Abstract
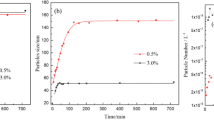
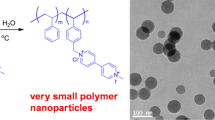
Selections of surfactants and their concentrations are both critical factors in emulsion polymerization for preparation of polymer nanoparticles with low polydispersity (i.e., low coefficient of variation of particle sizes, CV). Our previous report revealed that employment of an anionic surfactant of sodium octadecyl sulfate (SOS), which has a critical micellization concentration (CMC) much lower than sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) commonly used in conventional emulsion polymerization, is very effective for reducing particle sizes without deteriorating their monodispersity. However, the mechanism on formation of small polymer particles with low polydispersity was still not clarified in the previous report. In this report, the number (NP) and CV of polymer nanoparticles formed in the polymerization of styrene (St) using SOS were compared with the conventional polymerization using SDS in a wide range of surfactant concentrations including both their CMCs. The comparisons in NP and CV were also performed in copolymerizations with methylmethacrylate (MMA) less hydrophobic than St. These experimental comparisons in NP and CV have rationalized the St/MMA copolymerization using a low-CMC surfactant highly suitable for attaining the formation of nanoparticles with low polydispersity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harkins WD (1947) A general theory of the mechanism of emulsion polymerization. J Am Chem Soc 69:1428–1444. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01198a053
Atik SS, Thomas JK (1981) Polymerized microemulsions. J Am Chem Soc 103:4279–4280. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00404a065
Guo JS, El-Aasser MS, Vanderhoff JW (1989) Microemulsion polymerization of styrene. J Polym Sci: Part A: Polym Chem 27:691–710. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.1989.080270228
Kataoka K, Ohmura N, Kouzu M, Simamura Y, Okubo M (1995) Emulsion polymerization of styrene in a continuous Taylor vortex flow reactor. Chem Eng Sci 50(9):1409–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(94)00515-S
Landfester K, Bechthold N, Tiarks F, Antonietti M (1999) Formulation and stability mechanisms of polymerizable miniemulsions. Macromolucules 32:5222–5228. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma990299+
Landfester K (2001) Polyreactions in miniemulsions. Macromol Rapid Commun 22:896–936. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3927(20010801)22:12%3C896::AID-MARC896%3E3.0.CO;2-R
Schork FJ, Luo Y, Smulders W, Russum JP, Butté A, Fontenot K (2005) Miniemulsion polymerization Adv Polym Sci 175:129–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/b100115
Rao JP, Geckeler KE (2011) Polymer nanoparticles: preparation techniques and size-control parameters. Progress in Polym Sci 36:887–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.01.001
Nunes JS, Asua JM (2013) Synthesis of high solids content low surfactant/polymer ratio nanolatexes. Langmuir 29:3895–3902. https://doi.org/10.1021/la400686e
Lovell PA, Schork FJ (2020) Fundamentals of emulsion polymerization. Biomacromol 21:4396–4441. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00769
Smith WV, Ewart RH (1948) Kinetics of emulsion polymerization. J Chem Phys 16:592–599. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1746951
Roe CP (1968) Surface chemistry aspects of emulsion polymerization. Ind Eng Chem 60:20–33. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50705a006
Sütterlin N (1980) Influence of monomer polarity on particle formation in emulsion polymerization. In: Fitch RM (ed) Polymer Colloids II. Plenum Press, New York, pp 583–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-3635-8_29
Nomura M, Horie I, Kubo M, Fujita K (1989) Kinetics and mechanism of emulsion copolymerization. IV. Kinetic modeling of emulsion copolymerization of styrene and methyl methacrylate. J Appl Polym Sci 37:1029–1050. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1989.070370416
Konno M, Terunuma Y, Saito S (1991) Polymer particle formation in styrene polymerization in aqueous media at low surfactant concentrations. J Chem Eng Jpn 24:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1252/jcej.24.429
Zhendxing H, Xiaowei Y, Junliang L, Yuping Y, Ling W, Yanwei Z (2011) An investigation of the effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on quasi-emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization for highly monodisperse polystyrene nanospheres. Eur Polym J 47:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2010.09.036
Alfrey T, Bradford EB, Vanderhoff JW, Oster G (1954) J Opt Soc Am 44:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSA.44.000603
Fitch RM (1997) Order-disorder phenomena. In: Fitch RM (ed) Polymer colloids: a comprehensive introduction. Academic Press, London, pp 250–276 (Ch.9). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012257745-1/50011-0
Antonietti M, Berton B, Göltner C, Hentze H-P (1998) Synthesis of mesoporous silica with large pores and bimodal pore size distribution by templating of polymer Latices. Adv Mater 10:154–159. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-4095(199801)10:2%3C154::AID-ADMA154%3E3.0.CO;2-I
Jiang P, Ostojic GN, Narat R, Mittleman DM, Colvin VL (2001) The fabrication and bandgap engineering of photonic multilayers. Adv Mater 13:389–393. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-4095(200103)13:6%3C389::AID-ADMA389%3E3.0.CO;2-L
Fudouzi H, Xia Y (2003) Colloidal crystals with tunable colors and their use as photonic papers. Langmuir 19:9653–9660. https://doi.org/10.1021/la034918q
Guldin S, Hüttner S, Kolle M, Welland ME, Müller-Buschbaum P, Friend RH, Steiner U, Tétreault N (2010) Dye-sensitized solar cell based on a three-dimensional photonic crystal. Nano Lett 10:2303–2309. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl904017t
Mishchenko L, Hatton B, Kolle M, Aizenberg J (2012) Patterning hierarchy in direct and inverse opal crystals. Small 8:1904–1911. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201102691
Ding T, Long Y, Zhong K, Song K, Yang G, Tung C-H (2014) Modifying the symmetry of colloidal photonic crystals: a way towards complete photonic bandgap. J Mater Chem C 2:4100–4111. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC00351A
Utgenannt A, Maspero R, Fortini A, Turner R, Florescu M, Jeynes C, Kanaras AG, Muskens OL, Sear RP, Keddie JL (2016) Fast assembly of gold nanoparticles in large-area 2D nanogrids using a one-step, near-infrared radiation-assisted evaporation process. ACS Nano 10:2232–2242. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b06886
Zhang W, Tian Y, He H, Xu L, Li W, Zhao D (2020) Recent advances in the synthesis of hierarchically mesoporous TiO2 materials for energy and environmental applications. Natl Sci Rev 7:1702–1725. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwaa021
Goodwin JW, Hearn J, Ho CC, Ottewill RH (1974) Studies on the preparation and characterisation of monodisperse polystyrene laticee. Colloid Polym Sci 252:464–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01554752
Goodwin JW, Ottewill RH, Pelton R (1979) Studies on the preparation and characterization of monodisperse polystyrene latices V.: The preparation of cationic lattices. Colloid Polym Sci 257:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01539018
Hearn J, Wilkinson MC, Goodall AR, Chainey M (1985) Kinetics of the surfactant-free emulsion polymerization of styrene:-the post nucleation stage. J Polym Sci 23:1869–1883. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1985.170230703
Shouldice GTD, Vandezande GA, Rudin A (1994) Practical aspects of the emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization of styrene. EurPolym J 30:179–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-3057(94)90157-0
Gu S, Inukai S, Konno M (2002) Soapfree synthesis of monodisperse, micron-sized polystyrene particles in aqueous media. J Chem Eng Jpn 35:977–981. https://doi.org/10.1252/jcej.36.1231
Gu S, Akama H, Nagao D, Kobayashi Y, Konno M (2004) Langmuir 20:7948–7951. https://doi.org/10.1021/la049280c
Yamada Y, Sakamoto T, Gu S, Konno M (2005) Soap-free synthesis for producing highly monodisperse, micrometer-sized polystyrene particles up to 6 μm. J Colloid Interf Sci 281:249–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.030
Shibuya K, Nagao D, Ishii H, Konno M (2014) Advanced soap-free emulsion polymerization for highly pure, micron-sized, monodisperse polymer particles. Polymer 55:535–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2013.12.039
Tauer K (2004) Latex Particles. In: Caruso F (ed) Colloids and colloid assemblies. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, pp 1–51 (Ch.1). https://doi.org/10.1002/3527602100.ch1
Kong XZ, Zhu X, Jiang X, Li X (2009) Preparation and full characterization of cationic latex of styrene–butyl acrylate. Polymer 50:4220–4227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2009.06.041
Arunbabu D, Jana T (2011) Charged polystyrene nanoparticles: role of ionic comonomers structures. J Colloid Interf Sci 361:534–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.06.005
Nandiyanto ABD, Akane Y, Ogi T, Okuyama K (2012) Mesopore-free hollow silica particles with controllable diameter and shell thickness via additive-free synthesis. Langmuir 28:8616–8624. https://doi.org/10.1021/la301457v
Kim W, Choi SY, Jeon YM, Lee S-K, Kim SH (2014) Highly ordered, hierarchically porous TiO2 films via combination of two self-assembling templates. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:11484–11492. https://doi.org/10.1021/am502137d
Amri F, Septiani NLW, Rezki M, Iqbal M, Yamauchi Y, Golberg D, Kaneti YV, Yuliarto B (2021) Mesoporous TiO2-based architectures as promising sensing materials towards next-generation biosensing applications. J Mater Chem B 9:1189–1207. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TB02292F
Ishii H, Ishii M, Nagao D, Konno M (2014) Advanced synthesis for monodisperse polymer nanoparticles in aqueous media with sub-millimolar surfactants. Polymer 55:2772–2779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2014.04.011
Ishii H, Kuwasaki N, Nagao D, Konno M (2015) Environmentally adaptable pathway to emulsion polymerization for monodisperse polymer nanoparticle synthesis. Polymer 77:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2015.09.002
Piirma I, Chen S-R (1980) Adsorption of ionic surfactants on latex particles. J Colloid Interf Sci 74:90–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(80)90173-3
Yahata A, Ishii H, Nakamura K, Watanabe K, Nagao D (2019) Three-dimensional periodic structures of gold nanoclusters in the interstices of sub-100 nm polymer particles toward surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Adv Powd Tech 30(12):2957–2963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2019.09.003
Watanabe R, Yokoi T, Kobayashi E, Otsuka Y, Shimojima A, Okubo T, Tatsumi T (2011) Extension of size of monodisperse silica nanospheres and their well-ordered assembly. J Colloid Interf Sci 360:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.09.001
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the technical support staff in the department of Engineering, Tohoku University, for the measurements. This research was supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 16K06841, 17H02744, 20K21097, and Materials Processing Science project (“Materealize”) of MEXT, Grant Number JPMXP0219192801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishii, H., Nakazawa, H., Kuwasaki, N. et al. An experimental study on emulsion polymerization for formation of monodisperse particles smaller than 50 nm. Colloid Polym Sci 300, 397–405 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-022-04942-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-022-04942-w