Abstract
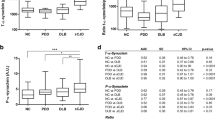
Several studies have addressed the utility of cerebrospinal (CSF) α-synuclein levels as a potential biomarker of α-synuclein aggregation disorders. However, its relevance in the differential diagnostic context of neurodegenerative and movement disorders is still a contentious subject. Here, we report total CSF α-synuclein levels in a cohort of clinically diagnosed α-synuclein-related disorders encompassing Parkinson’s disease, Parkinson’s disease dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies and multiple system atrophy in comparison to essential tremor and neurological control cases. α-synuclein levels in α-synuclein-related disorders were significantly lower than in controls (p < 0.001). However, in the differential diagnostic context, only Parkinson’s disease cases presented significant lower α-synuclein levels compared to essential tremor and neurological controls. In cases with clinically diagnosed α-synuclein pathology, CSF α-synuclein levels showed a moderate positive correlation with CSF tau and p-tau, but not with Aβ42 levels. Due to elevated CSF tau levels in dementia with Lewy bodies samples, tau/α-synuclein ratio showed a good clinical accuracy in discriminating controls from dementia with Lewy bodies cases (AUC = 0.8776) compared to single α-synuclein (AUC = 0.7192) and tau (AUC = 0.7739) levels. In conclusion, α-synuclein alone lacks of clinical value as a biomarker of α-synuclein-related disorders, but in combination with total tau, it may improve the diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PDD:
-
Parkinson’s disease dementia
- DLB:
-
Dementia with Lewy bodies
- MSA:
-
Multiple system atrophy
- ET:
-
Essential tremor
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
References
Boutin E, Vaugoyeau M, Eusebio A, Azulay JP, Witjas T (2015) News and controversies regarding essential tremor. Rev Neurol (Paris) 171(5):415–425
Cummings JL (1988) Intellectual impairment in Parkinson’s disease: clinical, pathologic, and biochemical correlates. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 1(1):24–36
Eller M, Williams DR (2011) alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Clin Chem Lab Med 49(3):403–408
Emre M, Aarsland D, Brown R, Burn DJ, Duyckaerts C, Mizuno Y, Broe GA, Cummings J, Dickson DW, Gauthier S, Goldman J, Goetz C, Korczyn A, Lees A, Levy R, Litvan I, McKeith I, Olanow W, Poewe W, Quinn N, Sampaio C, Tolosa E, Dubois B (2007) Clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22(12):1689–1707
Ferrer I, Lopez-Gonzalez I, Carmona M, Dalfo E, Pujol A, Martinez A (2012) Neurochemistry and the non-motor aspects of PD. Neurobiol Dis 46(3):508–526
Galvin JE, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2001) Synucleinopathies: clinical and pathological implications. Arch Neurol 58(2):186–190
Gao L, Tang H, Nie K, Wang L, Zhao J, Gan R, Huang J, Zhu R, Feng S, Duan Z, Zhang Y, Wang L (2015) Cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Neurosci 125(9):645–654
Gilman S, Wenning GK, Low PA, Brooks DJ, Mathias CJ, Trojanowski JQ, Wood NW, Colosimo C, Durr A, Fowler CJ, Kaufmann H, Klockgether T, Lees A, Poewe W, Quinn N, Revesz T, Robertson D, Sandroni P, Seppi K, Vidailhet M (2008) Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 71(9):670–676
Hall S, Ohrfelt A, Constantinescu R, Andreasson U, Surova Y, Bostrom F, Nilsson C, Hakan W, Decraemer H, Nagga K, Minthon L, Londos E, Vanmechelen E, Holmberg B, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Hansson O (2012) Accuracy of a panel of 5 cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of patients with dementia and/or parkinsonian disorders. Arch Neurol 69(11):1445–1452
Hall S, Surova Y, Ohrfelt A, Zetterberg H, Lindqvist D, Hansson O (2015) CSF biomarkers and clinical progression of Parkinson disease. Neurology 84(1):57–63
Halliday GM, Leverenz JB, Schneider JS, Adler CH (2014) The neurobiological basis of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 29(5):634–650
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55(3):181–184
Jellinger KA (2009) A critical evaluation of current staging of alpha-synuclein pathology in Lewy body disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792(7):730–740
Jimenez-Jimenez FJ, Alonso-Navarro H, Garcia-Martin E, Agundez JA (2012) The relationship between Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor: review of clinical, epidemiologic, genetic, neuroimaging and neuropathological data, and data on the presence of cardinal signs of parkinsonism in essential tremor. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y) 2:1–10
Kaerst L, Kuhlmann A, Wedekind D, Stoeck K, Lange P, Zerr I (2014) Using cerebrospinal fluid marker profiles in clinical diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 38(1):63–73
Kasai T, Tokuda T, Ishii R, Ishigami N, Tsuboi Y, Nakagawa M, Mizuno T, El-Agnaf OM (2014) Increased alpha-synuclein levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurol 261(6):1203–1209
Kruse N, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Schlossmacher MG, Mollenhauer B (2012) Development of electrochemiluminescence-based singleplex and multiplex assays for the quantification of alpha-synuclein and other proteins in cerebrospinal fluid. Methods 56(4):514–518
Li X, Li TQ, Andreasen N, Wiberg MK, Westman E, Wahlund LO (2014) The association between biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid and structural changes in the brain in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Intern Med 275(4):418–427
Lim X, Yeo JM, Green A, Pal S (2013) The diagnostic utility of cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein analysis in dementia with Lewy bodies—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19(10):851–858
Llorens F, Kruse N, Schmitz M, Shafiq M, da Cunha JE, Gotzman N, Zafar S, Thune K, de Oliveira JR, Mollenhauer B, Zerr I (2015) Quantification of CSF biomarkers using an electrochemiluminescence-based detection system in the differential diagnosis of AD and sCJD. J Neurol 262(10):2305–2311
Llorens F, Schmitz M, Gloeckner SF, Kaerst L, Hermann P, Schmidt C, Varges D, Zerr I (2015) Increased albumin CSF/serum ratio in dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neurol Sci 358(1–2):398–403
Llorens F, Schmitz M, Karch A, Cramm M, Lange P, Gherib K, Varges D, Schmidt C, Zerr I, Stoeck K (2016) Comparative analysis of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of neurodegenerative dementia. Alzheimers Dement 12(5):577–589
Louis ED, Honig LS, Vonsattel JP, Maraganore DM, Borden S, Moskowitz CB (2005) Essential tremor associated with focal nonnigral Lewy bodies: a clinicopathologic study. Arch Neurol 62(6):1004–1007
McKeith IG (2006) Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the Consortium on DLB International Workshop. J Alzheimers Dis 9(3 Suppl):417–423
McKeith IG, Galasko D, Kosaka K, Perry EK, Dickson DW, Hansen LA, Salmon DP, Lowe J, Mirra SS, Byrne EJ, Lennox G, Quinn NP, Edwardson JA, Ince PG, Bergeron C, Burns A, Miller BL, Lovestone S, Collerton D, Jansen EN, Ballard C, de Vos RA, Wilcock GK, Jellinger KA, Perry RH (1996) Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology 47(5):1113–1124
Mollenhauer B, Cullen V, Kahn I, Krastins B, Outeiro TF, Pepivani I, Ng J, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Kretzschmar HA, McLean PJ, Trenkwalder C, Sarracino DA, Vonsattel JP, Locascio JJ, El-Agnaf OM, Schlossmacher MG (2008) Direct quantification of CSF alpha-synuclein by ELISA and first cross-sectional study in patients with neurodegeneration. Exp Neurol 213(2):315–325
Mollenhauer B, Locascio JJ, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Sixel-Doring F, Trenkwalder C, Schlossmacher MG (2011) alpha-Synuclein and tau concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of patients presenting with parkinsonism: a cohort study. Lancet Neurol 10(3):230–240
Ohrfelt A, Grognet P, Andreasen N, Wallin A, Vanmechelen E, Blennow K, Zetterberg H (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative disorders-a marker of synapse loss? Neurosci Lett 450(3):332–335
Otto M, Wiltfang J, Cepek L, Neumann M, Mollenhauer B, Steinacker P, Ciesielczyk B, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Kretzschmar HA, Poser S (2002) Tau protein and 14-3-3 protein in the differential diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 58(2):192–197
Pahwa R, Koller WC (1993) Is there a relationship between Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor? Clin Neuropharmacol 16(1):30–35
Parnetti L, Chiasserini D, Bellomo G, Giannandrea D, De CC, Qureshi MM, Ardah MT, Varghese S, Bonanni L, Borroni B, Tambasco N, Eusebi P, Rossi A, Onofrj M, Padovani A, Calabresi P, El-Agnaf O (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid Tau/alpha-synuclein ratio in Parkinson’s disease and degenerative dementias. Mov Disord 26(8):1428–1435
Sako W, Murakami N, Izumi Y, Kaji R (2014) Reduced alpha-synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid in synucleinopathies: evidence from a meta-analysis. Mov Disord 29(13):1599–1605
Schade S, Mollenhauer B (2014) Biomarkers in biological fluids for dementia with Lewy bodies. Alzheimers Res Ther 6(5–8):72
Schoonenboom NS, Reesink FE, Verwey NA, Kester MI, Teunissen CE, van de Ven PM, Pijnenburg YA, Blankenstein MA, Rozemuller AJ, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM (2012) Cerebrospinal fluid markers for differential dementia diagnosis in a large memory clinic cohort. Neurology 78(1):47–54
Spies PE, Melis RJ, Sjogren MJ, Rikkert MG, Verbeek MM (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein does not discriminate between dementia disorders. J Alzheimers Dis 16(2):363–369
Spillantini MG, Goedert M (2000) The alpha-synucleinopathies: Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 920:16–27
Tapiola T, Alafuzoff I, Herukka SK, Parkkinen L, Hartikainen P, Soininen H, Pirttila T (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid {beta}-amyloid 42 and tau proteins as biomarkers of Alzheimer-type pathologic changes in the brain. Arch Neurol 66(3):382–389
Toledo JB, Korff A, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ, Zhang J (2013) CSF alpha-synuclein improves diagnostic and prognostic performance of CSF tau and Abeta in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 126(5):683–697
van Harten AC, Kester MI, Visser PJ, Blankenstein MA, Pijnenburg YA, van der Flier WM, Scheltens P (2011) Tau and p-tau as CSF biomarkers in dementia: a meta-analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med 49(3):353–366
Vann Jones SA, O’Brien JT (2014) The prevalence and incidence of dementia with Lewy bodies: a systematic review of population and clinical studies. Psychol Med 44(4):673–683
Walker Z, Possin KL, Boeve BF, Aarsland D (2015) Lewy body dementias. Lancet 386(10004):1683–1697
Wang ZY, Han ZM, Liu QF, Tang W, Ye K, Yao YY (2015) Use of CSF alpha-synuclein in the differential diagnosis between Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Int Psychogeriatr 27(9):1429–1438
Youden WJ (1950) Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 3(1):32–35
Zaccai J, McCracken C, Brayne C (2005) A systematic review of prevalence and incidence studies of dementia with Lewy bodies. Age Ageing 34(6):561–566
Zhou B, Wen M, Yu WF, Zhang CL, Jiao L (2015) The diagnostic and differential diagnosis utility of cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein levels in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Parkinsons Dis 2015:567386
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the JPND Neurodegenerative Disease Research grant: DEMTEST: Biomarker based diagnosis of rapidly progressive dementias-optimization of diagnostic protocols, 01ED1201A, by the Alzheimer-Forschungs-Initiative e.V. (AFI 12851) and by the DZNE-MiGAP study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
This study was conducted in compliance with the ethical standards.
Additional information
F. Llorens, M. Schmitz and D. Varges equally contributed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Llorens, F., Schmitz, M., Varges, D. et al. Cerebrospinal α-synuclein in α-synuclein aggregation disorders: tau/α-synuclein ratio as potential biomarker for dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neurol 263, 2271–2277 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8259-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8259-0