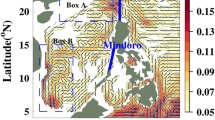
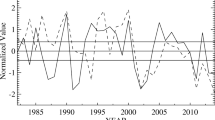
Abstract
The present study focuses on changes in synoptic-scale waves (SSWs) over the northwest Pacific (NWP) during boreal summer and compares them with intraseasonal oscillations (ISOs). The results show that the intensity of eddy kinetic energy (EKE)-based SSWs (2–10-day period) has greater climatological means and interannual variations than the 10–20-day and 30–60-day ISOs. Additionally, the distribution of the SSWs is similar to that of the 10–20-day ISO, which shows a greater amplitude in the monsoon trough region. Further investigation reveals that the EKE-based SSW intensity over the South China Sea-tropical NWP region, where the greatest SSW activity occurs, is positively correlated with central Pacific (CP) warming. The EKE-based SSW intensity tends to be higher in years of developing CP warming. The influences of the Indian Ocean sea surface temperature (SST) are limited and show a weak correlation with the EKE-based SSW intensity over the key region (5° N–20° N, 115° E–155° E). In turn, the SSWs have impacts on local SST anomalies, with active SSWs leading to SST cooling. CP warming induces a favorable environment for SSW origination over CP and SSW development in the monsoon trough region. Concurrent with the CP warming-associated easterly vertical wind shear, upward vertical motion and abundant moisture supply, significant synoptic-scale EKE conversion occurs over the key region, which indicates its dominant role in influencing the SSW intensity. The influences of CP warming on SSW intensity over the NWP demonstrate the potential of the El Niño Modoki index for predicting interannual variations in SSW intensity. Moreover, considering that influences related to SSWs bear a resemblance to the 10–20-day ISOs, future research should take into account the contributions of SSWs to avoid overestimating the impact from ISOs.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ashok K, Behera SK, Rao SA, Weng H, Yamagata T (2007) El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection. J Geophys Res Oceans (1978–2012) 112:C11007. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JC003798
Chen G (2012) A comparison of the transition of equatorial waves between two types of ENSO events in a multilevel model. J Atmos Sci 69:2364–2378. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-11-0292.1
Chen G, Chou C (2014) Joint contribution of multiple equatorial waves to tropical cyclogenesis over the western north Pacific. Mon Weather Rev 142:79–93. https://doi.org/10.1175/mwr-d-13-00207.1
Chen G, Huang R (2008) Role of equatorial wave transitions in tropical cyclogenesis over the western north Pacific. Atmos Oceanic Sci Lett 1:64–68
Chen G, Sui C-H (2010) Characteristics and origin of quasi-biweekly oscillation over the western north Pacific during boreal summer. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009jd013389
Chen T-C, Weng S-P (1998) Interannual variation of the summer synoptic-scale disturbance activity in the western tropical Pacific. Mon Weather Rev 126:1725–1733. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1998)126%3c1725:Ivotss%3e2.0.Co;2
Duchon CE (1979) Lanczos filtering in one and 2 dimensions. J Appl Meteorol 18:1016–1022. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1979)018%3c1016:Lfioat%3e2.0.Co;2
Feng J, Chen W (2014) Influence of the IOD on the relationship between El Niño Modoki and the east Asian-western north Pacific summer monsoon. Int J Climatol 34:1729–1736. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3790
Feng T, Chen G-H, Huang R-H, Shen X-Y (2014) Large-scale circulation patterns favourable to tropical cyclogenesis over the western north Pacific and associated barotropic energy conversions. Int J Climatol 34:216–227. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3680
Feng T, Yang X-Q, Zhou W, Huang R, Wu L, Yang D (2016) Synoptic-scale waves in sheared background flow over the western north Pacific. J Atmos Sci 73:4583–4603. https://doi.org/10.1175/jas-d-16-0064.1
Feng T, Yang X-Q, Yu J-Y, Huang R (2020a) Convective coupling in tropical-depression-type waves. Part I: rainfall characteristics and moisture structure. J Atmos Sci 77:3407–3422. https://doi.org/10.1175/jas-d-19-0172.1
Feng T, Yu J-Y, Yang X-Q, Huang R (2020b) Convective coupling in tropical-depression-type waves. Part II: Moisture and moist static energy budgets. J Atmos Sci 77:3423–3440
Frank WM, Roundy PE (2006) The role of tropical waves in tropical cyclogenesis. Mon Weather Rev 134:2397–2417. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR3204.1
Frauen C, Dommenget D, Tyrrell N, Rezny M, Wales S (2014) Analysis of the nonlinearity of El Niño-southern oscillation teleconnections. J Clim 27:6225–6244. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-13-00757.1
Hersbach H et al (2020) The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 146:1999–2049. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3803
Hsu PC, Li T, Tsou CH (2011) Interactions between boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations and synoptic-scale disturbances over the western north Pacific. Part I: energetics diagnosis. J Clim 24:927–941. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JCLI3833.1
Hu P, Huangfu J, Chen W, Huang R (2020) South China Sea summer monsoon withdrawal and the synoptic-scale wave train over the western north Pacific. Int J Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6538
Huang P, Huang R (2011) Climatology and interannual variability of convectively coupled equatorial waves activity. J Clim 24:4451–4465
Huangfu J, Huang R, Chen W (2017a) Statistical analysis and a case study of tropical cyclones that trigger the onset of the south China Sea summer monsoon. Sci Rep 7:12732. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13128-2
Huangfu J, Huang R, Chen W, Feng T, Wu L (2017b) Interdecadal variation of tropical cyclone genesis and its relationship to the monsoon trough over the western north Pacific. Int J Climatol 37:3587–3596. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4939
Huangfu J, Chen W, Wang X, Huang R (2018) The role of synoptic-scale waves in the onset of the South China Sea summer monsoon. Atmos Sci Lett 19:e858. https://doi.org/10.1002/asl.858
Hurley JV, Boos WR (2015) A global climatology of monsoon low-pressure systems. Q J R Meteorol Soc 141:1049–1064. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.2447
Karori MA, Li J, Jin F-F (2013) The asymmetric influence of the two types of El Niño and La Niña on summer rainfall over southeast China. J Clim 26:4567–4582. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-12-00324.1
Kemball-Cook S, Wang B (2001) Equatorial waves and air–sea interaction in the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J Clim 14:2923–2942. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014%3c2923:Ewaasi%3e2.0.Co;2
Keshavamurty RN (1972) On the vertical tilt of monsoon disturbances. J Atmos Sci 29:993–995. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1972)029%3c0993:otvtom%3e2.0.co;2
Kiladis GN, Wheeler MC, Haertel PT, Straub KH, Roundy PE (2009) Convectively coupled equatorial waves. Rev Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011RG000370
Klein SA, Soden BJ, Lau N-C (1999) Remote sea surface temperature variations during ENSO: evidence for a tropical atmospheric bridge. J Clim 12:917–932. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012%3c0917:rsstvd%3e2.0.co;2
Lau K-H, Lau N-C (1990) Observed structure and propagation characteristics of tropical summertime synoptic scale disturbances. Mon Weather Rev 118:1888–1913. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1990)118%3c1888:osapco%3e2.0.co;2
Lau K-H, Lau N-C (1992) The energetics and propagation dynamics of tropical summertime synoptic-scale disturbances. Mon Weather Rev 120:2523–2539. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1992)120%3c2523:teapdo%3e2.0.co;2
Lee S-S, Moon J-Y, Wang B, Kim H-J (2017) Subseasonal prediction of extreme precipitation over Asia: boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation perspective. J Clim 30:2849–2865. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-16-0206.1
Li T (2006) Origin of the summertime synoptic-scale wave train in the western north Pacific*. J Atmos Sci 63:1093–1102. https://doi.org/10.1175/jas3676.1
Li RCY, Zhou W (2013) Modulation of western north Pacific tropical cyclone activity by the ISO. Part I: genesis and intensity. J Clim 26:2904–2918. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-12-00210.1
Liebmann BCAS (1996) Description of a complete (interpolated) outgoing longwave radiation dataset. Bull Am Meteor Soc 77:1275–1277
Matsuno T (1966) Quasi-geostrophic motions in the equatorial area. J Meteor Soc Jpn 44:25–43
Rayner N et al (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res Atmos (1984–2012) 108(D14):4407. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002670
Rydbeck AV, Maloney ED (2014) Energetics of east Pacific easterly waves during intraseasonal events. J Clim 27:7603–7621. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00211.1
Saji NH, Goswami BN, Vinayachandran PN, Yamagata T (1999) A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 401:360–363. https://doi.org/10.1038/43854
Sullivan A, Luo J, Hirst A, Bi D, Cai W, He J (2016) Robust contribution of decadal anomalies to the frequency of central-Pacific El Niño. Sci Rep 6:38540
Sun M, Li T, Chen L (2020) El Niño phase-dependent high-frequency variability in western equatorial Pacific. Clim Dyn 55:2165–2184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-020-05376-2
Takayabu Y (1994) Large-scale cloud disturbances associated with equatorial waves. II: Westward propagating inertio-gravity waves. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 72:451–465
Tam C-Y, Li T (2006) The origin and dispersion characteristics of the observed tropical summertime synoptic-scale waves over the western Pacific*. Mon Weather Rev 134:1630–1646. https://doi.org/10.1175/mwr3147.1
Teng H, Wang B (2003) Interannual variations of the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation in the Asian-Pacific Region. J Clim 16:3572–3584. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016%3c3572:Ivotbs%3e2.0.Co;2
Tong HW, Chan JCL, Zhou W (2009) The role of MJO and mid-latitude fronts in the South China Sea summer monsoon onset. Clim Dyn 33:827–841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-008-0490-7
Trenberth KE (1997) The definition of El Niño. Bull Am Meteor Soc 78:2771–2778. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078%3c2771:Tdoeno%3e2.0.Co;2
Tsou C-H, Hsu H-H, Hsu P-C (2014) The role of multiscale interaction in synoptic-scale eddy kinetic energy over the western north Pacific in autumn. J Clim 27:3750–3766. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-13-00380.1
Wang X, Chen G, Huang R (2016) Different characteristics of the quasi-biweekly oscillation over the South China Sea in two boreal summer stages. Theoret Appl Climatol 126:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1550-7
Weng H, Wu G, Liu Y, Behera SK, Yamagata T (2011) Anomalous summer climate in China influenced by the tropical indo-Pacific oceans. Clim Dyn 36:769–782
Wheeler M, Kiladis GN (1999) Convectively coupled equatorial waves: analysis of clouds and temperature in the wavenumber-frequency domain. J Atmos Sci 56:374–399
Wu R, Cao X (2017) Relationship of boreal summer 10–20-day and 30–60-day intraseasonal oscillation intensity over the tropical western North Pacific to tropical Indo-Pacific SST. Clim Dyn 48:3529–3546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3282-5
Wu L, Wen Z, Li T, Huang R (2014) ENSO-phase dependent TD and MRG wave activity in the western north Pacific. Clim Dyn 42:1217–1227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1754-4
Wu L, Wen Z, Wu R (2015) Influence of the monsoon trough on westward-propagating tropical waves over the western north Pacific. Part I: Observations. J Clim 28:7108–7127. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00806.1
Wu R, Wang Y, Cao X (2021) What modulates the intensity of synoptic-scale variability over the western north Pacific during boreal summer and fall? J Clim 34:3645–3662. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-20-0477.1
Yuan Y, Yang S (2012) Impacts of different types of El Niño on the east Asian climate: focus on ENSO cycles. J Clim 25:7702–7722. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-11-00576.1
Zhao H, Jiang X, Wu L (2015) Modulation of northwest Pacific tropical cyclone genesis by the intraseasonal variability. J Meteorol Soc Jp Ser II 93:81–97. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2015-006
Zhao H, Jiang X, Wu L (2016) Boreal summer synoptic-scale waves over the western north Pacific in multimodel simulations. J Clim 29:4487–4508. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-15-0696.1
Zhou C, Li T (2010) Upscale feedback of tropical synoptic variability to intraseasonal oscillations through the nonlinear rectification of the surface latent heat flux. J Clim 23:5738–5754. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JCLI3468.1
Zhou X, Lu R, Chen G (2018a) Impact of interannual variation of synoptic disturbances on the tracks and landfalls of tropical cyclones over the western north Pacific. Adv Atmos Sci 35:1469–1477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-018-8055-0
Zhou X, Lu R, Chen G, Wu L (2018b) Interannual variations in synoptic-scale disturbances over the western north Pacific. Adv Atmos Sci 35:507–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-017-7143-x
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFA0600603), the Key Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant QYZDY-SSW-DQC024) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41705071).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFA0600603) from Wen Chen and Jingliang Huangfu, the Key Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant QYZDY-SSW-DQC024) from Jingliang Huangfu and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41705071) from Jingliang Huangfu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huangfu, J., Cao, X., Wu, R. et al. Influences of central Pacific warming on synoptic-scale wave intensity over the northwest Pacific. Clim Dyn 58, 555–567 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05922-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05922-6