Abstract
Objectives
Examine the acute effects (pre-, during, post-intervention) of two different intensities of aerobic exercise or rest on autonomic, oculomotor, and vestibular function and symptom burden in patients with a recent sport-related concussion (SRC) and compare their responses to sex-matched, age-stratified, non-concussed (HEALTHY) student-athletes.
Methods
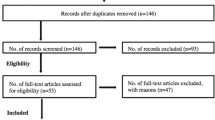
Student-athletes between the ages of 13 and 18 that presented to the sports medicine clinic within Day 3–7 post-SRC and from local schools were recruited for a randomized controlled trial (RCT). The participants were administered the Vestibular/Ocular Motor Screening (VOMS), King-Devick (K-D), and Post-Concussion Symptom Scale (PCSS) before and after the intervention. Heart rate variability (HRV) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) were collected before, during, and after the intervention. The intervention was either a single, 20-min session of treadmill walking at 40% (40HR) or 60% of age-predicted max heart rate (60HR), or seated, rest (NOEX).
Results
30 participants completed the intervention with the SRC group treated 4.5 ± 1.3 days post-injury. Pre-exercise HRV and MAP were significantly different (p’s < 0.001) during treatment but returned to pre-exercise values within 5 min of recovery in both the SRC and HEALTHY groups. Both the SRC and HEALTHY groups exhibited similar reductions pre- to post-intervention for symptom severity and count (p’s < 0.05), three VOMS items (p’s < 0.05) but not K-D time.
Conclusions
To date, this is the first adolescent RCT to report the acute, systemic effects of aerobic exercise on recently concussed adolescent athletes. The interventions appeared safe in SRC participants, were well-tolerated, and provided brief therapeutic benefit.
Trial registration
Clinicaltrials.gov Identifier NCT03575455.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data from the study can be made available upon request to the editorial board if there are any questions about data integrity or clarifications needed.
References
Accardo A, Merlo M, Silveri G, Del Popolo L, Dalla Libera L, Restivo L et al (2021) Influence of ageing on circadian rhythm of heart rate variability in healthy subjects. J Cardiovasc Med (hagerstown) 22:405–413
Aletti F, Ferrario M, Tam E, Cautero M, Cerutti S, Capelli C et al (2009) Identification of vascular responses to exercise and orthostatic stress in bed rest-induced cardiovascular deconditioning. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5332690
American College of Sports Medicine (2014) ACSM’s Health-Related Physical Fitness Assessment Manual, 4th edn. In: Kaminsky L (ed). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Balestrini CS, Moir ME, Abbott KC, Klassen SA, Fischer LK, Fraser DD et al (2021) Autonomic dysregulation in adolescent concussion is sex- and posture-dependent. Clin J Sport Med 31:257–265
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x
Borg GA (1970) Perceived exertion as an indicator of somatic stress. Scand J Rehabil Med 2:92–98
Brunner E, Domhof S, Langer F (2002) Nonparametric analysis of longitudinal data in factorial experiments. Wiley, New York
Bryan MA, Rowhani-Rahbar A, Comstock RD, Rivara F (2016) Sports- and recreation-related concussions in US youth. Pediatrics. 138:e20154635–e20154635. http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/doi/10.1542/peds.2015-4635
Buckley TA, Munkasy BA, Clouse BP (2016) Acute cognitive and physical rest may not improve concussion recovery time. J Head Trauma Rehabil 31:233–241
Burgeat M, Toupet M, Loth D, Ingster I, Guell A, Coll J (1981) Status of vestibular function after prolonged bedrest. Acta Astronaut 8:1019–1027. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11543091/
Burma JS, Copeland PV, Macaulay A, Smirl JD (2021) The impact of high- and moderate-intensity exercise on near-point of convergence metrics. Brain Inj 35:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2021.1871953
Camm A, Malik M, Bigger J, Breithardt G, Cerutti S, Cohen R et al (1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Eur Heart J 17:354–381
Covassin T, Weiss L, Powell J, Womack C (2007) Effects of a maximal exercise test on neurocognitive function. Br J Sports Med 41:370–374
Dematteo C, Volterman KA, Breithaupt PG, Claridge EA, Adamich J, Timmons BW et al (2015) Exertion testing in youth with mild traumatic brain injury/concussion. Med Sci Sport Exerc 47:2283–2290
DiFazio M, Silverberg ND, Kirkwood MW, Bernier R, Iverson GL (2016) Prolonged activity restriction after concussion: are we worsening outcomes? Clin Pediatr (phila) 55:443–451
Eddy R, Goetschius J, Hertel J, Resch J (2018) Test-retest reliability and the effects of exercise on the King-Devick test. Clin J Sport Med. https://doi.org/10.1097/JSM.0000000000000586
Elbin RJ, Eagle SR, Marchetti GF, Anderson M, Schatz P, Womble MN et al (2021) Using change scores on the vestibular ocular motor screening (VOMS) tool to identify concussion in adolescents. Appl Neuropsychol Child. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622965.2021.1911806
Elkington TJ, Cassar S, Nelson AR, Levinger I (2017) Psychological responses to acute aerobic, resistance, or combined exercise in healthy and overweight individuals: a systematic review. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.1177/1179546817701725
Gaetz MB, Iverson GL (2009) Sex differences in self-reported symptoms after aerobic exercise in non-injured athletes: implications for concussion management programmes. Br J Sports Med 43:508–513
Gagnon I, Galli C, Friedman D, Grilli L, Iverson GL (2009) Active rehabilitation for children who are slow to recover following sport-related concussion. Brain Inj 23:956–964
Gagnon I, Grilli L, Friedman D, Iverson GL (2016) A pilot study of active rehabilitation for adolescents who are slow to recover from sport-related concussion. Scand J Med Sci Sports 26:299–306
Galetta KM, Barrett J, Allen M, Madda F, Delicata D, Tennanta T et al (2011a) The King-Devick test as a determinant of head trauma and concussion in boxers and MMA fighters. Neurology 76:1456–1462. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21288984
Galetta KM, Brandes LE, Maki K, Dziemianowicz MS, Laudano E, Allen M et al (2011b) The King-Devick test and sports-related concussion: study of a rapid visual screening tool in a collegiate cohort. J Neurol Sci 309:34–39
Gall B, Parkhouse WS, Goodman D (2004a) Exercise following a sport induced concussion. Br J Sports Med 38:773–777
Gall B, Parkhouse W, Goodman D (2004b) Heart rate variability of recently concussed athletes at rest and exercise. Med Sci Sport Exerc 36:1269–1274
Ghulyan-Bedikian V, Paolino M, Paolino F (2013) Short-term retention effect of rehabilitation using head position-based electrotactile feedback to the tongue: influence of vestibular loss and old-age. Gait Posture 38:777–783
Gibbons RJ, Balady GJ, Bricker JT, Chaitman BR, Fletcher GF, Froelicher VF et al (2002) ACC/AHA 2002 guideline update for exercise testing: summary article: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee to Update the 1997 Exercise Testing Guidelines). Circulation 106:1883–1892
Gibson S, Nigrovic LE, O’Brien M, Meehan WP (2013) The effect of recommending cognitive rest on recovery from sport-related concussion. Brain Inj 27:839–842
Giles DA, Draper N (2018) Heart rate variability during exercise: a comparison of artefact correction methods. J Strength Cond Res 32:726–735
Griesbach GS (2011) Exercise after traumatic brain injury: is it a double-edged sword? PM R 3:S64–S72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2011.02.008
Guthrie R (2018) Physical activity following acute concussion and persistent postconcussive symptoms in children and adolescents. Phys Sportsmed 46:416–419. https://doi.org/10.1080/00913847.2018.1516479
Haider MN, Worts PR, Viera KB, Villarrubia B, Wilber CG, Willer BS et al (2020) Postexercise slowing on the King-Devick test and longer recovery from sport-related concussion in adolescents: a validation study. J Athl Train. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-264-19
Haider MN, Patel KS, Willer BS, Videira V, Wilber CG, Mayer AR et al (2021) Symptoms upon postural change and orthostatic hypotension in adolescents with concussion. Brain Inj 35:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2021.1871951
Harmon KG, Clugston JR, Dec K, Hainline B, Herring S, Kane SF et al (2019) American Medical Society for Sports Medicine position statement on concussion in sport. Br J Sports Med 53:213–225
Heick JD, Bay C (2021) Determining near point of convergence: exploring a component of the vestibular/ocular motor screen comparing varied target sizes. Int J Sports Phys Ther 16:21–30
Iverson GL, Lovell MR, Collins MW (2003) Interpreting change on ImPACT following sport concussion. Clin Neuropsychol 17:460–467
Johnson BD, Leary MCO, Mcbryde M, Sackett JR, Schlader ZJ, Leddy JJ et al (2018) Face cooling exposes cardiac parasympathetic and sympathetic dysfunction in recently concussed college athletes. Physiol Rep 6:1–11
Jones H, George K, Edwards B, Atkinson G (2008) Effects of time of day on post-exercise blood pressure: circadian or sleep-related influences? Chronobiol Int 25:987–998
King D, Brughelli M, Hume P, Gissane C (2013) Concussions in amateur rugby union identified with the use of a rapid visual screening tool. J Neurol Sci 326:59–63
La Fountaine MF, Heffernan KS, Gossett JD, Bauman WA, De Meersman RE (2009) Transient suppression of heart rate complexity in concussed athletes. Auton Neurosci Basic Clin 148:101–103
Langsrud Ø (2003) ANOVA for unbalanced data: Use type II instead of type III sums of squares. Stat Comput 13:163–167. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023260610025
Laurens J, Angelaki DE (2011) The functional significance of velocity storage and its dependence on gravity. Exp Brain Res 210:407–422
Lawrence JB, Haider MN, Leddy JJ, Hinds A, Miecznikowski JC, Willer BS (2019) The King-Devick test in an outpatient concussion clinic: Assessing the diagnostic and prognostic value of a vision test in conjunction with exercise testing among acutely concussed adolescents. J Neurol Sci 398:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2018.12.020
Leddy JJ, Kozlowski K, Fung M, Pendergast DR, Willer B (2007) Regulatory and autoregulatory physiological dysfunction as a primary characteristic of post concussion syndrome: implications for treatment. Neuro Rehabil 22:199–205. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17917170
Leddy JJ, Kozlowski K, Donnelly JP, Pendergast DR, Epstein LH, Willer B (2010) A preliminary study of subsymptom threshold exercise training for refractory post-concussion syndrome. Clin J Sport Med 20:21–27
Leddy JJ, Hinds AL, Miecznikowski J, Darling S, Matuszak J, Baker JG et al (2018) Safety and prognostic utility of provocative exercise testing in acutely concussed adolescents: a randomized trial. Clin J Sport Med 28:13–20
Leddy JJ, Haider MN, Ellis MJ, Mannix R, Darling S, Freitas M et al (2019a) Early subthreshold aerobic exercise for sport-related concussion: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr 173:319–325
Leddy JJ, Haider MN, Hinds AL, Darling S, Willer BS (2019b) A preliminary study of the effect of early aerobic exercise treatment for sport-related concussion in males. Clin J Sport Med 29:353–360
Leddy JJ, Master CL, Mannix R, Wiebe DJ, Grady MF, Meehan WP et al (2021) Early targeted heart rate aerobic exercise versus placebo stretching for sport-related concussion in adolescents: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Child Adolesc Heal 5:792–799. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34600629/
Ledoux A-A, Barrowman N, Bijelić V, Borghese MM, Davis A, Reid S et al (2021) Is early activity resumption after paediatric concussion safe and does it reduce symptom burden at 2 weeks post injury? The Pediatric Concussion Assessment of Rest and Exertion (PedCARE) multicentre randomised clinical trial. Br J Sports Med 56:271–278
Legrand FD, Albinet C, Canivet A, Gierski F, Morrone I, Besche-Richard C (2018) Brief aerobic exercise immediately enhances visual attentional control and perceptual speed. Testing the mediating role of feelings of energy. Acta Psychol 191:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2018.08.020
Leong DF, Balcer LJ, Galetta SL, Evans G, Gimre M, Watt D (2015) The King-Devick test for sideline concussion screening in collegiate football. J Optom 8:131–139
Liu Q, Zhou R, Zhao X, Oei T (2015) Effects of prolonged head-down bed rest on working memory. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S76292
Lovell MR, Iverson GL, Collins MW, Podell K, Johnston KM, Pardini D et al (2006) Measurement of symptoms following sports-related concussion: reliability and normative data for the post-concussion scale. Appl Neuropsychol 13:166–174. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17361669
Marusic U, Kavcic V, Giordani B, Gerževič M, Meeusen R, Pišot R (2015) Computerized spatial navigation training during 14 days of bed rest in healthy older adult men: effect on gait performance. Psychol Aging 30:334–340. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25938245/
McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Dvořák J, Aubry M, Bailes J, Broglio S et al (2017) Consensus statement on concussion in sport-the 5th international conference on concussion in sport held in Berlin, October 2016. Br J Sports Med. 51:838–47. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28446457
Merritt VC, Bradson ML, Meyer JE, Arnett PA (2018) Evaluating the test–retest reliability of symptom indices associated with the ImPACT post-concussion symptom scale (PCSS). J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 40:377–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803395.2017.1353590
Micay R, Richards D, Hutchison MG (2018) Feasibility of a postacute structured aerobic exercise intervention following sport concussion in symptomatic adolescents: a randomised controlled study. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med 4:4–9
Mohler S, Elbin RJ, Ott S, Butts CL, Mcdermott B, Ganio MS et al (2021) How long after maximal physical exertion should baseline computerized neurocognitive testing and symptom assessment be administered? Brain Inj. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2021.1872098
Moran RN, Murray NG, Esco MR, Dobbs W, Mcallister-Deitrick J (2020) Effects of exercise on symptoms, vestibular/ocular motor screening and postural stability in a college-aged sample. Concussion. https://doi.org/10.2217/cnc-2020-0003
Morres ID, Hatzigeorgiadis A, Stathi A, Comoutos N, Arpin-Cribbie C, Krommidas C et al (2019) Aerobic exercise for adult patients with major depressive disorder in mental health services: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Depress Anxiety 36:39–53
Morris M, Steinberg H, Sykes EA, Salmon P (1990) Effects of temporary withdrawal from regular running. J Psychosom Res 34:493–500
Mucha A, Collins MW, Elbin RJ, Furman JM, Troutman-Enseki C, DeWolf RM et al (2014) A Brief Vestibular/Ocular Motor Screening (VOMS) assessment to evaluate concussions: preliminary findings. Am J Sports Med 42:2479–2486. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25106780
Noguchi K, Gel YR, Brunner E, Konietschke F (2012) nparLD: An R software package for the nonparametric analysis of longitudinal data in factorial experiments. J Stat Softw http://www.jstatsoft.org/
Perini R, Veicsteinas A (2003) Heart rate variability and autonomic activity at rest and during exercise in various physiological conditions. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:317–325
Perini R, Orizio C, Baselli G, Cerutti S, Veicsteinas A (1990) The influence of exercise intensity on the power spectrum of heart rate variability. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 61:143–148
Petit KM, Covassin T (2020) College athletic trainers’ perceptions of rest and physical activity when managing athletes with a sport-related concussion. J Sport Rehabil 1–6. https://journals.humankinetics.com/view/journals/jsr/aop/article-10.1123-jsr.2019-0084/article-10.1123-jsr.2019-0084.xml
Phillips J, Tierney R (2015) Effect of target type on near point of convergence in a healthy, active, young adult population. J Eye Mov Res 8:1–6
Popovich M, Almeida A, Lorincz M, Eckner JT, Freeman J, Streicher N et al (2021) Does exercise increase vestibular and ocular motor symptom detection after sport-related concussion? J Neurol Phys Ther 45:214–220
R Core Team (2022) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Root JM, Sady MD, Gai J, Vaughan CG, Madati PJ (2020) Effect of cognitive and physical rest on persistent postconcussive symptoms following a pediatric head injury. J Pediatr 227:184-190.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.07.049
Rutschmann TD, Miutz LN, Toomey CM, Yeates KO, Emery CA, Schneider KJ (2021) Changes in exertion-related symptoms in adults and youth who have sustained a sport-related concussion. J Sci Med Sport 24:2–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2020.06.005
Samani A, Heath M (2018) Executive-related oculomotor control is improved following a 10-min single-bout of aerobic exercise: Evidence from the antisaccade task. Neuropsychologia 108:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.11.029
Scherr J, Wolfarth B, Christle JW, Pressler A, Wagenpfeil S, Halle M (2013) Associations between Borg’s rating of perceived exertion and physiological measures of exercise intensity. Eur J Appl Physiol 113:147–155
Silverberg ND, Otamendi T (2019) Advice to rest for more than 2 days after mild traumatic brain injury is associated with delayed return to productivity: a case-control study. Front Neurol 10:1–6
Silverberg ND, Iverson GL, McCrea M, Apps JN, Hammeke TA, Thomas DG (2016) Activity-related symptom exacerbations after pediatric concussion. JAMA Pediatr 170:946–953. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27479847
Snyder A, Sheridan C, Tanner A, Bickart K, Sullan M, Craske M et al (2021) Cardiorespiratory functioning in youth with persistent post-concussion symptoms: a pilot study. J Clin Med 10:561
Stubbs B, Vancampfort D, Rosenbaum S, Firth J, Cosco T, Veronese N et al (2017) An examination of the anxiolytic effects of exercise for people with anxiety and stress-related disorders: a meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res 249:102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2016.12.020
Sufrinko AM, Howie EK, Charek DB, Elbin RJ, Collins MW, Kontos AP (2019) Mobile ecological momentary assessment of postconcussion symptoms and recovery outcomes. J Head Trauma Rehabil 1. http://insights.ovid.com/crossref?an=00001199-900000000-99435
Swain DP (2014) ACSM’s resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, 7th edn. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Tanaka H, Monahan KD, Seals DR (2001) Age-predicted maximal heart rate revisited. J Am Coll Cardiol 37:153–156
Thomas DG, Apps JN, Hoffmann RG, McCrea M, Hammeke T (2015) Benefits of strict rest after acute concussion: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics 135:213–223
Wells EM, Goodkin HP, Griesbach GS (2016) Challenges in determining the role of rest and exercise in the management of mild traumatic brain injury. J Child Neurol 31:86–92
Wickham H, Averick M, Bryan J, Chang W, McGowan LD, François R, Grolemund G, Hayes A, Henry L, Hester J, Kuhn M, Pedersen TL, Miller E, Bache SM, Müller K, Ooms J, Robinson D, Seidel DP, Spinu V, Takahashi K, Vaughan D, Wilke C, Woo K, Yutani H (2019) Welcome to the tidyverse. J Open Source Softw 4(43):1686. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01686
Willer BS, Haider MN, Bezherano I, Wilber CG, Mannix R, Kozlowski K et al (2019) Comparison of rest to aerobic exercise and placebo-like treatment of acute sport-related concussion in male and female adolescents. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 100:2267–2275
Worts PR, Schatz P, Burkhart SO (2018) Test performance and test-retest reliability of the vestibular/ocular motor screening and King-Devick test in adolescent athletes during a competitive sport season. Am J Sports Med 46:2004–2010
Worts PR, Burkhart SO, Kim J-S (2019) A Physiologically based approach to prescribing exercise following a sport-related concussion. Sports Med 49:683–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-019-01065-1
Worts PR, Haider MN, Mason JR, Schatz P (2021) Norm-based cutoffs as predictors of prolonged recovery after adolescent sport-related concussion. Clin J Sport Med. https://doi.org/10.1097/JSM.0000000000000952
Yakushin SB, Raphan T, Cohen B (2017) Coding of velocity storage in the vestibular nuclei. Front Neurol 8:1–19
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of: the clinical team for study execution (Drs. Scott Burkhart, Daniel Petty, Scott Porter, and Todd Hewitt and Tallahassee Orthopedic Clinic); the scientific advisors for study development (Drs. Lynn Panton, Michael Ormsbee, and Cathy Levenson); and the athletic trainers for assistance with coordination of recruitment (Alan Morales, Jordan Bush, and Kaydi Blackstock).
Funding
The publication was made possible in part with support from Tallahassee Orthopedic Clinic and funded by Tallahassee Orthopedic Clinic Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PRW was responsible for study conceptualization, design, coordination, and data collection and prepared and edited the article and supplemental file. JRM was responsible for data analysis and prepared and edited the article and supplemental file. SOB was responsible for study conceptualization, design, coordination and prepared and edited the article. MASG was responsible for study design, data analysis and edited the article. J-SK was responsible for study conceptualization, design, coordination, and edited the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Phillip Worts and Scott Burkhart are co-authors of the Frequency of Concussion Symptoms (FOCS) survey. Opinions, interpretations, conclusions, and recommendations are those of the authors and are not necessarily endorsed by Tallahassee Orthopedic Clinic or Tallahassee Orthopedic Clinic Foundation. The remaining authors have no conflicts.
Ethics approval
The Florida State University Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Consent to participate
Adult-age participants provided consent after a review of study methods and questions answered. For minors, parents/guardians provided permission, and minors provided assent after a review of study methods and questions answered.
Additional information
Communicated by Ellen Adele Dawson.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Worts, P.R., Mason, J.R., Burkhart, S.O. et al. The acute, systemic effects of aerobic exercise in recently concussed adolescent student-athletes: preliminary findings. Eur J Appl Physiol 122, 1441–1457 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-04932-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-04932-4