS, King JW (2007) Abrupt change in tropical African climate linked to the bipolar seesaw over the past 55,000 years. Geophys Res Lett 34:L20702. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL031240
Builes-Jaramillo A, Marwan N, Poveda G, Kurths J (2018) Nonlinear interactions between the Amazon River basin and the Tropical North Atlantic at interannual timescales. Clim Dyn 50:2951–2969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3785-8
Campisano CJ, Cohen AS, Arrowsmith JR, Asrat A, Behrensmeyer AK, Brown ET, Deino AL, Deocampo DM, Feibel CS, Kingston JD, Lamb HF, Lowenstein TK, Noren A, Olago DO, Owen RB, Pelletier JD, Potts R, Reed KE, Renaut RW, Russell JM, Russell JL, Schäbitz F, Stone JR, Trauth MH, Wynn JG (2017) The Hominin Sites and Paleolakes Drilling Project: high-resolution paleoclimate records from the East African Rift System and their implications for understanding the environmental context of hominin evolution. PaleoAnthropology 2017:1–43. https://doi.org/10.4207/PA.2017.ART104
Carto SL, Weaver AJ, Hetherington R, Lam Y, Wiebe EC (2009) Out of Africa and into an ice age: On the role of global climate change in the late Pleistocene expansion of early modern humans out of Africa. J Hum Evol 56:139–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2008.09.004
Castañeda IS, Mulitza S, Schefuß E, Santos RAL, Damste JSS, Schouten S (2009) Wet phases in the Sahara/Sahel region and human expansion patterns in North Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0905771106
Cheung WH, Senay GB, Singh A (2008) Trends and spatial distribution of annual and seasonal rainfall in Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 28:1723–1734. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1623
Clark J, Brooks N, Banning EB, Bar-Matthews M, Campbell S, Clare L, Cremaschi M, di Lernia S, Drake N, Gallinaro M, Manning S, Nicoll K, Philip G, Rosen S, Schoop UD, Tafuri MA, Weninger B, Zerboni A (2016) Climatic changes and social transformations in the Near East and North Africa during the ‘long’ 4th millennium BC: a comparative study of environmental and archaeological evidence. Quatern Sci Rev 136:96–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.10.003
Cohen A, Campisano C, Arrowsmith R, Asrat A, Behrensmeyer AK, Deino A, Feibel C, Hill A, Johnson R, Kingson J, Lamb H, Lowenstein T, Noren A, Olago D, Owen RB, Potts R, Reed K, Renaut R, Schäbitz F, Tiercelin JJ, Trauth MH, Wynn J, Ivory S, Brady K, O’Grady R, Rodysill J, Githiri J, Russell J, Foerster V, Dommain R, Rucina S, Deocampo D, Russell J, Billingsley A, Beck C, Dorenbeck G, Dullo L, Feary D, Garello D, Gromig R, Johnson T, Junginger A, Karanja M, Kimburi E, Mbuthia A, McCartney T, McNulty E, Muiruri V, Nambiro E, Negash EW, Njagi D, Wilson JN, Rabideaux N, Raub T, Sier MJ, Smith P, Urban J, Warren M, Yadeta M, Yost C, Zinaye B (2016) The hominin sites and Paleolakes drilling project: inferring the environmental context of human evolution from eastern African Rift Lake deposits. Sci Drill 21:1–16. https://doi.org/10.5194/sd-21-1-2016
Cuthbert MO, Gleeson T, Reynolds SC, Bennett MR, Newton AC, McCormack CJ, Ashley GM (2017) Modelling the role of groundwater hydro-refugia in East African hominin evolution and dispersal. Nat Commun 8:15696
Davidson A (1983) The Omo River project: reconnaissance geology and geochemistry of parts of Ilubabor, Kefa, Gemu Gofa and Sidamo. Ethiopian Inst Geol Surv Bull 2:1–89
de Ramos AMT, Zou Y, de Oliviera GS, Kurths J, Macau EEN (2018) Unveiling non-stationary coupling between Amazon and ocean during recent extreme events. Clim Dyn 50:767–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3640-y
deMenocal P, Ortiz J, Guilderson T, Adkins J, Sarnthein M, Baker L, Yarusinsky M (2000) Abrupt onset and termination of the African Humid Period: rapid climate responses to gradual insolation forcing. Quatern Sci Rev 19:347–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00081-5
Ditlevsen PD, Johnsen SJ (2010) Tipping points: Early warning and wishful thinking. Geophys Res Lett 37:L19703. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL044486
Donges JF, Donner RV, Trauth MH, Marwan N, Schellnhuber HJ, Kurths J (2011) Nonlinear detection of paleoclimate-variability transitions possibly related to human evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:20423–20427. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1117052108
Eckmann JP, Kamphorst SO, Ruelle D (1987) Recurrence plots of dynamical systems. Europhys Lett 5:973–977. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/4/9/004
Eroglu D, McRobie FH, Ozken I, Stemler T, Wyrwoll KH, Breitenbach SFM, Marwan N, Kurths J (2016) See-saw relationship of the Holocene East Asian-Australian summer monsoon. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12929
Feldhoff JH, Donner RV, Donges JF, Marwan N, Kurths J (2013) Geometric signature of complex synchronisation scenarios. Europhys Lett 102:30007. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/102/30007
Flohr P, Fleitmann D, Matthews R, Matthews W, Black S (2016) Evidence of resilience to past climate change in Southwest Asia: Early farming communities and the 9.2 and 8.2 ka events. Quatern Sci Rev 136:23–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.06.022
Foerster V, Junginger A, Langkamp O, Gebru T, Asrat A, Umer M, Lamb H, Wennrich V, Rethemeyer J, Nowaczyk N, Trauth MH, Schäbitz F (2012) Climatic change recorded in the sediments of the Chew Bahir basin, southern Ethiopia, during the last 45,000 year. Quatern Int 274:25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2012.06.028
Foerster V, Vogelsang R, Junginger A, Asrat A, Lamb HF, Schaebitz F, Trauth MH (2015) Environmental change and human occupation of southern Ethiopia and Northern Kenya during the last 20,000 year. Quatern Sci Rev 129:333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.10.026
Foerster V, Deocampo DM, Asrat A, Günter C, Junginger A, Kraemer H, Stroncik NA, Trauth MH (2018) Towards an understanding of climate proxy formation in the Chew Bahir basin, southern Ethiopian Rift. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 501:111–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.04.009
Garcin Y (2008) Comment on “Abrupt change in tropical African climate linked to the bipolar seesaw over the past 55,000 yr” by Brown, E. T, Johnson, T. C, Scholz, C. A, Cohen, A. S, and King, J. W. (2007). Geophys Res Lett 35:L04701. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL032399
Garcin Y, Deschamps P, Ménot G, de Saulieu G, Schefuß E, Sebag D, Dupont LM, Oslisly R, Brademann B, Mbusnum KG, Onana JM, Ako AA, Epp LS, Tjallingii R, Strecker MR, Brauer A, Sachse D (2018) Early anthropogenic impact on Western Central African rainforests 2,600 y ago. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115:3261–3266. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1715336115
Gasse F (2000) Hydrological changes in the African tropics since the Last Glacial Maximum. Quatern Sci Rev 19:189–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00061-X
Gatto MC, Zerboni A (2015) Holocene supra-regional environmental changes as trigger for major socio-cultural processes in Northeastern Africa and the Sahara. African Archaeol Rev 32:301–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10437-015-9191-x
Goswami B, Marwan N, Feulner G, Kurths J (2013) How do global temperature drivers influence each other? A network perspective using recurrences. Eur Phys J Spec Top 222:861–873. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01889-8
Hailemeskel A, Fekadu H (2004) Geological map of Yabello. Geological Survey of Ethiopia, Addis Ababa (ISN 0000 0001 0674 8528)
Hassen N, Yemane T, Genzebu W (1997) Geology of the Agere Maryam Area. Geological Survey of Ethiopia, Addis Ababa
Hildebrand E, Grillo K (2012) Early herders and monumental sites in eastern Africa: New radiocarbon dates. Antiquity 86:338–352. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0003598X00062803
Ivory SJ, Russell J (2018) Lowland forest collapse and early human impacts at the end of the African Humid Period at Lake Edward, equatorial East Africa. Quatern Res 89:7–20. https://doi.org/10.1017/qua.2017.48
Iwanski J, Bradley E (1998) Recurrence plot analysis: To embed or not to embed? Chaos 8:861–871. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.166372
Kantz H, Schreiber T (1997) Nonlinear time series analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511755798
Key RM (1988) Geology of the Sabarei area: degree sheets 3 and 4, with coloured 1:250 000 geological map and results of geochemical exploration (Report). Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources, Mines and Geology Dept., Nairobi, Kenya
Klein RG (1995) Anatomy, behavior, and modern human origins. J World Prehist 9:167–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02221838
Klein RG, Steele TE (2013) Archaeological shellfish size and later human evolution in Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:10910–10915. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1304750110
Lahr M (2016) The shaping of human diversity: filters, boundaries and transitions. Philos Trans R Soc B 371:20150241. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0241
Lamb HF, Bates CR, Bryant CL, Davies SJ, Huws DG, Marshall MH, Roberts HM (2018) 150,000-year palaeoclimate record from northern Ethiopia supports early, multiple dispersals of modern humans from Africa. Sci Rep 8:1077. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19601-w
Lenton TM, Held H, Kriegler E, Hall JW, Lucht W, Rahmstorf S, Schellnhuber HJ (2008) Tipping elements in the Earth’s climate system. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:1786–1796. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0705414105
Maley J, Doumenge C, Giresse P, Mahé G, Philippon N, Hubau W, Lokonda MO, Tshibamba JM, Chepstow-Lusty A (2018) Late Holocene forest contraction and fragmentation in central Africa. Quatern Res 89:43–59. https://doi.org/10.1017/qua.2017.97
Manning K, Timpson A (2014) The demographic response to Holocene climate change in the Sahara. Quatern Sci Rev 101:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.07.003
Marchant R, Richer S, Boles O, Capitani C, Courtney-Mustaphi CJ, Lane PJ et al (2018) Drivers and trajectories of land cover change in East Africa: Human and environmental interactions from 6000 years ago to present. Earth Sci Rev 178:322–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.12.010
Marshall F, Hildebrand E (2002) Cattle before the crops: the beginnings of food production in Africa. J World Prehist 16:99–143. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:10199549
Marwan N (2008) A Historical Review of Recurrence Plots. European Physical Journal. Spec Top 164:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2008-00829-1
Marwan N (2011) How to avoid potential pitfalls in recurrence plot based data analysis. J Biofurcation Chaos 21:1003–1017. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127411029008
Marwan N, Kurths J (2015) Complex network based techniques to identify extreme events and (sudden) transitions in spatio-temporal systems. Chaos 25:097609. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4916924
Marwan N, Trauth MH, Vuille M, Kurths J (2003) Comparing modern and Pleistocene ENSO-like influences in NW Argentina using nonlinear time series analysis methods. Clim Dyn 21:317–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-003-0335-3
Marwan N, Romano MC, Thiel M, Kurths J (2007) Recurrence plots for the analysis of complex systems. Phys Rep 438:237–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2006.11.001
Marwan N, Schinkel S, Kurths J (2013) Recurrence plots 25 years later - Gaining confidence in dynamical transitions. Europhys Lett 101:20007. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/101/20007
Moore JM, Davidson A (1978) Rift structure in southern Ethiopia. Tectonophysics 46:159–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(78)90111-7
Mudelsee M (2014) Climate time series analysis: classical statistical and bootstrap methods, 2nd edn. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04450-7
Nicholson SE (2017) Climate and climatic variability of rainfall over eastern Africa. Rev Geophys 55:590–635. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016RG000544
Packard NH, Crutchfield JP, Farmer JD, Shaw RS (1980) Geometry from a time series. Phys Rev Lett 45:712–716. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.45.712
Renfrew C (2009) Situating the creative explosion: universal or local? In: Renfrew C, Morley I (eds) Becoming human: innovation in prehistoric material and spiritual culture. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 74–92 (ISBN-13:978-0521734660)
Richter J, Hauck T, Vogersang R, Widlock T, Le Tensorer JM, Schmid P (2012) “Contextual areas” of early Homo sapiens and their significance for human dispersal from Africa into Eurasia between 200 ka and 70 ka. Quatern Int 274:5–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2012.04.017
Rodó X, Rodríguez-Arias MA (2006) A new method to detect transitory signatures and local time/space variability structures in the climate system: the scale-dependent correlation analysis. Clim Dyn 27:441–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-005-0106-4
Runge J, Heitzig J, Marwan N, Kurths J (2012) Quantifying causal coupling strength: a lag-specific measure for multivariate time series related to transfer entropy. Phys Rev E 86:061121. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.86.061121
Runge J, Petoukhov V, Kurths J (2014) Quantifying the strength and delay of climatic interactions: the ambiguities of cross correlation and a novel measure based on graphic models. J Clim 27:720–739. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00159.1
Saji NH, Goswami BN, Vinayachandran PN, Yamagata T (1999) A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 401:360–363. https://doi.org/10.1038/43854
Segele ZT, Lamb PJ, Leslie LM (2009) Seasonal-to-interannual variability of Ethiopia/Horn of Africa Monsoon. Part I: associations of wavelet-filtered large-scale atmospheric circulation and global sea surface temperature. J Clim 22:3396–3421. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008JCLI2859.1
Seleshi Y, Zanke U (2004) Recent changes in rainfall and rainy days in Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 24:973–983. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1052
Shakun JD, Carlson AE (2010) A global perspective on Last Glacial Maximum to Holocene climate change. Quatern Sci Rev 29:1801–1816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.03.016
Shanahan TM, McKay NP, Hughen KA, Overpeck JT, Otto-Bliesner B, Heil CW, King J, Scholz CA, Peck J (2015) The time-transgressive termination of the African Humid Period. Nat Geosci 8:140–144. https://doi.org/10.1038/NGEO2329
Takens F (1981) Detecting strange attractors in turbulence, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol 898. Springer, Berlin, pp 366–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0091924
Tierney JE, deMenocal PB (2013) Abrupt shifts in horn of Africa hydroclimate since the last glacial maximum. Science 342:843–846. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1240411
Tierney JE, Pausata FSR, deMenocal PB (2017) Rainfall regimes of the Green Sahara. Sci Adv 3:e1601503. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1601503
Timmerman A, Friedrich T (2016) Late Pleistocene climate drivers of early human migration. Nature 538:92–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19365
Trauth MH (2015) MATLAB recipes for earth sciences, 4th edn. Springer, New York (ISBN: 978-3-662-46244-7)
Trauth MH, Maslin MA, Deino A, Strecker MR, Bergner AGN, Dühnforth M (2007) High- and low-latitude forcing of Plio-Pleistocene African climate and human evolution. J Hum Evol 53:475–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2006.12.009
Trauth MH, Bergner AGN, Foerster V, Junginger A, Maslin MA, Schaebitz F (2015) Episodes of environmental stability and instability in late Cenozoic lake records of Eastern Africa. J Hum Evol 87:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2015.03.011
Trauth MH, Foerster V, Junginger A, Asrat A, Lamb HF, Schaebitz F (2018) Abrupt or gradual? Change point analysis of the late Pleistocene-Holocene climate record from Chew Bahir, southern Ethiopia. Quatern Res 90:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1017/qua.2018.30
Tsonis AA (2018) Advances in nonlinear geosciences. Springer, New York (ISBN: 978-3-319-58894-0)
Turcotte DL (2010) Fractals and Chaos in geology and geophysics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139174695
Vogelsang R, Keding B (2013) Climate, culture, and change: From hunters to herders in northeastern and southwestern Africa. In: Comparative Archaeology and Paleoclimatology—Socio-cultural responses to a changing world, Baldia MO, Perttula TK, Frink DS, eds.), BAR International Series, 2456, Archaeopress, Oxford, UK, pp 43–62
Webber CL, Zbilut JP (2005) Recurrence quantification analysis of nonlinear dynamical systems. In: Riley MA, Van Orden GC (eds) Tutorials in contemporary nonlinear methods for the behavioral sciences. http://www.saistmp.com/publications/spiegorqa.pdf. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07155-8
Zbilut JP, Webber CL Jr (1992) Embeddings and delays as derived from quantification of recurrence plots. Phys Lett A 171:199–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9601(92)90426-M
Acknowledgements
Our project was funded by the DFG priority program SPP 1006 ICDP to M.H.T. and F.S. as well as the CRC 806 “Our Way to Europe” to F.S. at the University of Cologne. The project also received funds from a DFG grant to N.M. and M.H.T. to improve the recurrence plots/recurrence quantification analysis methods. This paper is publication number 19 of the Hominin Sites and Paleolakes Drilling Project (HSPDP). The MATLAB code to calculate the RPs and to perform the RQA is available at http://mres.uni-potsdam.de and on request from the corresponding author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trauth, M.H., Asrat, A., Duesing, W. et al. Classifying past climate change in the Chew Bahir basin, southern Ethiopia, using recurrence quantification analysis. Clim Dyn 53, 2557–2572 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04641-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04641-3