Abstract
Purpose
Considering the relevance of muscle strength for sustaining good musculoskeletal health among workers who perform physically demanding work, the aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of a therapeutic exercise program on muscle strength and low back symptoms among hospital nursing assistants.
Methods
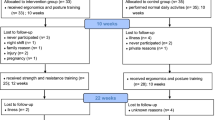
One hundred and twenty-nine nursing assistants filled out a questionnaire on personal, occupational information and health status, which allowed the identification of workers able to exercise. Ninety participants were randomly allocated to an intervention and a reference group. The therapeutic exercise program (TEP) lasted 12 weeks and included warm-up, strengthening and stretching exercises. Muscle strength of trunk flexors and trunk extensors, hamstring flexibility, and low back symptoms were evaluated before and after the intervention period by two blinded assessors. The comparison between groups was carried out using Mann–Whitney and χ2 tests at a significance level of 0.05.
Results
The average participation in the exercise program was 17.5 sessions. Results showed increased trunk flexors muscle strength (p = 0.002; effect size: 0.77), improved pressure pain threshold for dorsal longissimus (p = 0.001; effect size > 0.8), and reduced low back symptoms (p = 0.002; OR = 6.25). No differences between groups were identified for back extensor muscle strength or flexibility.
Conclusion
The exercise program applied is a feasible intervention which resulted clinically relevant results for nursing assistants’ musculoskeletal health expressed through trunk flexors muscle strength improvement and low back symptoms control among nursing assistants. This RCT brings contribution to the Occupational Health field as the exercise program applied resulted in clinically relevant results for nursing assistants’ musculoskeletal health. This study brings contribution especially for low-income and middle-income countries where low back pain and disability can be considered more severe as adequate resources to address the problem are scarce. Thus, we must highlight the importance of low-cost preventive strategies, like exercise programs carried out in hospital settings to avoid the progress of disability among active nursing personnel.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen LL (2011) Influence of psychosocial work environment on adherence to workplace exercise. J Occup Environ Med 53(2):182–184. https://doi.org/10.1097/JOM.0b013e3181207a01f
Andersen LL, Christensen KB, Holtermann A, Poulsen OM, Sjøgaard G, Pedersen MT, Hansen EA (2010) Effect of physical exercise interventions on musculoskeletal pain in all body regions among office workers: a one-year randomized controlled trial. Man Ther 15(1):100–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2009.08.004
Attarchi M, Raeisi S, Namvar M, Golabadi M (2014) Association between shift working and musculoskeletal symptoms among nursing personnel. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res 19(3):309–314
Bos E, Krol B, van der Star L, Groothoff J (2007) Risk factors and musculoskeletal complaints in non-specialized nurses, IC nurses, operation room nurses, and X-ray technologists. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 80(3):198–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-006-0121-8
Buchbinder R, van Tulder M, Öberg B, Menezes Costa L, Woolf A, Schoene M, Croft P (2018) Low back pain: a call for action. Lancet 391(10137):2384–2388. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30488-4
Cabral AM, Moreira RFC, de Barros FC, Sato TO (2019) Is physical capacity associated with the occurrence of musculoskeletal symptoms among office workers? A cross-sectional study. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 92(8):1159–1172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-019-01455-y
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey
Collins JW, Menzel NN (2006) Scope of the problem. In: Nelson A (ed) Safe patient handling and movement: a practical guide for health care professionals. Springer, New York, pp 8–9
Coury H, Moreira R, Dias N (2009) Evaluation of the effectiveness of workplace exercise in controlling neck, shoulder and low back pain: a systematic review. Braz J Phys Ther 13(6):461–479. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-35552009000600002
Cohen-Mansfield J, Culpepper WJ, Carter P (1996) Nursing staff back injuries: prevalence and cost in long term care facilities. AAOHN J 44(1):9–17
Dawson AP, McLennan SN, Schiller SD, Jull GA, Hodges PW, Stewart S (2007) Interventions to prevent back pain and back injury in nurses: a systematic review. Occup Environ Med 64:642–650. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.2006.030643
Davis KG, Kotowski SE (2015) Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders for nurses in hospitals, long-term care facilities, and home health care: a comprehensive review. Hum Factors 57(5):754–792. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018720815581933
De Barros ENC, Alexandre NMC (2003) Cross-cultural adaptation of the Nordic musculoskeletal questionnaire. Int Nurs Rev 50(2):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1466-7657.2003.00188.x
Ellapen TJ, Narsigan S (2014) Work related musculoskeletal disorders among nurses: systematic review. J Ergon S4:1–6. https://doi.org/10.4172/2165-7556.S4-003
Eriksen W (2004) Work factors as predictors of intense or disabling low back pain; a prospective study of nurses’ aides. Occup Environ Med 61(5):398–404. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.2003.008482
Essendrop M, Schibye B, Hansen K (2001) Reliability of isometric muscle strength tests for the trunk, hands and shoulders. Int J Ind Ergon 28(6):379–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-8141(01)00044-0
Farasyn A, Meeusen R (2005) The influence of non-specific low back pain on pressure pain thresholds and disability. Eur J Pain 9(4):375–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpain.2004.09.005
Feng C-K, Chen M-L, Mao I-F (2007) Prevalence of and risk factors for different measures of low back pain among female nursing aides in Taiwanese nursing homes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 8(52):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-8-52
Ferguson SA, Marras WS (1997) A literature review of low back disorder surveillance measures and risk factors. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 12(4):211–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/s02680033(96)00073-3
Froud R, Eldridge S, Kovacs F, Breen A, Bolton J, Dunn K, Fritz J, Keller A, Kent P, Lauridsen HH, Ostelo R, Pincus T, van Tulder M, Vogel S, Underwood M (2011) Reporting outcomes of back pain trials: a modified Delphi study. Eur J Pain 15:1068–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpain.2011.04.015
Gundewall B, Liljeqvist M, Hansson T (1993) Primary prevention of back symptoms and absence from work. A prospective randomized study among hospital employees. Spine 18(5):587–594. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-199304000-00011
Hamberg-van Reenen HH, Ariëns GAM, Blatter BM, van der Beek AJ, Twisk JWR, van Mechelen W, Bongers PM (2006) Is an imbalance between physical capacity and exposure to work-related physical factors associated with lower-back, neck or shoulder pain? Scand J Work Environ Health 32(3):190–197. https://doi.org/10.5271/sjweh.998
Hayden J, Van Tulder M, Malmivaara A, Koes B (2005a) Exercise therapy for treatment of non-specific low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 20(3):CD000335. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000335.pub2
Hayden JA, van Tulder MW, Tomlinson G (2005b) Systematic review: strategies for using exercise therapy to improve outcomes in chronic low back pain. Ann Intern Med 142:776–785. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-142-9-200505030-00014
Holtermann A, Blangsted K, Hansen K, Christensen H, Søgaard K (2009) What characterizes cleaners sustaining good musculoskeletal health after years with physically heavy work? Int Arch Occup Environ Health 82(8):1015–1022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-009-0401-1
Holtermann A, Jørgensen MB, Gram B, Christensen JR, Faber A, Overgaard K, Ektor-Andersen J, Mortensen OS, Sjøgaard G, Søgaard K (2010) Worksite interventions for preventing physical deterioration among employees in job-groups with high physical work demands: background, design and conceptual model of FINALE. BMC Public Health 10:120. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-10-120
Hoy D, March L, Brooks P et al (2014) The global burden of low back pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis 73:968–974. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204428
Jakobsen MD, Sundstrup E, Brandt M, Kristensen AZ, Jay K, Stelter R, Lavendt E, Aagaard P, Andersen LL (2014) Effect of workplace—versus home-based physical exercise on pain in healthcare workers: study protocol for a single blinded cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 15:119. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-15-119
Jørgensen M, Ektor-Andersen J, Sjøgaard G, Holtermann A, Søgaard K (2011) A randomised controlled trial among cleaners—effects on strength, balance and kinesiophobia. BMC Public Health 11:776. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-11-776
June KJ, Cho S-H (2011) Low back pain and work-related factors among nurses in intensive care units. J Clin Nurs 20(3–4):479–487. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2010.03210.x
Kisner C, Colby L (2012) Therapeutic exercise: foundations and techniques. FA Davis Company, Philadelphia
Kuorinka I, Jonsson B, Kilbom A, Vinterberg H, Biering-Sørensen F, Andersson G, Jørgensen K (1987) Standardised Nordic questionnaires for the analysis of musculoskeletal symptoms. Appl Ergon 18:233–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-6870(87)90010-X
Lewis R, Gómez Álvarez CB, Rayman Lanham-New S, Woolf A, Mobasher A (2019) Strategies for optimising musculoskeletal health in the 21st century. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 20:164. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2510-7
Lipscomb J, Trinkoff A, Brady B, Geiger-Brown J (2004) Health care system changes and reported musculoskeletal disorders among registered nurses. Am J Public Health 94(8):1431–1435 (PMID: 15284055)
MacNeela P, Doyle C, O’Gorman D, Ruane N, McGuire BE (2015) Experiences of chronic low back pain: a meta-ethnography of qualitative research. Health Psychol Rev 9:63–82. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437199.2013.840951
Madeleine P (2010) On functional motor adaptations: from the quantification of motor strategies to the prevention of musculoskeletal disorders in the neck-shoulder region. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 199(679):1–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02145.x
McGill S (2007) Lumbar spine stability: myths and realities. In: McGill S (ed) Low back disorders: evidence-based prevention and rehabilitation, 2nd edn. Human Kinetics, Champaign, pp 137–147
Nelson A, Lloyd JD, Menzel N, Gross C (2003) Preventing nursing back injuries: redesigning patient handling tasks. AAOHN J 51(3):126–134
Nielsen PK, Andersen LL, Olsen HB, Rosendal L, Sjøgaard G, Søgaard K (2010) Effect of physical training on pain sensitivity and trapezius muscle morphology. Muscle Nerve 41(6):836–844. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.21577
Philadelphia Panel Members (2001) Philadelphia Panel evidence-based clinical practice guidelines on selected rehabilitation interventions for low back pain. Phys Ther 81:1641–1674. https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/81.10.1641
Pompeii LA, Lipscomb HJ, Schoenfisch AL, Dement JM (2009) Musculoskeletal injuries resulting from patient handling tasks among hospital workers. Am J Ind Med 52(7):571–578. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajim.20704
Rainville J, Hartigan C, Martinez E, Limke J, Jouve C, Finno M (2004) Exercise as a treatment for chronic low back pain. Spine J 4(1):106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1529-9430(03)00174-8
Rosendal L, Larsson B, Kristiansen J, Peolsson M, Søgaard K, Kjaer M, Sørensen J, Gerdle B (2004) Increase in muscle nociceptive substances and anaerobic metabolism in patients with trapezius myalgia: microdialysis in rest and during exercise. Pain 112(3):324–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2004.09.017
Sjøgaard G, Lundberg U, Kadefors R (2000) The role of muscle activity and mental load in the development of pain and degenerative processes at the muscle cell level during computer work. Eur J Appl Physiol 83(2–3):99–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210000285
Søgaard K, Jull G (2014) Therapeutic exercise for prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of musculoskeletal pain and function as well as general health and life quality: a call for papers. Man Ther 19(4):277–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2014.05.002
Strazdins L, Bammer G (2004) Women, work and musculoskeletal health. Soc Sci Med 58(6):997–1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0277-9536(03)00260-0
Tuomi K, Ilmarinen J, Jahkola A, Katajarinne L, Tulkki A (1998) Work Ability Index. Finnish Institute of Occupational Health, Helsinki
Van Hoof W, O'Sullivan K, O'Keeffe M, Verschueren S, O'Sullivan P, Dankaerts W (2018) The efficacy of interventions for low back pain in nurses: a systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud 77:222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2017.10.015
van Middelkoop M, Rubinstein SM, Kuijpers T, Verhagen AP, Ostelo R, Koes BW, van Tulder MW (2011) A systematic review on the effectiveness of physical and rehabilitation interventions for chronic non-specific low back pain. Eur Spine J 20(1):19–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-010-1518-3
Vos T, Allen C, Arora M et al (2016) Disease and injury incidence and prevalence collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388:1545–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6
Wells KF, Dillon EK (1952) The sit and reach—a test of back and leg flexibility, research quarterly. Am Associ Health Phys Educ Recreat 23(1):115–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/10671188.1952.10761965
Yassi A, Lockhart K (2013) Work-relatedness of low back pain in nursing personnel: a systematic review. Int J Occup Environ Health 19(3):223–244. https://doi.org/10.1179/2049396713Y.0000000027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This study was funded by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), Brazil. The authors declare no financial as well non-financial conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All participants signed the informed consent form and gave their permission to participate in the study, which was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreira, R.F.C., Moriguchi, C.S., Carnaz, L. et al. Effects of a workplace exercise program on physical capacity and lower back symptoms in hospital nursing assistants: a randomized controlled trial. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 94, 275–284 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-020-01572-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-020-01572-z