Abstract
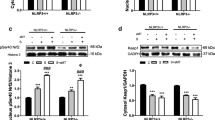
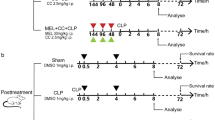
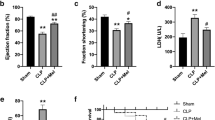
Myocardial dysfunction is an important manifestation of sepsis. Previous studies suggest that melatonin is protective against sepsis. In addition, activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) signaling pathway has been reported to be beneficial in sepsis. However, the role of PI3K/Akt signaling in the protective effect of melatonin against sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction remains unclear. Here, LY294002, a PI3K inhibitor, was used to investigate the role of PI3K/Akt signaling in mediating the effects of melatonin on sepsis-induced myocardial injury. Cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) surgery was used to establish a rat model of sepsis. Melatonin was administrated to rats intraperitoneally (30 mg/kg). The survival rate, measures of myocardial injury and cardiac performance, serum lactate dehydrogenase level, inflammatory cytokine levels, oxidative stress level, and the extent of myocardial apoptosis were assessed. The results suggest that melatonin administration after CLP surgery improved survival rates and cardiac function, attenuated myocardial injury and apoptosis, and decreased the serum lactate dehydrogenase level. Melatonin decreased the production of the inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and HMGB1, increased anti-oxidant enzyme activity, and decreased the expression of markers of oxidative damage. Levels of phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt), unphosphorylated Akt (Akt), Bcl-2, and Bax were measured by Western blot. Melatonin increased p-Akt levels, which suggests Akt pathway activation. Melatonin induced higher Bcl-2 expression and lower Bax expression, suggesting inhibition of apoptosis. All protective effects of melatonin were abolished by LY294002, the PI3K inhibitor. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that melatonin mitigates myocardial injury in sepsis via PI3K/Akt signaling activation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adi N, Mash DC, Ali Y, Singer C, Shehadeh L, Papapetropoulos S (2010) Melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptor expression in Parkinson’s disease. Med Sci Monit 16:BR61–BR67
Agil A, Reiter RJ, Jimenez-Aranda A, Iban-Arias R, Navarro-Alarcon M, Marchal JA, Adem A, Fernandez-Vazquez G (2013) Melatonin ameliorates low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress in young Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Pineal Res 54:381–388. doi:10.1111/jpi.12012
Ali T, Kim MO (2015) Melatonin ameliorates amyloid beta-induced memory deficits, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration via PI3/Akt/GSk3beta pathway in the mouse hippocampus. J Pineal Res. doi:10.1111/jpi.12238
Amin AH, El-Missiry MA, Othman AI (2015) Melatonin ameliorates metabolic risk factors, modulates apoptotic proteins, and protects the rat heart against diabetes-induced apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol 747:166–173. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.12.002
Andersson U, Tracey KJ (2003) HMGB1 in sepsis. Scand J Infect Dis 35:577–584
Annane D, Bellissant E, Cavaillon JM (2005) Septic shock. Lancet 365:63–78. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17667-8
Annane D, Sharshar T (2015) Cognitive decline after sepsis. Lancet Respir Med 3:61–69. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70246-2
Antonucci E, Fiaccadori E, Donadello K, Taccone FS, Franchi F, Scolletta S (2014) Myocardial depression in sepsis: from pathogenesis to clinical manifestations and treatment. J Crit Care 29:500–511. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.03.028
Belosjorow S, Schulz R, Dorge H, Schade FU, Heusch G (1999) Endotoxin and ischemic preconditioning: TNF-alpha concentration and myocardial infarct development in rabbits. Am J Physiol 277:H2470–H2475
Benitez-King G (2006) Melatonin as a cytoskeletal modulator: implications for cell physiology and disease. J Pineal Res 40:1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2005.00282.x
Benitez-King G, Anton-Tay F (1993) Calmodulin mediates melatonin cytoskeletal effects. Experientia 49:635–641
Bommhardt U, Chang KC, Swanson PE, Wagner TH, Tinsley KW, Karl IE, Hotchkiss RS (2004) Akt decreases lymphocyte apoptosis and improves survival in sepsis. J Immunol 172:7583–7591
Bondor CI, Potra AR, Moldovan D, Rusu CC, Ciorba Pop M, Muresan A, Vladutiu DS, Kacso IM (2015) Relationship of adiponectin to markers of oxidative stress in type 2 diabetic patients: influence of incipient diabetes-associated kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol. doi:10.1007/s11255-015-1004-2
Bonnefond A, Clement N, Fawcett K, Yengo L, Vaillant E, Guillaume JL, Dechaume A, Payne F, Roussel R, Czernichow S, Hercberg S, Hadjadj S, Balkau B, Marre M, Lantieri O, Langenberg C, Bouatia-Naji N, Meta-Analysis of G, Insulin-Related Traits C, Charpentier G, Vaxillaire M, Rocheleau G, Wareham NJ, Sladek R, McCarthy MI, Dina C, Barroso I, Jockers R, Froguel P (2012) Rare MTNR1B variants impairing melatonin receptor 1B function contribute to type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 44:297–301. doi:10.1038/ng.1053
Brealey D, Brand M, Hargreaves I, Heales S, Land J, Smolenski R, Davies NA, Cooper CE, Singer M (2002) Association between mitochondrial dysfunction and severity and outcome of septic shock. Lancet 360:219–223. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09459-X
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296:1655–1657. doi:10.1126/science.296.5573.1655
Chandra J, Samali A, Orrenius S (2000) Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 29:323–333
Chen G, Zhao J, Yin Y, Wang B, Liu Q, Li P, Zhao L, Zhou H (2014) C-type natriuretic peptide attenuates LPS-induced endothelial activation: involvement of p38, Akt, and NF-kappaB pathways. Amino Acids 46:2653–2663. doi:10.1007/s00726-014-1816-x
Chen HH, Lin KC, Wallace CG, Chen YT, Yang CC, Leu S, Chen YC, Sun CK, Tsai TH, Chen YL, Chung SY, Chang CL, Yip HK (2014) Additional benefit of combined therapy with melatonin and apoptotic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell against sepsis-induced kidney injury. J Pineal Res 57:16–32. doi:10.1111/jpi.12140
Cohen MV, Yang XM, Downey JM (2007) The pH hypothesis of postconditioning: staccato reperfusion reintroduces oxygen and perpetuates myocardial acidosis. Circulation 115:1895–1903. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.675710
Court O, Kumar A, Parrillo JE, Kumar A (2002) Clinical review: myocardial depression in sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care 6:500–508
Crouser ED (2004) Mitochondrial dysfunction in septic shock and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Mitochondrion 4:729–741. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2004.07.023
Cuello F, Shankar-Hari M, Mayr U, Yin X, Marshall M, Suna G, Willeit P, Langley SR, Jayawardhana T, Zeller T, Terblanche M, Shah AM, Mayr M (2014) Redox state of pentraxin 3 as a novel biomarker for resolution of inflammation and survival in sepsis. Mol Cell Proteomics 13:2545–2557. doi:10.1074/mcp.M114.039446
Dai X, Zeng Z, Fu C, Zhang S, Cai Y, Chen Z (2015) Diagnostic value of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, cystatin C and soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 in critically ill patients with sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Crit Care 19:223. doi:10.1186/s13054-015-0941-6
Ekelof SV, Halladin NL, Jensen SE, Zaremba T, Aaroe J, Kjaergaard B, Simonsen CW, Rosenberg J, Gogenur I (2014) Effects of intracoronary melatonin on ischemia-reperfusion injury in ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels. doi:10.1007/s00380-014-0589-1
Ekmekcioglu C, Haslmayer P, Philipp C, Mehrabi MR, Glogar HD, Grimm M, Leibetseder VJ, Thalhammer T, Marktl W (2001) Expression of the MT1 melatonin receptor subtype in human coronary arteries. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 21:85–91. doi:10.1081/RRS-100107144
Ersahin C, Masana MI, Dubocovich ML (2002) Constitutively active melatonin MT(1) receptors in male rat caudal arteries. Eur J Pharmacol 439:171–172
Faria JA, Kinote A, Ignacio-Souza LM, de Araujo TM, Razolli DS, Doneda DL, Paschoal LB, Lellis-Santos C, Bertolini GL, Velloso LA, Bordin S, Anhe GF (2013) Melatonin acts through MT1/MT2 receptors to activate hypothalamic Akt and suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 305:E230–E242. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00094.2013
Fink T, Glas M, Wolf A, Kleber A, Reus E, Wolff M, Kiefer D, Wolf B, Rensing H, Volk T, Mathes AM (2014) Melatonin receptors mediate improvements of survival in a model of polymicrobial sepsis. Crit Care Med 42:e22–e31. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182a63e2b
Fruman DA, Cantley LC (2002) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase in immunological systems. Semin Immunol 14:7–18. doi:10.1006/smim.2001.0337
Fujio Y, Nguyen T, Wencker D, Kitsis RN, Walsh K (2000) Akt promotes survival of cardiomyocytes in vitro and protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse heart. Circulation 101:660–667
Gamkrelidze M, Intskirveli N, Vardosanidze K, Goliadze L, Chikhladze K, Ratiani L (2014) Myocardial dysfunction during septic shock (review). Georgian Med News 237:40–46
Gao M, Ha T, Zhang X, Wang X, Liu L, Kalbfleisch J, Singh K, Williams D, Li C (2013) The Toll-like receptor 9 ligand, CpG oligodeoxynucleotide, attenuates cardiac dysfunction in polymicrobial sepsis, involving activation of both phosphoinositide 3 kinase/Akt and extracellular-signal-related kinase signaling. J Infect Dis 207:1471–1479. doi:10.1093/infdis/jit036
Garcia JA, Volt H, Venegas C, Doerrier C, Escames G, Lopez LC, Acuna-Castroviejo D (2015) Disruption of the NF-kappaB/NLRP3 connection by melatonin requires retinoid-related orphan receptor-alpha and blocks the septic response in mice. FASEB J. doi:10.1096/fj.15-273656
Garcia JJ, Lopez-Pingarron L, Almeida-Souza P, Tres A, Escudero P, Garcia-Gil FA, Tan DX, Reiter RJ, Ramirez JM, Bernal-Perez M (2014) Protective effects of melatonin in reducing oxidative stress and in preserving the fluidity of biological membranes: a review. J Pineal Res 56:225–237. doi:10.1111/jpi.12128
Gogenur I, Kucukakin B, Panduro Jensen L, Reiter RJ, Rosenberg J (2014) Melatonin reduces cardiac morbidity and markers of myocardial ischemia after elective abdominal aortic aneurism repair: a randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. J Pineal Res 57:10–15. doi:10.1111/jpi.12138
Gottlieb RA (2003) Mitochondrial signaling in apoptosis: mitochondrial daggers to the breaking heart. Basic Res Cardiol 98:242–249. doi:10.1007/s00395-003-0404-0
Gyurkovska V, Ivanovska N (2015) Tyrosine kinase inhibitor tyrphostin AG490 reduces liver injury in LPS-induced shock. Eur J Pharmacol 751:118–126. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.01.045
Hardeland R (2009) Melatonin: signaling mechanisms of a pleiotropic agent. BioFactors 35:183–192. doi:10.1002/biof.23
Harris HE, Andersson U, Pisetsky DS (2012) HMGB1: a multifunctional alarmin driving autoimmune and inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8:195–202. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2011.222
Hernandez-Resendiz S, Palma-Flores C, De Los Santos S, Roman-Anguiano NG, Flores M, de la Pena A, Flores PL, Fernandez GJ, Coral-Vazquez RM, Zazueta C (2015) Reduction of no-reflow and reperfusion injury with the synthetic 17beta-aminoestrogen compound Prolame is associated with PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling cascade. Basic Res Cardiol 110:1. doi:10.1007/s00395-015-0464-y
Hevia D, Gonzalez-Menendez P, Quiros-Gonzalez I, Miar A, Rodriguez-Garcia A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ, Mayo JC, Sainz RM (2015) Melatonin uptake through glucose transporters: a new target for melatonin inhibition of cancer. J Pineal Res 58:234–250. doi:10.1111/jpi.12210
Hill SM, Belancio VP, Dauchy RT, Xiang S, Brimer S, Mao L, Hauch A, Lundberg P, Summers W, Yuan L, Frasch T, Blask DE (2015) Melatonin: an inhibitor of breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. doi:10.1530/ERC-15-0030
Hirano Y, Aziz M, Yang WL, Wang Z, Zhou M, Ochani M, Khader A, Wang P (2015) Neutralization of osteopontin attenuates neutrophil migration in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Crit Care 19:53. doi:10.1186/s13054-015-0782-3
Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE (2003) The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med 348:138–150. doi:10.1056/NEJMra021333
Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE (1992) Reevaluation of the role of cellular hypoxia and bioenergetic failure in sepsis. JAMA 267:1503–1510
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Freeman BD, Tinsley KW, Cobb JP, Matuschak GM, Buchman TG, Karl IE (1999) Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med 27:1230–1251
Hsu JT, Kuo CJ, Chen TH, Wang F, Lin CJ, Yeh TS, Hwang TL, Jan YY (2012) Melatonin prevents hemorrhagic shock-induced liver injury in rats through an Akt-dependent HO-1 pathway. J Pineal Res 53:410–416. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.01011.x
Jang JH, Chun JN, Godo S, Wu G, Shimokawa H, Jin CZ, Jeon JH, Kim SJ, Jin ZH, Zhang YH (2015) ROS and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)-dependent trafficking of angiotensin II type 2 receptor begets neuronal NOS in cardiac myocytes. Basic Res Cardiol 110:21. doi:10.1007/s00395-015-0477-6
Jezek P, Hlavata L (2005) Mitochondria in homeostasis of reactive oxygen species in cell, tissues, and organism. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:2478–2503. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.05.013
Jiang S, Zhu W, Li C, Zhang X, Lu T, Ding Z, Cao K, Liu L (2013) alpha-Lipoic acid attenuates LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction through a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Int Immunopharmacol 16:100–107. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2013.03.024
Johansson L, Snall J, Sendi P, Linner A, Thulin P, Linder A, Treutiger CJ, Norrby-Teglund A (2014) HMGB1 in severe soft tissue infections caused by Streptococcus pyogenes. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:4. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2014.00004
Jonassen AK, Sack MN, Mjos OD, Yellon DM (2001) Myocardial protection by insulin at reperfusion requires early administration and is mediated via Akt and p70s6 kinase cell-survival signaling. Circ Res 89:1191–1198
Karbownik M, Reiter RJ (2000) Antioxidative effects of melatonin in protection against cellular damage caused by ionizing radiation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 225:9–22
Kim TH, Kim SJ, Lee SM (2014) Stimulation of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor protects against sepsis by inhibiting Toll-like receptor via phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation. J Infect Dis 209:1668–1677. doi:10.1093/infdis/jit669
Klune JR, Dhupar R, Cardinal J, Billiar TR, Tsung A (2008) HMGB1: endogenous danger signaling. Mol Med 14:476–484. doi:10.2119/2008-00034.Klune
Korkmaz B, Cuez T, Buharalioglu CK, Demiryurek AT, Sahan-Firat S, Sari AN, Tunctan B (2012) Contribution of MEK1/ERK1/2/iNOS pathway to oxidative stress and decreased caspase-3 activity in endotoxemic rats. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem 11:243–252
Kumar A, Haery C, Parrillo JE (2000) Myocardial dysfunction in septic shock. Crit Care Clin 16:251–287
Lee I, Huttemann M (2014) Energy crisis: the role of oxidative phosphorylation in acute inflammation and sepsis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:1579–1586. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.05.031
Lew WY, Yasuda S, Yuan T, Hammond HK (1996) Endotoxin-induced cardiac depression is associated with decreased cardiac dihydropyridine receptors in rabbits. J Mol Cell Cardiol 28:1367–1371
Li C, Hua F, Ha T, Singh K, Lu C, Kalbfleisch J, Breuel KF, Ford T, Kao RL, Gao M, Ozment TR, Williams DL (2012) Activation of myocardial phosphoinositide-3-kinase p110alpha ameliorates cardiac dysfunction and improves survival in polymicrobial sepsis. PLoS ONE 7:e44712. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044712
Li L, Ling Y, Huang M, Yin T, Gou SM, Zhan NY, Xiong JX, Wu HS, Yang ZY, Wang CY (2015) Heparin inhibits the inflammatory response induced by LPS and HMGB1 by blocking the binding of HMGB1 to the surface of macrophages. Cytokine 72:36–42. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2014.12.010
Li P, Guo Y, Bledsoe G, Yang ZR, Fan H, Chao L, Chao J (2015) Kallistatin treatment attenuates lethality and organ injury in mouse models of established sepsis. Crit Care 19:200. doi:10.1186/s13054-015-0919-4
Li Volti G, Musumeci T, Pignatello R, Murabito P, Barbagallo I, Carbone C, Gullo A, Puglisi G (2012) Antioxidant potential of different melatonin-loaded nanomedicines in an experimental model of sepsis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 237:670–677. doi:10.1258/ebm.2012.011425
Li XQ, Cao W, Li T, Zeng AG, Hao LL, Zhang XN, Mei QB (2009) Amlodipine inhibits TNF-alpha production and attenuates cardiac dysfunction induced by lipopolysaccharide involving PI3K/Akt pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 9:1032–1041. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2009.04.010
Liu L, Wang P, Liang C, He D, Yu Y, Liu X (2013) Distinct effects of Nampt inhibition on mild and severe models of lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial impairment. Int Immunopharmacol 17:342–349. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2013.06.017
Liu L, Xie K, Chen H, Dong X, Li Y, Yu Y, Wang G, Yu Y (2014) Inhalation of hydrogen gas attenuates brain injury in mice with cecal ligation and puncture via inhibiting neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis. Brain Res 1589:78–92. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.030
Liu LF, Qin Q, Qian ZH, Shi M, Deng QC, Zhu WP, Zhang H, Tao XM, Liu Y (2014) Protective effects of melatonin on ischemia-reperfusion induced myocardial damage and hemodynamic recovery in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 18:3681–3686
Liu XY, Zhou XY, Hou JC, Zhu H, Wang Z, Liu JX, Zheng YQ (2015) Ginsenoside Rd promotes neurogenesis in rat brain after transient focal cerebral ischemia via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36:421–428. doi:10.1038/aps.2014.156
Lorente L, Martin MM, Abreu-Gonzalez P, de la Cruz T, Ferreres J, Sole-Violan J, Labarta L, Diaz C, Jimenez A, Borreguero-Leon JM (2015) Serum melatonin levels are associated with mortality in severe septic patients. J Crit Care 30(860):e861–e866. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.03.023
Lorigados CB, Ariga SK, Batista TR, Velasco IT, Soriano FG (2015) Endotoxaemic myocardial dysfunction: the role of coronary driving pressure in subendocardial perfusion. Crit Care Resusc 17:12–22
Lu B, Antoine DJ, Kwan K, Lundback P, Wahamaa H, Schierbeck H, Robinson M, Van Zoelen MA, Yang H, Li J, Erlandsson-Harris H, Chavan SS, Wang H, Andersson U, Tracey KJ (2014) JAK/STAT1 signaling promotes HMGB1 hyperacetylation and nuclear translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:3068–3073. doi:10.1073/pnas.1316925111
Lyssenko V, Nagorny CL, Erdos MR, Wierup N, Jonsson A, Spegel P, Bugliani M, Saxena R, Fex M, Pulizzi N, Isomaa B, Tuomi T, Nilsson P, Kuusisto J, Tuomilehto J, Boehnke M, Altshuler D, Sundler F, Eriksson JG, Jackson AU, Laakso M, Marchetti P, Watanabe RM, Mulder H, Groop L (2009) Common variant in MTNR1B associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes and impaired early insulin secretion. Nat Genet 41:82–88. doi:10.1038/ng.288
Macias M, Escames G, Leon J, Coto A, Sbihi Y, Osuna A, Acuna-Castroviejo D (2003) Calreticulin-melatonin. An unexpected relationship. Eur J Biochem 270:832–840
Mao L, Lin W, Nie T, Hui X, Gao X, Li K, Ding M, Tang X, Li P, Wang Y, Xu A, Liu P, Wu D (2014) Absence of Appl2 sensitizes endotoxin shock through activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Biosci 4:60. doi:10.1186/2045-3701-4-60
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M (2003) The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med 348:1546–1554. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa022139
Masana MI, Doolen S, Ersahin C, Al-Ghoul WM, Duckles SP, Dubocovich ML, Krause DN (2002) MT(2) melatonin receptors are present and functional in rat caudal artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:1295–1302
Mauriz JL, Collado PS, Veneroso C, Reiter RJ, Gonzalez-Gallego J (2013) A review of the molecular aspects of melatonin’s anti-inflammatory actions: recent insights and new perspectives. J Pineal Res 54:1–14. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.01014.x
Melendez J, Maldonado V, Ortega A (1996) Effect of melatonin on beta-tubulin and MAP2 expression in NIE-115 cells. Neurochem Res 21:653–658
Merx MW, Weber C (2007) Sepsis and the heart. Circulation 116:793–802. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.678359
Miki T, Miura T, Tanno M, Nishihara M, Naitoh K, Sato T, Takahashi A, Shimamoto K (2007) Impairment of cardioprotective PI3K-Akt signaling by post-infarct ventricular remodeling is compensated by an ERK-mediated pathway. Basic Res Cardiol 102:163–170. doi:10.1007/s00395-006-0622-3
Mukherjee D, Ghosh AK, Dutta M, Mitra E, Mallick S, Saha B, Reiter RJ, Bandyopadhyay D (2015) Mechanisms of isoproterenol-induced cardiac mitochondrial damage: protective actions of melatonin. J Pineal Res 58:275–290. doi:10.1111/jpi.12213
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature 403:98–103. doi:10.1038/47513
Neviere R, Fauvel H, Chopin C, Formstecher P, Marchetti P (2001) Caspase inhibition prevents cardiac dysfunction and heart apoptosis in a rat model of sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:218–225. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.163.1.2003109
Ortiz F, Garcia JA, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Doerrier C, Lopez A, Venegas C, Volt H, Luna-Sanchez M, Lopez LC, Escames G (2014) The beneficial effects of melatonin against heart mitochondrial impairment during sepsis: inhibition of iNOS and preservation of nNOS. J Pineal Res 56:71–81. doi:10.1111/jpi.12099
Parrillo JE, Parker MM, Natanson C, Suffredini AF, Danner RL, Cunnion RE, Ognibene FP (1990) Septic shock in humans. Advances in the understanding of pathogenesis, cardiovascular dysfunction, and therapy. Ann Intern Med 113:227–242
Pasqua T, Filice E, Mazza R, Quintieri AM, Carmela Cerra M, Iannacone R, Melfi D, Indiveri C, Gattuso A, Angelone T (2015) Cardiac and hepatic role of r-AtHSP70: basal effects and protection against ischemic and sepsis conditions. J Cell Mol Med. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12491
Penna C, Brancaccio M, Tullio F, Rubinetto C, Perrelli MG, Angotti C, Pagliaro P, Tarone G (2014) Overexpression of the muscle-specific protein, melusin, protects from cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol 109:418. doi:10.1007/s00395-014-0418-9
Prabhu MM, Yalakala SK, Shetty R, Thakkar A, Sitapara T (2015) Prognosis of left ventricular systolic dysfunction in septic shock patients. J Clin Diagn Res 9:OC05–OC08. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2015/10812.5640
Rajaram MV, Ganesan LP, Parsa KV, Butchar JP, Gunn JS, Tridandapani S (2006) Akt/Protein kinase B modulates macrophage inflammatory response to Francisella infection and confers a survival advantage in mice. J Immunol 177:6317–6324
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Gitto E, Sainz RM, Mayo JC, Leon J, Manchester LC, Vijayalaxmi Kilic E, Kilic U (2004) Pharmacological utility of melatonin in reducing oxidative cellular and molecular damage. Pol J Pharmacol 56:159–170
Reppert SM (1997) Melatonin receptors: molecular biology of a new family of G protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Rhythms 12:528–531
Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, Peterson E, Tomlanovich M, Early Goal-Directed Therapy Collaborative G (2001) Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 345:1368–1377. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa010307
Rudiger A, Singer M (2007) Mechanisms of sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med 35:1599–1608. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000266683.64081.02
Sanfilippo F, Corredor C, Fletcher N, Landesberg G, Benedetto U, Foex P, Cecconi M (2015) Diastolic dysfunction and mortality in septic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. doi:10.1007/s00134-015-3748-7
Schmidt HB, Werdan K, Muller-Werdan U (2001) Autonomic dysfunction in the ICU patient. Curr Opin Crit Care 7:314–322
Sharshar T, Gray F, Lorin de la Grandmaison G, Hopkinson NS, Ross E, Dorandeu A, Orlikowski D, Raphael JC, Gajdos P, Annane D (2003) Apoptosis of neurons in cardiovascular autonomic centres triggered by inducible nitric oxide synthase after death from septic shock. Lancet 362:1799–1805
Shim DW, Shin HJ, Han JW, Ji YE, Jang CH, Koppula S, Kang TB, Lee KH (2015) A novel synthetic derivative of melatonin, 5-hydroxy-2′-isobutyl-streptochlorin (HIS), inhibits inflammatory responses via regulation of TRIF-dependent signaling and inflammasome activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2015.02.006
Siddall HK, Warrell CE, Yellon DM, Mocanu MM (2008) Ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection: investigating PTEN, the phosphatase that negatively regulates PI3K, using a congenital model of PTEN haploinsufficiency. Basic Res Cardiol 103:560–568. doi:10.1007/s00395-008-0735-y
Skyschally A, van Caster P, Boengler K, Gres P, Musiolik J, Schilawa D, Schulz R, Heusch G (2009) Ischemic postconditioning in pigs: no causal role for RISK activation. Circ Res 104:15–18. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.186429
Song JQ, Teng X, Cai Y, Tang CS, Qi YF (2009) Activation of Akt/GSK-3beta signaling pathway is involved in intermedin(1-53) protection against myocardial apoptosis induced by ischemia/reperfusion. Apoptosis 14:1061–1069. doi:10.1007/s10495-009-0382-2
Stanley WC, Recchia FA, Lopaschuk GD (2005) Myocardial substrate metabolism in the normal and failing heart. Physiol Rev 85:1093–1129. doi:10.1152/physrev.00006.2004
Steven S, Hausding M, Kroller-Schon S, Mader M, Mikhed Y, Stamm P, Zinssius E, Pfeffer A, Welschof P, Agdauletova S, Sudowe S, Li H, Oelze M, Schulz E, Klein T, Munzel T, Daiber A (2015) Gliptin and GLP-1 analog treatment improves survival and vascular inflammation/dysfunction in animals with lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia. Basic Res Cardiol 110:6. doi:10.1007/s00395-015-0465-x
Sun B, Xiao J, Sun XB, Wu Y (2013) Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates cardiac dysfunction in endotoxemic mice: an insight into oestrogen receptor activation and PI3K/Akt signalling. Br J Pharmacol 168:1758–1770. doi:10.1111/bph.12063
Turner KL, Moore LJ, Todd SR, Sucher JF, Jones SA, McKinley BA, Valdivia A, Sailors RM, Moore FA (2011) Identification of cardiac dysfunction in sepsis with B-type natriuretic peptide. J Am Coll Surg 213:139–146. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2011.03.027 (discussion 146–147)
van de Sandt AM, Windler R, Godecke A, Ohlig J, Zander S, Reinartz M, Graf J, van Faassen EE, Rassaf T, Schrader J, Kelm M, Merx MW (2013) Endothelial NOS (NOS3) impairs myocardial function in developing sepsis. Basic Res Cardiol 108:330. doi:10.1007/s00395-013-0330-8
Vanmassenhove J, Glorieux G, Lameire N, Hoste E, Dhondt A, Vanholder R, Van Biesen W (2015) Influence of severity of illness on neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin performance as a marker of acute kidney injury: a prospective cohort study of patients with sepsis. BMC Nephrol 16:18. doi:10.1186/s12882-015-0003-y
Vazan R, Ravingerova T (2015) Protective effect of melatonin against myocardial injury induced by epinephrine. J Physiol Biochem 71:43–49. doi:10.1007/s13105-014-0377-5
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM, Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, Manogue KR, Faist E, Abraham E, Andersson J, Andersson U, Molina PE, Abumrad NN, Sama A, Tracey KJ (1999) HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 285:248–251
Wang X, Liu D, Chai W, Long Y, Su L, Yang R (2014) The role of uncoupling protein-2 (UCP2) during myocardial dysfunction in a canine model of endotoxin shock. Shock. doi:10.1097/SHK.0000000000000286
Whelan RS, Kaplinskiy V, Kitsis RN (2010) Cell death in the pathogenesis of heart disease: mechanisms and significance. Annu Rev Physiol 72:19–44. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163111
Williams DL, Ozment-Skelton T, Li C (2006) Modulation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathway alters host response to sepsis, inflammation, and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Shock 25:432–439. doi:10.1097/01.shk.0000209542.76305.55
Wu JY, Tsou MY, Chen TH, Chen SJ, Tsao CM, Wu CC (2008) Therapeutic effects of melatonin on peritonitis-induced septic shock with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in rats. J Pineal Res 45:106–116. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00567.x
Wu YH, Zhou JN, Van Heerikhuize J, Jockers R, Swaab DF (2007) Decreased MT1 melatonin receptor expression in the suprachiasmatic nucleus in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 28:1239–1247. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.06.002
Xu C, Yi C, Wang H, Bruce IC, Xia Q (2012) Mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase participates in septic shock myocardial depression by nitric oxide overproduction and mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. Shock 37:110–115. doi:10.1097/SHK.0b013e3182391831
Yang J, Zong X, Wu G, Lin S, Feng Y, Hu J (2015) Taurine increases testicular function in aged rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-015-1995-0
Yang Y, Jiang S, Dong Y, Fan C, Zhao L, Yang X, Li J, Di S, Yue L, Liang G, Reiter RJ, Qu Y (2015) Melatonin prevents cell death and mitochondrial dysfunction via a SIRT1-dependent mechanism during ischemic-stroke in mice. J Pineal Res 58:61–70. doi:10.1111/jpi.12193
Yao K, Ye P, Zhang L, Tan J, Tang X, Zhang Y (2008) Epigallocatechin gallate protects against oxidative stress-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human lens epithelial cells. Mol Vis 14:217–223
Yeung HM, Hung MW, Lau CF, Fung ML (2015) Cardioprotective effects of melatonin against myocardial injuries induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia in rats. J Pineal Res 58:12–25. doi:10.1111/jpi.12190
You W, Min X, Zhang X, Qian B, Pang S, Ding Z, Li C, Gao X, Di R, Cheng Y, Liu L (2009) Cardiac-specific expression of heat shock protein 27 attenuated endotoxin-induced cardiac dysfunction and mortality in mice through a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Shock 32:108–117. doi:10.1097/SHK.0b013e318199165d
Yu L, Sun Y, Cheng L, Jin Z, Yang Y, Zhai M, Pei H, Wang X, Zhang H, Meng Q, Zhang Y, Yu S, Duan W (2014) Melatonin receptor-mediated protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: role of SIRT1. J Pineal Res 57:228–238. doi:10.1111/jpi.12161
Zhang B, Liu Y, Zhang JS, Zhang XH, Chen WJ, Yin XH, Qi YF (2015) Cortistatin protects myocardium from endoplasmic reticulum stress induced apoptosis during sepsis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 406:40–48. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2015.02.016
Zhang H, Liu D, Wang X, Chen X, Long Y, Chai W, Zhou X, Rui X, Zhang Q, Wang H, Yang Q (2013) Melatonin improved rat cardiac mitochondria and survival rate in septic heart injury. J Pineal Res 55:1–6. doi:10.1111/jpi.12033
Zhang HM, Zhang Y (2014) Melatonin: a well-documented antioxidant with conditional pro-oxidant actions. J Pineal Res 57:131–146. doi:10.1111/jpi.12162
Zhang T, Lu X, Li J, Chidiac P, Sims SM, Feng Q (2012) Inhibition of Na/K-ATPase promotes myocardial tumor necrosis factor-alpha protein expression and cardiac dysfunction via calcium/mTOR signaling in endotoxemia. Basic Res Cardiol 107:254. doi:10.1007/s00395-012-0254-8
Zhang WJ, Wei H, Hagen T, Frei B (2007) Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory responses by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:4077–4082. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700305104
Zhang Z (2015) Biomarkers, diagnosis and management of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: a narrative review. Heart Lung Vessel 7:64–73
Zhong J, Hwang TC, Adams HR, Rubin LJ (1997) Reduced L-type calcium current in ventricular myocytes from endotoxemic guinea pigs. Am J Physiol 273:H2312–H2324
Zhou H, Qian J, Li C, Li J, Zhang X, Ding Z, Gao X, Han Z, Cheng Y, Liu L (2011) Attenuation of cardiac dysfunction by HSPA12B in endotoxin-induced sepsis in mice through a PI3K-dependent mechanism. Cardiovasc Res 89:109–118. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvq268
Zweier JL, Flaherty JT, Weisfeldt ML (1987) Direct measurement of free radical generation following reperfusion of ischemic myocardium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1404–1407
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81170185).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Additional information
R. An and L. Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, R., Zhao, L., Xi, C. et al. Melatonin attenuates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction via a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Basic Res Cardiol 111, 8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-015-0526-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-015-0526-1