Abstract
Introduction
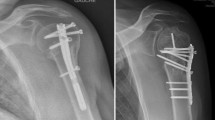
Complications after internal fixation of proximal humerus fracture are common and may require surgical revision. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (RTSA) is frequently performed in such cases. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the functional results and complications after RTSA for the treatment of type I fracture sequelae after internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures.
Materials and methods
26 patients (18 female, 8 male) underwent surgical revision of type I fracture sequelae of the proximal humerus after locking plate (n = 22) or intramedullary nail (n = 4) fixation. The mean age of the patients at the time of the revision was 75 years (range 65–89). After a mean follow-up of 36 months (range 18-58), clinical examination was performed and the age- and gender-related Constant–Murley Score (CMS) and the Oxford Shoulder Score (OSS) were obtained from all patients and compared to the pre-revision values.
Results
The mean age- and gender-related CMS of the affected shoulder increased from 44% (range 17–65) to 73% (range 44–97). This difference was statistically significant (p < 0.001). The CMS of the unaffected shoulder was 93% (range 72–98). This relates to a ratio in the CMS of 78% between the affected and the contralateral shoulder. The mean OSS was 28 points (range 12–54) for the operated shoulder and 43 points (range 34–48) for the unaffected side, resulting in 66% ratio. Again, the OSS improved significantly when compared with the preoperative values (p < 0.001). A total of five complications including two periprosthetic fractures were observed and required surgical revision.
Conclusion
Satisfying results can be obtained with RTSA as a salvage procedure for type I fracture sequelae after previous internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audige L, Goldhahn S, Daigl M, Goldhahn J, Blauth M, Hanson B (2014) How to document and report orthopedic complications in clinical studies? A proposal for standardization. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134(2):269–275
Baron JA, Barrett JA, Karagas MR (1996) The epidemiology of peripheral fractures. Bone 18(3 Suppl):209S–213S
Boileau P, Chuinard C, Le Huec JC, Walch G, Trojani C (2006) Proximal humerus fracture sequelae: impact of a new radiographic classification on arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 442:121–130
Cicak N, Klobucar H, Medancic N (2015) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty in acute fractures provides better results than in revision procedures for fracture sequelae. Int Orthop 39(2):343–348
Constant CR, Murley AH (1987) A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res 214:160–164
Court-Brown CM, Caesar B (2006) Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury 37(8):691–697
Dawson J, Fitzpatrick R, Carr A (1996) Questionnaire on the perceptions of patients about shoulder surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br 78(4):593–600
Grubhofer F, Wieser K, Meyer DC, Catanzaro S, Beeler S, Riede U, Gerber C (2016) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for acute head-splitting, 3- and 4-part fractures of the proximal humerus in the elderly. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25(10):1690–1698. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2016.02.024
Grubhofer F, Wieser K, Meyer DC, Catanzaro S, Schurholz K, Gerber C (2017) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for failed open reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 26(1):92–100. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2016.05.020
Hattrup SJ, Waldrop R, Sanchez-Sotelo J (2016) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for posttraumatic sequelae. J Orthop Trauma 30(2):e41–e47
Hussey MM, Hussey SE, Mighell MA (2015) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty as a salvage procedure after failed internal fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus: outcomes and complications. Bone Joint J 97(7):967–972
Ockert B, Siebenburger G, Kettler M, Braunstein V, Mutschler W (2014) Long-term functional outcomes (median 10 years) after locked plating for displaced fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 23(8):1223–1231
Raiss P, Edwards TB, Bruckner T, Loew M, Zeifang F, Walch G (2016) Reverse arthroplasty for patients with chronic locked dislocation of the shoulder (type 2 fracture sequela). J Shoulder Elbow Surg. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2016.05.028
Raiss P, Edwards TB, Bruckner T, Loew M, Zeifang F, Walch G (2017) Reverse arthroplasty for patients with chronic locked dislocation of the shoulder (type 2 fracture sequela). J Shoulder Elbow Surg 26(2):279–287
Raiss P, Edwards TB, Collin P, Bruckner T, Zeifang F, Loew M, Boileau P, Walch G (2016) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for malunions of the proximal part of the humerus (type-4 fracture sequelae). J Bone Joint Surg Am 98(11):893–899. doi:10.2106/JBJS.15.00506
Raiss P, Edwards TB, da Silva MR, Bruckner T, Loew M, Walch G (2014) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of nonunions of the surgical neck of the proximal part of the humerus (type-3 fracture sequelae). J Bone Joint Surg Am 96(24):2070–2076
Schliemann B, Siemoneit J, Theisen C, Kösters C, Weimann A, Raschke MJ (2012) Complex fractures of the proximal humerus in the elderly–outcome and complications after locking plate fixation. Musculoskelet Surg 96(Suppl 1):S3–11
Schliemann B, Theisen C, Barz L, Weimann A, Raschke MJ (2016) Reosteosynthese versus Prothese nach fehlgeschlagener Humeruskopfosteosynthese. Obere Extremität 11:239–247
Shannon SF, Wagner ER, Houdek MT, Cross WW 3rd, Sanchez-Sotelo J (2016) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: outcomes comparing primary reverse arthroplasty for fracture versus reverse arthroplasty after failed osteosynthesis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25(10):1655–1660
Sproul RC, Iyengar JJ, Devcic Z, Feeley BT (2011) A systematic review of locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures. Injury 42(4):408–413
Thanasas C, Kontakis G, Angoules A, Limb D, Giannoudis P (2009) Treatment of proximal humerus fractures with locking plates: a systematic review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 18(6):837–844
Thomas M, Dieball O, Busse M (2003) Normal values of the shoulder strength in dependency on age and gender–comparison with the constant, UCLA, ASES scores and SF36 health survey. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 141(2):160–170
Wellmann M, Struck M, Pastor MF, Gettmann A, Windhagen H, Smith T (2013) Short and midterm results of reverse shoulder arthroplasty according to the preoperative etiology. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133(4):463–471
Zafra M, Uceda P, Flores M, Carpintero P (2014) Reverse total shoulder replacement for nonunion of a fracture of the proximal humerus. Bone Joint J 96(9):1239–1243
Zhang AL, Schairer WW, Feeley BT (2014) Hospital readmissions after surgical treatment of proximal humerus fractures: is arthroplasty safer than open reduction internal fixation? Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(8):2317–2324
Acknowledgements
A native speaker edited the manuscript prior to submission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A.W. is a consultant for LIMA Corporate. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schliemann, B., Theisen, C., Kösters, C. et al. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for type I fracture sequelae after internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137, 1677–1683 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2789-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2789-5