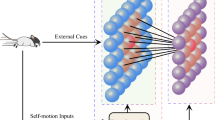
Abstract
Animals are able to update their knowledge about their current position solely by integrating the speed and the direction of their movement, which is known as path integration. Recent discoveries suggest that grid cells in the medial entorhinal cortex might perform some of the essential underlying computations of path integration. However, a major concern over path integration is that as the measurement of speed and direction is inaccurate, the representation of the position will become increasingly unreliable. In this paper, we study how allothetic inputs can be used to continually correct the accumulating error in the path integrator system. We set up the model of a mobile agent equipped with the entorhinal representation of idiothetic (grid cell) and allothetic (visual cells) information and simulated its place learning in a virtual environment. Due to competitive learning, a robust hippocampal place code emerges rapidly in the model. At the same time, the hippocampo-entorhinal feed-back connections are modified via Hebbian learning in order to allow hippocampal place cells to influence the attractor dynamics in the entorhinal cortex. We show that the continuous feed-back from the integrated hippocampal place representation is able to stabilize the grid cell code.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral DG, Lavenex P (2006) Hippocampal neuroanatomy, chap 3. In: The hippocampus book. Oxford University Press, NY
Amaral DG, Witter MP (1989) The three dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: a review of anatomical data. Neuroscience 31: 571–591
Arleo A, Gerstner W (2000) Spatial cognition and neuro-mimetic navigation: a model of hippocampal place cell activity. Biol Cybern 83: 287–299
Barry C, Burgess N (2007) Learning in a geometric model of place cell firing. Hippocampus 17: 786–800
Barry C, Lever C, Hayman R, Hartley T, Burton S, O’Keefe J, Jeffery K, Burgess N (2006) The boundary vector cell model of place cell firing and spatial memory. Rev Neurosci 17: 71–97
Barry C, Hayman R, Burgess N, Jeffery KJ (2007) Experience-dependent rescaling of entorhinal grids. Nat Neurosci 10: 682–684
Bi Gq, Poo Mm (2001) Synapticmodification by correlated activity: Hebb’s postulate revisited. Annu Rev Neurosci 24: 139–166
Blair HT, Welday AC, Zhang K (2007) Scale-invariant memory representations emerge from moiré interference between grid fields that produce theta oscillations: a computational model. J Neurosci 27: 3211–3229
Blais BS, Shouval HZ, Cooper LN (1999) The role of presynaptic activity in monocular deprivation: comparison of homosynaptic and heterosynaptic mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(3): 1083–1084
Burgess N, O’Keefe J (1996) Neuronal computations underlying the firing of place cells and their role in navigation. Hippocampus 6: 749–762
Burgess N, Recce M, O’Keefe J (1994) A model of hippocampal function. Neural Netw 7: 1065–1081
Burgess N, Jackson A, Hartley T, O‘Keefe J (2000) Predictions derived from modelling the hippocampal role in navigation. Biol Cybern 83(3): 301–312
Burgess N, Barry C, O’Keefe J (2007) An oscillatory interference model of grid cell firing. Hippocampus 17(9): 801–812
Collett T, Zeil J (1998) Places and landmarks: an arthropod perspective. In: Healy S (eds) Spatial representation in animals. Oxford University Press, NY, pp 18–53
Érdi P, Somogyvári Z (2002) Post-Hebbian learning algorithms. In: Arbib MA (eds) The handbook of brain theory and neural networks, 2nd edn. The MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 533–539
Etienne AS, Jeffery KJ (2004) Path integration in mammals. Hippocampus 14: 180–192
Etienne AS, Maurer R, Séguinot V (1996) Path integration in mammals and its interaction with visual landmarks. J Exp Biol 199: 201–209
Etienne AS, Berlie J, Georgakopoulos J, Maurer R (1998) Role of dead reckoning in navigation. In: Healy S (ed) Spatial representation in animals, Oxford University Press, NY, pp 54–68
Fuhs MC, Touretzky DS (2006) A spin glass model of path integration in rat medial entorhinal cortex. J Neurosci 26: 4266–4276
Fyhn M, Hafting T, Treves A, Moser MB, Moser EI (2007) Hippocampal remapping and grid realignment in entorhinal cortex. Nature 446: 190–194
Gaussier P, Banquet JP, Sargolini F, Giovannangeli C, Save E, Poucet B (2007) A model of grid cells involving extra hippocampal path integration, and the hippocampal loop. J Integr Neurosci 6: 447–476
Gerstner W, Kistler W (2002) Spiking Neuron Models. Cambridge University Press, London. http://icwww.epfl.ch/~gerstner/SPNM
Giocomo L, Zilli E, Fransen E, Hasselmo M (2007) Temporal frequency of subthreshold oscillations scales with entorhinal grid cell field spacing. Science 315(5819): 1719–1722
Gothard KM, Skaggs WE, McNaughton BL (1996) Dynamics of mismatch correction in the hippocampal ensemble code for space: Interaction between path integration and environmental cues. J Neurosci 16: 8027–8040
Grossberg S (1974) Classical and instrumental conditioning by neural networks. Prog Theor Biol 3: 51–141
Grossberg S (1976a) Adaptive pattern classification and universal recoding I: parallel development and coding of neural feature detectors. Biol Cybern 23: 121–134
Grossberg S (1976b) Adaptive pattern classification and universal recoding II: feedback, expectation, olfaction, and illusions. Biol Cybern 23: 187–202
Guanella A, Verschure PFMJ (2006) A model of grid cells based on a path integration mechanism. In: Kollias S, Stafylopatis A, Duch W, Oja E (eds) Artificial Neural Networks—ICANN 2006, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4131. Springer, Berlin, pp 740–749
Hafting T, Fyhn M, Molden S, Moser MB, Moser EI (2005) Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex. Nature 436: 801– 806
Hafting T, Fyhn M, Bonnevie T, Moser MB, Moser EI (2008) Hippocampus-independent phase precession in entorhinal grid cells. Nature 453(7199): 1248–1252
Hasselmo M, Giocomo L, Zilli E (2007) Grid cell firing may arise from interference of theta frequency membrane potential oscillations in single neurons. Hippocampus 17(12): 1252–1271
Hebb DO (1949) The organization of behavior. Wiley, New York
Jeffery KJ (1998) Learning of landmark stability and instability by hippocampal place cells. Neuropharmacology 37: 677–687
Jeffery KJ (2007) Integration of the sensory inputs to place cells: what, where, why, and how. Hippocampus 17: 775–785
Jeffery KJ, O’Keefe J (1999) Learned interaction of visual and idiothetic cues in the control of place field orientation. Exp Brain Res 127: 151–161
Kloosterman F, Van Haeften T, Witter MP, Lopes Da Silva FH (2003) Electrophysiological characterization of interlaminar entorhinal connections: an essential link for re-entrance in the hippocampal-entorhinal system. Eur J Neurosci 18: 3037–3052
Knierim JJ, Kudrimoti HS, McNaughton BL (1995) Place cells, head direction cells, and the learning of landmark stability. J Neurosci 15: 1648–1659
Lengyel M, Kwag J, Paulsen O, Dayan P (2005) Matching storage and recall: hippocampal spike timing-dependent plasticity and phase response curves. Nat Neurosci 8(12): 1677–1683
Leutgeb JK, Leutgeb S, Moser MB, Moser EI (2007) Pattern separation in the dentate gyrus and CA3 of the hippocampus. Science 315: 961–966
Lőrincz A, Buzsáki G (2000) Two-phase computational model training long-term memories in the entorhinal-hippocampal region. Ann NY Acad Sci 911: 83–111
Maaswinkel H, Whishaw IQ (1999) Homing with locale, taxon, and dead reckoning strategies by foraging rats: sensory hierarchy in spatial navigation. Behav Brain Res 99: 143–152
McNaughton BL, Barnes C, Gerrard J, Gothard K, Jung M, Knierim J, Kudrimoti H, Qin Y, Skaggs W, Suster M, Weaver K (1996) Deciphering the hippocampal polyglot: the hippocampus as a path integration system. J Exp Biol 199: 173–185
McNaughton BL, Battaglia FP, Jensen O, Moser EI, Moser MB (2006) Path integration and the neural basis of the ‘cognitive map’. Nat Rev Neurosci 7: 663–678
Michel O (2004) Webots: professional mobile robot simulation. J Adv Robot Syst 1(1):39–42. http://www.ars-journal.com/ars/SubscriberArea/Volume1/39-42.pdf
Muller RU, Kubie JL (1987) The effects of changes in the environment on the spatial firing of hippocampal complex-spike cells. J Neurosci 7: 1951–1968
Nardini M, Jones P, Bedford R, Braddick O (2008) Development of cue integration in human navigation. Curr Biol 18: 689–693
O’Keefe J, Dostrovsky J (1971) The hippocampus as a spatial map. preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res 34: 171–175
O’Keefe J, Nadel L (1978) The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map. Oxford University Press, NY. http://www.cognitivemap.net/
O’Keefe J, Burgess N (2005) Dual phase and rate coding in hippocampal place cells: theoretical significance and relationship to entorhinal grid cells. Hippocampus 15: 853–866
Oser HJ, Murchland JD, Daley DJ, Vaughan RJ (1990) An average distance. In: Klamkin MS (ed) Problems in Applied Mathematics: Selections from SIAM Review, Society for Industrial Mathematics, Philadelphia, pp 76–79
R Development Core Team (2007) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org, ISBN 3-900051-07-0
Rolls ET (1995) A model of the operation of the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex in memory. Int J Neural Syst 6: 51–71
Rolls ET, Kesner RP (2006) A computational theory of hippocampal function, and empirical tests of the theory. Prog Neurobiol 79: 1–48
Rolls ET, Stringer SM, Elliot T (2006) Entorhinal cortex grid cells can map to hippocampal place cells by competitive learning. Network 17: 447–465
Sargolini F, Fyhn M, Hafting T, McNaughton BL, Witter MP, Moser MB, Moser EI (2007) Conjunctive representation of position, direction, and velocity in entorhinal cortex. Science 312: 758–762
Séguinot V, Maurer R, Etienne AS (1993) Dead reckoning in a small mammal: the evaluation of distance. J Comp Physiol A 173: 103–113
Sharp PE (1991) Computer simulation of hippocampal place cells. Psychobiology 19(2): 103–115
Shibata H (1988) A direct projection from the entorhinal cortex to the mammillary nuclei in the rat. Neurosci Lett 90: 6–10
Solstad T, Moser EI, Einevoll GT (2006) From grid cells to place cells: a mathematical model. Hippocampus 16: 1026–1031
Solstad T, Boccara CN, Kropff E, Moser MB, Moser EI (2008) Representation of geometric borders in the entorhinal cortex. Science 19(5909): 1865–1868
Taube JS (2007) The head direction signal: Origins and sensory-motor integration. Annu Rev Neurosci 30: 181–207
Touretzky DS, Redish AD (1996) Theory of rodent navigation based on interacting representations of space. Hippocampus 6(3): 247–270
Treves A, Rolls ET (1994) Computational analysis of the role of the hippocampus in memory. Hippocampus 4: 374–391
Ujfalussy B, Erős P, Somogyvári Z, Kiss T (2008) Episodes in space: a modelling study of hippocampal place representation. In: Asada M, Hallam JCT, Meyer JA, Tani J (eds) From animals to animats, ISAB, Springer, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, vol 5040, pp 123–136
van Haeften T, Baks-te-Bulte L, Goede PH, Wouterlood FG, Witter MP (2003) Morphological and numerical analysis of synaptic interactions between neurons in deep and superficial layers of the entorhinal cortex of the rat. Hippocampus 13: 943–952
Wiener SI, Korshunov VA, Garcia R, A B (1995) Inertial, substratal and landmark cue control of hippocampal CA1 place cell activity. Eur J Neurosci 7: 2206–2219
Wilson MA, McNaughton BL (1993) Dynamics of the hippocampal ensemble code for space. Science 261: 1055–1058
Witter MP, Naber PA, van Haeften T, Machielsen WCM, Rombouts SARB, Barkhof F, Scheltens P, Lopesda Silva FH (2000) Cortico-hippocampal communication by way of parallel parahippocampal-subicular pathways. Hippocampus 10: 398–410
Zipser D (1985) A computational model of hippocampal place fields. Behav Neurosci 99(5): 1006–1018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by the EU Framework 6 ICEA project (IST-4-027819-IP).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samu, D., Erős, P., Ujfalussy, B. et al. Robust path integration in the entorhinal grid cell system with hippocampal feed-back. Biol Cybern 101, 19–34 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-009-0311-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-009-0311-z