Abstract
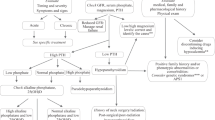
Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH; OMIM: 241530) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder with an estimated prevalence of 1:250,000 that was originally described by Tieder et al. Individuals with HHRH carry compound-heterozygous or homozygous (comp/hom) loss-of-function mutations in the sodium-phosphate co-transporter NPT2c. These mutations result in the development of urinary phosphate (Pi) wasting and hypophosphatemic rickets, bowing, and short stature, as well as appropriately elevated 1,25(OH)2D levels, which sets this fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23)-independent disorder apart from the more common X-linked hypophosphatemia. The elevated 1,25(OH)2D levels in turn result in hypercalciuria due to enhanced intestinal calcium absorption and reduced parathyroid hormone (PTH)-dependent calcium-reabsorption in the distal renal tubules, leading to the development of kidney stones and/or nephrocalcinosis in approximately half of the individuals with HHRH. Even heterozygous NPT2c mutations are frequently associated with isolated hypercalciuria (IH), which increases the risk of kidney stones or nephrocalcinosis threefold in affected individuals compared with the general population. Bone disease is generally absent in individuals with IH, in contrast to those with HHRH. Treatment of HHRH and IH consists of monotherapy with oral Pi supplements, while active vitamin D analogs are contraindicated, mainly because the endogenous 1,25(OH)2D levels are already elevated but also to prevent further worsening of the hypercalciuria. Long-term studies to determine whether oral Pi supplementation alone is sufficient to prevent renal calcifications and bone loss, however, are lacking. It is also unknown how therapy should be monitored, whether secondary hyperparathyroidism can develop, and whether Pi requirements decrease with age, as observed in some FGF23-dependent hypophosphatemic disorders, or whether this can lead to osteoporosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets is associated with mutations in FGF23. Nat Genet 26: 345–348, 2000
Acar S, BinEssa HA, Demir K, Al-Rijjal RA, Zou M, Catli G, Anik A, Al-Enezi AF, Ozisik S, Al-Faham MSA, Abaci A, Dundar B, Kattan WE, Alsagob M, Kavukcu S, Tamimi HE, Meyer BF, Bober E, Shi Y (2018) Clinical and genetic characteristics of 15 families with hereditary hypophosphatemia: novel mutations in PHEX and SLC34A3. PLoS One 13:e0193388
Alon U, Hellerstein S (1994) Assessment and interpretation of the tubular threshold for phosphate in infants and children. Pediatr Nephrol 8:250–251
Andrukhova O, Zeitz U, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Lanske B, Erben RG (2012) FGF23 acts directly on renal proximal tubules to induce phosphaturia through activation of the ERK1/2-SGK1 signaling pathway. Bone 51:621–628
Aono Y, Hasegawa H, Yamazaki Y, Shimada T, Fujita T, Yamashita T, Fukumoto S (2011) Anti-FGF-23 neutralizing antibodies ameliorate muscle weakness and decreased spontaneous movement of Hyp mice. J Bone Miner Res 26:803–810
Arcidiacono T, Mingione A, Macrina L, Pivari F, Soldati L, Vezzoli G (2014) Idiopathic calcium nephrolithiasis: a review of pathogenic mechanisms in the light of genetic studies. Am J Nephrol 40:499–506
Bachmann S, Schlichting U, Geist B, Mutig K, Petsch T, Bacic D, Wagner CA, Kaissling B, Biber J, Murer H, Willnow TE (2004) Kidney-specific inactivation of the megalin gene impairs trafficking of renal inorganic sodium phosphate cotransporter (NaPi-IIa). J Am Soc Nephrol 15:892–900
Bacic D, Lehir M, Biber J, Kaissling B, Murer H, Wagner CA (2006) The renal Na+/phosphate cotransporter NaPi-IIa is internalized via the receptor-mediated endocytic route in response to parathyroid hormone. Kidney Int 69:495–503
Bai X, Miao D, Li J, Goltzman D, Karaplis AC (2004) Transgenic mice overexpressing human fibroblast growth factor 23 (R176Q) delineate a putative role for parathyroid hormone in renal phosphate wasting disorders. Endocrinology 145:5269–5279
Beck L, Karaplis AC, Amizuka N, Hewson AS, Ozawa H, Tenenhouse HS (1998) Targeted inactivation of Npt2 in mice leads to severe renal phosphate wasting, hypercalciuria, and skeletal abnormalities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:5372–5377
Bergwitz C, Bastepe M (2008) NHERF1 mutations and responsiveness of renal parathyroid hormone. NEJM 359:2615–2617
Bergwitz C, Roslin NM, Tieder M, Loredo-Osti JC, Bastepe M, Abu-Zahra H, Frappier D, Burkett K, Carpenter TO, Anderson D, Garabedian M, Sermet I, Fujiwara TM, Morgan K, Tenenhouse HS, Jüppner H (2006) SLC34A3 mutations in patients with hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria predict a key role for the sodium-phosphate cotransporter NaPi-IIc in maintaining phosphate homeostasis. Am J Hum Genet 78:179–192
Berndt TJ, Schiavi S, Kumar R (2005) “Phosphatonins” and the regulation of phosphorus homeostasis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F1170–F1182
Biber J, Hernando N, Forster I (2013) Phosphate transporters and their function. Annu Rev Physiol 75:535–550
Boger CA, Gorski M, Li M, Hoffmann MM, Huang C, Yang Q, Teumer A, Krane V, O'Seaghdha CM, Kutalik Z, Wichmann HE, Haak T, Boes E, Coassin S, Coresh J, Kollerits B, Haun M, Paulweber B, Kottgen A, Li G, Shlipak MG, Powe N, Hwang SJ, Dehghan A, Rivadeneira F, Uitterlinden A, Hofman A, Beckmann JS, Kramer BK, Witteman J, Bochud M, Siscovick D, Rettig R, Kronenberg F, Wanner C, Thadhani RI, Heid IM, Fox CS, Kao WH, Consortium CK (2011) Association of eGFR-related loci identified by GWAS with incident CKD and ESRD. PLoS Genet 7:e1002292
Bringhurst FR, Leder BZ (2006) Regulation of calcium and phosphate homeostasis. In: DeGroot LJ, Jameson JL (eds) Endocrinology. W.B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, pp 805–843
Brodehl J, Gellissen K, Weber HP (1982) Postnatal development of tubular phosphate reabsorption. Clin Nephrol 17:163–171
Burnett CH, Dent CE, Harper C, Warland BJ (1964) Vitamin D-resistant rickets. Analysis of twenty-four pedigrees with hereditary and sporadic cases. Am J Med 36:222–232
Caballero D, Li Y, Fetene J, Ponsetto J, Chen A, Zhu C, Braddock DT, Bergwitz C (2017) Intraperitoneal pyrophosphate treatment reduces renal calcifications in Npt2a null mice. PLoS One 12:e0180098
Caballero D, Li Y, Ponsetto J, Zhu C, Bergwitz C (2017) Impaired urinary osteopontin excretion in Npt2a−/− mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 312:F77–F83
Carpenter TO, Ellis BK, Insogna KL, Philbrick WM, Sterpka J, Shimkets R (2005) Fibroblast growth factor 7: an inhibitor of phosphate transport derived from oncogenic osteomalacia-causing tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:1012–1020
Chen C, Carpenter T, Steg N, Baron R, Anast C (1989) Hypercalciuric hypophosphatemic rickets, mineral balance, bone histomorphometry, and therapeutic implications of hypercalciuria. Pediatrics 84:276–280
Cheung M, Roschger P, Klaushofer K, Veilleux LN, Roughley P, Glorieux FH, Rauch F (2013) Cortical and trabecular bone density in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:E954–E961
Chi Y, Zhao Z, He X, Sun Y, Jiang Y, Li M, Wang O, Xing X, Sun AY, Zhou X, Meng X, Xia W (2014) A compound heterozygous mutation in SLC34A3 causes hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria in a Chinese patient. Bone 59:114–121
Chiang C, Yu Peng JZ, Wang X-F, Bala Y, Ghasem-Zadeh A, Zebaze R, and Seeman E. Quantifying tissue mineralization in vivo for diagnosing osteomalacia. Journal of Bone and Mineral Disease Annual Conference, Baltimore: abstract MO0174, 2013
Clarke GD, Kainer G, Conway WF, Chan JC (1990) Intramyocellular phosphate metabolism in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. J Pediatr 116:288–292
Consortium GT (2013) The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat Genet 45:580–585
Daga A, Majmundar AJ, Braun DA, Gee HY, Lawson JA, Shril S, Jobst-Schwan T, Vivante A, Schapiro D, Tan W, Warejko JK, Widmeier E, Nelson CP, Fathy HM, Gucev Z, Soliman NA, Hashmi S, Halbritter J, Halty M, Kari JA, El-Desoky S, Ferguson MA, MJG S, Traum AZ, Stein DR, Daouk GH, Rodig NM, Katz A, Hanna C, Schwaderer AL, Sayer JA, Wassner AJ, Mane S, Lifton RP, Milosevic D, Tasic V, Baum MA, Hildebrandt F (2018) Whole exome sequencing frequently detects a monogenic cause in early onset nephrolithiasis and nephrocalcinosis. Kidney Int 93:204–213
Dasgupta D, Wee MJ, Reyes M, Li Y, Simm PJ, Sharma A, Schlingmann KP, Janner M, Biggin A, Lazier J, Gessner M, Chrysis D, Tuchman S, Baluarte HJ, Levine MA, Tiosano D, Insogna K, Hanley DA, Carpenter TO, Ichikawa S, Hoppe B, Konrad M, Savendahl L, Munns CF, Lee H, Jüppner H, Bergwitz C (2014) Mutations in SLC34A3/NPT2c are associated with kidney stones and nephrocalcinosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:2366–2375
Devuyst O, Pirson Y (2007) Genetics of hypercalciuric stone forming diseases. Kidney Int 72:1065–1072
Dhir G, Li D, Hakonarson H, Levine MA (2017) Late-onset hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH) due to mutation of SLC34A3/NPT2c. Bone 97:15–19
DiMeglio LA, Econs MJ (2001) Hypophosphatemic rickets. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2:165–173
Donohue MM, Demay MB (2002) Rickets in VDR null mice is secondary to decreased apoptosis of hypertrophic chondrocytes. Endocrinology 143:3691–3694
Econs MJ, Samsa GP, Monger M, Drezner MK, Feussner JR (1994) X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: a disease often unknown to affected patients. Bone Miner 24:17–24
Endo I, Fukumoto S, Ozono K, Namba N, Tanaka H, Inoue D, Minagawa M, Sugimoto T, Yamauchi M, Michigami T, Matsumoto T (2008) Clinical usefulness of measurement of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) in hypophosphatemic patients: proposal of diagnostic criteria using FGF23 measurement. Bone 42:1235–1239
Farrow EG, Davis SI, Ward LM, Summers LJ, Bubbear JS, Keen R, Stamp TC, Baker LR, Bonewald LF, White KE (2009) Molecular analysis of DMP1 mutants causing autosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets. Bone 44:287–294
Forster I, and Wagner A. SLC34. In: Encyclopedia of Signalling Molecules, edited by Choi SSpringer, 2018, p. 5013–5022
Forster IC, Hernando N, Biber J, Murer H (2006) Proximal tubular handling of phosphate: a molecular perspective. Kidney Int 70:1548–1559
Francis RM, Selby PL (1997) Osteomalacia. Bailliere Clin Endocrinol Metab 11:145–163
Gazit D, Tieder M, Liberman UA, Passi-Even L, Bab IA (1991) Osteomalacia in hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria: a correlative clinical-histomorphometric study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:229–235
Gudbjartsson DF, Holm H, Indridason OS, Thorleifsson G, Edvardsson V, Sulem P, de Vegt F, d'Ancona FC, den Heijer M, Wetzels JF, Franzson L, Rafnar T, Kristjansson K, Bjornsdottir US, Eyjolfsson GI, Kiemeney LA, Kong A, Palsson R, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K (2010) Association of variants at UMOD with chronic kidney disease and kidney stones-role of age and comorbid diseases. PLoS Genet 6:e1001039
Haito-Sugino S, Ito M, Ohi A, Shiozaki Y, Kangawa N, Nishiyama T, Aranami F, Sasaki S, Mori A, Kido S, Tatsumi S, Segawa H, Miyamoto K (2012) Processing and stability of type IIc sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter mutations in patients with hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 302:C1316–C1330
Hilfiker H, Kvietikova II, Hartmann CM, Stange G, Murer H (1998) Characterization of the human type II Na/Pi-cotransporter promoter. Pflugers Arch 436:591–598
Holm IA, Huang X, Kunkel LM (1997) Mutational analysis of the PEX gene in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Am J Hum Genet 60:790–797
Hu MC, Shi M, Zhang J, Pastor J, Nakatani T, Lanske B, Shawkat Razzaque M, Rosenblatt KP, Baum MG, Kuro OM, Moe OW (2010) Klotho: a novel phosphaturic substance acting as an autocrine enzyme in the renal proximal tubule. FASEB J 24:3438–3450
HYP-Consortium (1995) A gene (PEX) with homologies to endopeptidases is mutated in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Nat Genet 11:130–136
Ichikawa S, Sorenson AH, Imel EA, Friedman NE, Gertner JM, Econs MJ (2006) Intronic deletions in the SLC34A3 gene cause hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:4022–4027
Ichikawa S, Tuchman S, Padgett LR, Gray AK, Baluarte HJ, Econs MJ (2014) Intronic deletions in the SLC34A3 gene: a cautionary tale for mutation analysis of hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria. Bone 59:53–56
Imel EA, Hui SL, Econs MJ (2007) FGF23 concentrations vary with disease status in autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets. J Bone Miner Res 22:520–526
Imel EA, Peacock M, Pitukcheewanont P, Heller HJ, Ward LM, Shulman D, Kassem M, Rackoff P, Zimering M, Dalkin A, Drobny E, Colussi G, Shaker JL, Hoogendoorn EH, Hui SL, Econs MJ (2006) Sensitivity of fibroblast growth factor 23 measurements in tumor-induced osteomalacia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:2055–2061
Inoue M, Digman MA, Cheng M, Breusegem SY, Halaihel N, Sorribas V, Mantulin WW, Gratton E, Barry NP, Levi M (2004) Partitioning of NaPi cotransporter in cholesterol-, sphingomyelin-, and glycosphingolipid-enriched membrane domains modulates NaPi protein diffusion, clustering, and activity. J Biol Chem 279:49160–49171
Iwaki T, Sandoval-Cooper MJ, Tenenhouse HS, Castellino FJ (2008) A missense mutation in the sodium phosphate co-transporter Slc34a1 impairs phosphate homeostasis. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1753–1762
Jaureguiberry G, Carpenter TO, Forman S, Jüppner H, Bergwitz C (2008) A novel missense mutation in SLC34A3 that causes hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria in humans identifies threonine 137 as an important determinant of sodium-phosphate cotransport in NaPi-IIc. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 295:F371–F379
Jones A, Tzenova J, Frappier D, Crumley M, Roslin N, Kos C, Tieder M, Langman C, Proesmans W, Carpenter T, Rice A, Anderson D, Morgan K, Fujiwara T, Tenenhouse H (2001) Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria is not caused by mutations in the Na/Pi cotransporter NPT2 gene. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:507–514
Jonsson KB, Zahradnik R, Larsson T, White KE, Sugimoto T, Imanishi Y, Yamamoto T, Hampson G, Koshiyama H, Ljunggren O, Oba K, Yang IM, Miyauchi A, Econs MJ, Lavigne J, Jüppner H (2003) Fibroblast growth factor 23 in oncogenic osteomalacia and X-linked hypophosphatemia. N Engl J Med 348:1656–1663
Karim Z, Gerard B, Bakouh N, Alili R, Leroy C, Beck L, Silve C, Planelles G, Urena-Torres P, Grandchamp B, Friedlander G, Prie D (2008) NHERF1 mutations and responsiveness of renal parathyroid hormone. N Engl J Med 359:1128–1135
Kavanaugh MP, Kabat D (1996) Identification and characterization of a widely expressed phosphate transporter/retrovirus receptor family. Kidney Int 49:959–963
Kestenbaum B, Glazer NL, Kottgen A, Felix JF, Hwang SJ, Liu Y, Lohman K, Kritchevsky SB, Hausman DB, Petersen AK, Gieger C, Ried JS, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Wichmann HE, Campbell H, Hayward C, Rudan I, de Boer IH, Psaty BM, Rice KM, Chen YD, Li M, Arking DE, Boerwinkle E, Coresh J, Yang Q, Levy D, van Rooij FJ, Dehghan A, Rivadeneira F, Uitterlinden AG, Hofman A, van Duijn CM, Shlipak MG, Kao WH, Witteman JC, Siscovick DS, Fox CS (2010) Common genetic variants associate with serum phosphorus concentration. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1223–1232
Keusch I, Traebert M, Lotscher M, Kaissling B, Murer H, Biber J (1998) Parathyroid hormone and dietary phosphate provoke a lysosomal routing of the proximal tubular Na/Pi-cotransporter type II. Kidney Int 54:1224–1232
Khan SR, Rodriguez DE, Gower LB, Monga M (2012) Association of Randall plaque with collagen fibers and membrane vesicles. J Urol 187:1094–1100
Kos CH, Tihy F, Econs MJ, Murer H, Lemieux N, Tenenhouse HS (1994) Localization of a renal sodium-phosphate cotransporter gene to human chromosome 5q35. Genomics 19:176–177
Kremke B, Bergwitz C, Ahrens W, Schutt S, Schumacher M, Wagner V, Holterhus PM, Jüppner H, Hiort O (2009) Hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria due to mutation in SLC34A3/NaPi-IIc can be masked by vitamin D deficiency and can be associated with renal calcifications. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 117:49–56
Kuro-o M (2006) Klotho as a regulator of fibroblast growth factor signaling and phosphate/calcium metabolism. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 15:437–441
Kurosu H, Kuro-o M (2008) The klotho gene family and the endocrine fibroblast growth factors. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17:368–372
Langman CB (2004) The molecular basis of kidney stones. Curr Opin Pediatr 16:188–193
Larsson T, Davis SI, Garringer HJ, Mooney SD, Draman MS, Cullen MJ, White KE (2005) Fibroblast growth factor-23 mutants causing familial tumoral calcinosis are differentially processed. Endocrinology 146:3883–3891
Larsson T, Marsell R, Schipani E, Ohlsson C, Ljunggren O, Tenenhouse HS, Jüppner H, Jonsson KB (2004) Transgenic mice expressing fibroblast growth factor 23 under the control of the alpha1(I) collagen promoter exhibit growth retardation, osteomalacia, and disturbed phosphate homeostasis. Endocrinology 145:3087–3094
Leonard MB (2007) A structural approach to the assessment of fracture risk in children and adolescents with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 22:1815–1824
Li Y, Caballero D, Ponsetto J, Chen A, Zhu C, Guo J, Demay M, Jüppner H, Bergwitz C (2017) Response of Npt2a knockout mice to dietary calcium and phosphorus. PLoS One 12:e0176232
Liu S, Quarles LD (2007) How fibroblast growth factor 23 works. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:1637–1647
Lloyd SE, Pearce SH, Fisher SE, Steinmeyer K, Schwappach B, Scheinman SJ, Harding B, Bolino A, Devoto M, Goodyer P, Rigden SP, Wrong O, Jentsch TJ, Craig IW, Thakker RV (1996) A common molecular basis for three inherited kidney stone diseases. Nature 379:445–449
Lorenz-Depiereux B, Benet-Pages A, Eckstein G, Tenenbaum-Rakover Y, Wagenstaller J, Tiosano D, Gershoni-Baruch R, Albers N, Lichtner P, Schnabel D, Hochberg Z, Strom TM (2006) Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria is caused by mutations in the sodium-phosphate cotransporter gene SLC34A3. Am J Hum Genet 78:193–201
Ma SL, Vega-Warner V, Gillies C, Sampson MG, Kher V, Sethi SK, Otto EA (2015) Whole exome sequencing reveals novel PHEX splice site mutations in patients with Hypophosphatemic rickets. PLoS One 10:e0130729
Magen D, Adler L, Mandel H, Efrati E, Zelikovic I (2004) Autosomal recessive renal proximal tubulopathy and hypercalciuria: a new syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 43:600–606
Magen D, Berger L, Coady MJ, Ilivitzki A, Militianu D, Tieder M, Selig S, Lapointe JY, Zelikovic I, Skorecki K (2010) A loss-of-function mutation in NaPi-IIa and renal Fanconi's syndrome. N Engl J Med 362:1102–1109
Mannstadt M, Magen D, Segawa H, Stanley T, Sharma A, Sasaki S, Bergwitz C, Mounien L, Boepple P, Thorens B, Zelikovic I, Jüppner H (2012) Fanconi-Bickel syndrome and autosomal recessive proximal tubulopathy with hypercalciuria (ARPTH) are allelic variants caused by GLUT2 mutations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:E1978–E1986
Mejia-Gaviria N, Gil-Pena H, Coto E, Perez-Menendez TM, Santos F (2010) Genetic and clinical peculiarities in a new family with hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria: a case report. Orphanet J Rare Dis 5(1):1
Miyamoto K, Ito M, Tatsumi S, Kuwahata M, Segawa H (2007) New aspect of renal phosphate reabsorption: the type IIc sodium-dependent phosphate transporter. Am J Nephrol 27:503–515
Miyamoto K, Segawa H, Ito M, Kuwahata M (2004) Physiological regulation of renal sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporters. Jpn J Physiol 54:93–102
Murer H, Forster I, Biber J (2004) The sodium phosphate cotransporter family SLC34. Pflugers Arch 447:763–767
Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, Biber J (2000) Proximal tubular phosphate reabsorption: molecular mechanisms. Physiol Rev 80:1373–1409
Myakala K, Motta S, Murer H, Wagner CA, Koesters R, Biber J, Hernando N (2014) Renal-specific and inducible depletion of NaPi-IIc/Slc34A3, the cotransporter mutated in HHRH, does not affect phosphate or calcium homeostasis in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 306:F833–F843
Narchi H, El Jamil M, Kulaylat N (2001) Symptomatic rickets in adolescence. Arch Dis Child 84:501–503
Nishimura M, Naito S (2008) Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human solute carrier transporter superfamilies. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 23:22–44
Ohkido I, Hara S, Segawa H, Yokoyama K, Yamamoto H, Miyamoto K, Kawaguchi H, and Hosoya T (2007) Localization of sodium-phosphate cotransporter NaPi-IIa and -IIc in human proximal renal and distal tubules. In: RENAL WEEK 2006. San Francisco: JASN, p. abstract SU-PO704
Ohkido I, Segawa H, Yanagida R, Nakamura M, Miyamoto K (2003) Cloning, gene structure and dietary regulation of the type-IIc Na/Pi cotransporter in the mouse kidney. Pflugers Arch 446:106–115
Page K, Bergwitz C, Jaureguiberry G, Harinarayan CV, Insogna K (2008) A patient with hypophosphatemia, a femoral fracture, and recurrent kidney stones: report of a novel mutation in SLC34A3. Endocr Pract 14:869–874
Patsch JM, Burghardt AJ, Kazakia G, Majumdar S (2011) Noninvasive imaging of bone microarchitecture. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1240:77–87
Pattaro C, Teumer A, Gorski M, Chu AY, Li M, Mijatovic V, Garnaas M, Tin A, Sorice R, Li Y, Taliun D, Olden M, Foster M, Yang Q, Chen MH, Pers TH, Johnson AD, Ko YA, Fuchsberger C, Tayo B, Nalls M, Feitosa MF, Isaacs A, Dehghan A, d'Adamo P, Adeyemo A, Dieffenbach AK, Zonderman AB, Nolte IM, van der Most PJ, Wright AF, Shuldiner AR, Morrison AC, Hofman A, Smith AV, Dreisbach AW, Franke A, Uitterlinden AG, Metspalu A, Tonjes A, Lupo A, Robino A, Johansson A, Demirkan A, Kollerits B, Freedman BI, Ponte B, Oostra BA, Paulweber B, Kramer BK, Mitchell BD, Buckley BM, Peralta CA, Hayward C, Helmer C, Rotimi CN, Shaffer CM, Muller C, Sala C, van Duijn CM, Saint-Pierre A, Ackermann D, Shriner D, Ruggiero D, Toniolo D, Lu Y, Cusi D, Czamara D, Ellinghaus D, Siscovick DS, Ruderfer D, Gieger C, Grallert H, Rochtchina E, Atkinson EJ, Holliday EG, Boerwinkle E, Salvi E, Bottinger EP, Murgia F, Rivadeneira F, Ernst F, Kronenberg F, Hu FB, Navis GJ, Curhan GC, Ehret GB, Homuth G, Coassin S, Thun GA, Pistis G, Gambaro G, Malerba G, Montgomery GW, Eiriksdottir G, Jacobs G, Li G, Wichmann HE, Campbell H, Schmidt H, Wallaschofski H, Volzke H, Brenner H, Kroemer HK, Kramer H, Lin H, Mateo Leach I, Ford I, Guessous I, Rudan I, Prokopenko I, Borecki I, Heid IM, Kolcic I, Persico I, Jukema JW, Wilson JF, Felix JF, Divers J, Lambert JC, Stafford JM, Gaspoz JM, Smith JA, Faul JD, Wang JJ, Ding J, Hirschhorn JN, Attia J, Whitfield JB, Chalmers J, Viikari J, Coresh J, Denny JC, Karjalainen J, Fernandes JK, Endlich K, Butterbach K, Keene KL, Lohman K, Portas L, Launer LJ, Lyytikainen LP, Yengo L, Franke L, Ferrucci L, Rose LM, Kedenko L, Rao M, Struchalin M, Kleber ME, Cavalieri M, Haun M, Cornelis MC, Ciullo M, Pirastu M, de Andrade M, McEvoy MA, Woodward M, Adam M, Cocca M, Nauck M, Imboden M, Waldenberger M, Pruijm M, Metzger M, Stumvoll M, Evans MK, Sale MM, Kahonen M, Boban M, Bochud M, Rheinberger M, Verweij N, Bouatia-Naji N, Martin NG, Hastie N, Probst-Hensch N, Soranzo N, Devuyst O, Raitakari O, Gottesman O, Franco OH, Polasek O, Gasparini P, Munroe PB, Ridker PM, Mitchell P, Muntner P, Meisinger C, Smit JH, Consortium I, Consortium A, Cardiogram, Group CH-HF, Consortium EC, Kovacs P, Wild PS, Froguel P, Rettig R, Magi R, Biffar R, Schmidt R, Middelberg RP, Carroll RJ, Penninx BW, Scott RJ, Katz R, Sedaghat S, Wild SH, Kardia SL, Ulivi S, Hwang SJ, Enroth S, Kloiber S, Trompet S, Stengel B, Hancock SJ, Turner ST, Rosas SE, Stracke S, Harris TB, Zeller T, Zemunik T, Lehtimaki T, Illig T, Aspelund T, Nikopensius T, Esko T, Tanaka T, Gyllensten U, Volker U, Emilsson V, Vitart V, Aalto V, Gudnason V, Chouraki V, Chen WM, Igl W, Marz W, Koenig W, Lieb W, Loos RJ, Liu Y, Snieder H, Pramstaller PP, Parsa A, O'Connell JR, Susztak K, Hamet P, Tremblay J, de Boer IH, Boger CA, Goessling W, Chasman DI, Kottgen A, Kao WH, Fox CS (2016) Genetic associations at 53 loci highlight cell types and biological pathways relevant for kidney function. Nat Commun 7:10023
Pesta DH, Tsirigotis DN, Befroy DE, Caballero D, Jurczak MJ, Rahimi Y, Cline GW, Dufour S, Birkenfeld AL, Rothman DL, Carpenter TO, Insogna K, Petersen KF, Bergwitz C, Shulman GI (2016) Hypophosphatemia promotes lower rates of muscle ATP synthesis. FASEB J 30:3378–3387
Pfister MF, Ruf I, Stange G, Ziegler U, Lederer E, Biber J, Murer H (1998) Parathyroid hormone leads to the lysosomal degradation of the renal type II Na/Pi cotransporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:1909–1914
Phulwani P, Bergwitz C, Jaureguiberry G, Rasoulpour M, Estrada E (2011) Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria and nephrolithiasis-identification of a novel SLC34A3/NaPi-IIc mutation. Am J Med Genet A 155A:626–633
Picard N, Capuano P, Stange G, Mihailova M, Kaissling B, Murer H, Biber J, Wagner CA (2010) Acute parathyroid hormone differentially regulates renal brush border membrane phosphate cotransporters. Pflugers Arch 460:677–687
Prie D, Beck L, Friedlander G, Silve C (2004) Sodium-phosphate cotransporters, nephrolithiasis and bone demineralization. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 13:675–681
Prie D, Huart V, Bakouh N, Planelles G, Dellis O, Gerard B, Hulin P, Benque-Blanchet F, Silve C, Grandchamp B, Friedlander G (2002) Nephrolithiasis and osteoporosis associated with hypophosphatemia caused by mutations in the type 2a sodium-phosphate cotransporter. N Engl J Med 347:983–991
Pronicka E, Ciara E, Halat P, Janiec A, Wojcik M, Rowinska E, Rokicki D, Pludowski P, Wojciechowska E, Wierzbicka A, Ksiazyk JB, Jacoszek A, Konrad M, Schlingmann KP, Litwin M (2017) Biallelic mutations in CYP24A1 or SLC34A1 as a cause of infantile idiopathic hypercalcemia (IIH) with vitamin D hypersensitivity: molecular study of 11 historical IIH cases. J Appl Genet 58:349–353
Rafaelsen S, Johansson S, Raeder H, Bjerknes R (2016) Hereditary hypophosphatemia in Norway: a retrospective population-based study of genotypes, phenotypes, and treatment complications. Eur J Endocrinol 174:125–136
Reed BY, Heller HJ, Gitomer WL, Pak CY (1999) Mapping a gene defect in absorptive hypercalciuria to chromosome 1q23.3-q24. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:3907–3913
Reginato AJ, Coquia JA (2003) Musculoskeletal manifestations of osteomalacia and rickets. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 17:1063–1080
Romero V, Akpinar H, Assimos DG (2010) Kidney stones: a global picture of prevalence, incidence, and associated risk factors. Rev Urol 12:e86–e96
Santer R, Schneppenheim R, Dombrowski A, Gotze H, Steinmann B, Schaub J (1997) Mutations in GLUT2, the gene for the liver-type glucose transporter, in patients with Fanconi-Bickel syndrome. Nat Genet 17:324–326
Santer R, Steinmann B, Schaub J (2002) Fanconi-Bickel syndrome—a congenital defect of facilitative glucose transport. Curr Mol Med 2:213–227
Schissel BL, Johnson BK (2011) Renal stones: evolving epidemiology and management. Pediatr Emerg Care 27:676–681
Schlingmann KP, Kaufmann M, Weber S, Irwin A, Goos C, John U, Misselwitz J, Klaus G, Kuwertz-Broking E, Fehrenbach H, Wingen AM, Guran T, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ, Prosser DE, Jones G, Konrad M (2011) Mutations in CYP24A1 and idiopathic infantile hypercalcemia. N Engl J Med 365:410–421
Schlingmann KP, Ruminska J, Kaufmann M, Dursun I, Patti M, Kranz B, Pronicka E, Ciara E, Akcay T, Bulus D, Cornelissen EAM, Gawlik A, Sikora P, Patzer L, Galiano M, Boyadzhiev V, Dumic M, Vivante A, Kleta R, Dekel B, Levtchenko E, Bindels RJ, Rust S, Forster IC, Hernando N, Jones G, Wagner CA, Konrad M (2016) Autosomal-recessive mutations in SLC34A1 encoding sodium-phosphate cotransporter 2A cause idiopathic infantile hypercalcemia. J Am Soc Nephrol 27:604–614
Scott P, Ouimet D, Valiquette L, Guay G, Proulx Y, Trouve ML, Gagnon B, Bonnardeaux A (1999) Suggestive evidence for a susceptibility gene near the vitamin D receptor locus in idiopathic calcium stone formation. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:1007–1013
Segawa H, Kaneko I, Takahashi A, Kuwahata M, Ito M, Ohkido I, Tatsumi S, Miyamoto K (2002) Growth-related renal type II Na/Pi cotransporter. J Biol Chem 277:19665–19672
Segawa H, Onitsuka A, Aranami F, Tomoe Y, Kaneko I, Furutani J, Ito M, Matsumoto M, Li M, Amizuka N, Kuwahata M, and Miyamoto K (2007) Npt2a and Npt2c in mice play distinct and synergistic roles in inorganic phosphate metabolism and skeletal development. In: RENAL WEEK 2006. San Francisco: JASN, p. abstract SA-FC101
Segawa H, Onitsuka A, Furutani J, Kaneko I, Aranami F, Matsumoto N, Tomoe Y, Kuwahata M, Ito M, Matsumoto M, Li M, Amizuka N, Miyamoto K (2009) Npt2a and Npt2c in mice play distinct and synergistic roles in inorganic phosphate metabolism and skeletal development. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297:F671–F678
Sermet-Gaudelus I, Garabedian M, Dechaux M, Lenoir G, Rey J, Tieder M (2001) Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria: report of a new kindred. Nephron 88:83–86
Shaikh A, Berndt T, Kumar R (2008) Regulation of phosphate homeostasis by the phosphatonins and other novel mediators. Pediatr Nephrol 23:1203–1210
Shimada T, Hasegawa H, Yamazaki Y, Muto T, Hino R, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Nakahara K, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2004) FGF-23 is a potent regulator of vitamin D metabolism and phosphate homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res 19:429–435
Shimada T, Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Hasegawa H, Hino R, Yoneya T, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2004) FGF-23 transgenic mice demonstrate hypophosphatemic rickets with reduced expression of sodium phosphate cotransporter type IIa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314:409–414
Shimada T, Yoneya T, Hino R, Takeuchi Y, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2001) Transgenic mice expressing fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) demonstrate hypophosphatemia with low serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D] and rickets/osteomalacia. In: Twenty-third Annual Meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. Phoenix, Arizona: J. Bone mineral res, p 1059
Shiozaki Y, Segawa H, Ohnishi S, Ohi A, Ito M, Kaneko I, Kido S, Tatsumi S, Miyamoto K (2015) Relationship between sodium-dependent phosphate transporter (NaPi-IIc) function and cellular vacuole formation in opossum kidney cells. J Med Investig 62:209–218
Sinha A, Hollingsworth KG, Ball S, Cheetham T (2013) Improving the vitamin D status of vitamin D deficient adults is associated with improved mitochondrial oxidative function in skeletal muscle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:E509–E513
Smith R, Newman RJ, Radda GK, Stokes M, Young A (1984) Hypophosphataemic osteomalacia and myopathy: studies with nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clin Sci (Lond) 67:505–509
Stechman MJ, Loh NY, Thakker RV (2009) Genetic causes of hypercalciuric nephrolithiasis. Pediatr Nephrol 24:2321–2332
Strom TM, Jüppner H (2008) PHEX, FGF23, DMP1 and beyond. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17:357–362
Taguchi K, Yasui T, Milliner DS, Hoppe B, Chi T (2017) Genetic risk factors for idiopathic urolithiasis: a systematic review of the literature and causal network analysis. Eur Urol Focus 3:72–81
Tencza AL, Ichikawa S, Dang A, Kenagy D, McCarthy E, Econs MJ, Levine MA (2009) Hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria due to mutation in SLC34A3/type IIc sodium-phosphate cotransporter: presentation as hypercalciuria and nephrolithiasis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4433–4438
Tenenhouse HS (2005) Regulation of phosphorus homeostasis by the type IIA NA/phosphate cotransporter. Annu Rev Nutr 25:197–214
Tenenhouse HS, Econs MJ (2001) Mendelian hypophosphatemias. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Valle D, Sly WS, Vogelstein B, Childs B, Kinzler KW (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited diseases. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 5039–5067
Tenenhouse HS, Gauthier C, Chau H, St-Arnaud R (2004) 1alpha-hydroxylase gene ablation and pi supplementation inhibit renal calcification in mice homozygous for the disrupted Npt2a gene. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F675–F681
Tenenhouse HS, Martel J, Gauthier C, Segawa H, Miyamoto K (2003) Differential effects of Npt2a gene ablation and X-linked Hyp mutation on renal expression of Npt2c. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F1271–F1278
Tenenhouse HS, Martel J, Gauthier C, Zhang MY, Portale AA (2001) Renal expression of the sodium/phosphate cotransporter gene, Npt2, is not required for regulation of renal 1 alpha-hydroxylase by phosphate. Endocrinology 142:1124–1129
Tenenhouse HS, Roy S, Martel J, Gauthier C (1998) Differential expression, abundance, and regulation of Na+-phosphate cotransporter genes in murine kidney. Am J Phys 275:F527–F534
Thakker RV (2000) Pathogenesis of Dent’s disease and related syndromes of X-linked nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int 57:787–793
Tieder M, Arie R, Modai D, Samuel R, Weissgarten J, Liberman UA (1988) Elevated serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D concentrations in siblings with primary Fanconi's syndrome. N Engl J Med 319:845–849
Tieder M, Modai D, Samuel R, Arie R, Halabe A, Bab I, Gabizon D, Liberman UA (1985) Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria. N Engl J Med 312:611–617
Tieder M, Modai D, Shaked U, Samuel R, Arie R, Halabe A, Maor J, Weissgarten J, Averbukh Z, Cohen N, and et al. (1987) “Idiopathic” hypercalciuria and hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets. Two phenotypical expressions of a common genetic defect. N Engl J Med 316: 125–129
Tomoe Y, Segawa H, Kaneko I, Furutani J, Aranami F, Kuwahara S, Tominaga R, Hanabusa E, Ito M, and Miyamoto K-i (2008) Effect of fibroblast growth factor (FGF)23 on Npt2a−/−, Npt2c−/− double-knockout (WKO) mice. In: J Am Soc Nephrol Philadelphia, p. [SA-PO2780]
Tore S, Casula S, Casu G, Concas MP, Pistidda P, Persico I, Sassu A, Maestrale GB, Mele C, Caruso MR, Bonerba B, Usai P, Deiana I, Thornton T, Pirastu M, Forabosco P (2011) Application of a new method for GWAS in a related case/control sample with known pedigree structure: identification of new loci for nephrolithiasis. PLoS Genet 7:e1001281
Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Shimada T, Iijima K, Hasegawa H, Okawa K, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2006) Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Nature 444:770–774
van den Heuvel L, Op de Koul K, Knots E, Knoers N, Monnens L (2001) Autosomal recessive hypophosphataemic rickets with hypercalciuria is not caused by mutations in the type II renal sodium/phosphate cotransporter gene. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:48–51
Virkki LV, Forster IC, Hernando N, Biber J, Murer H (2003) Functional characterization of two naturally occurring mutations in the human sodium-phosphate cotransporter type IIa. J Bone Miner Res 18:2135–2141
Wagner CA, Rubio-Aliaga I, Hernando N (2017) Renal phosphate handling and inherited disorders of phosphate reabsorption: an update. Pediatr Nephrol
Walton RJ, Bijvoet OL (1975) Nomogram for derivation of renal threshold phosphate concentration. Lancet 2:309–310
White AJ, Northcutt MJ, Rohrback SE, Carpenter RO, Niehaus-Sauter MM, Gao Y, Wheatly MG, Gillen CM (2011) Characterization of sarcoplasmic calcium binding protein (SCP) variants from freshwater crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 160:8–14
White KE, Larsson TE, Econs MJ (2006) The roles of specific genes implicated as circulating factors involved in normal and disordered phosphate homeostasis: frizzled related protein-4, matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein, and fibroblast growth factor 23. Endocr Rev 27:221–241
Wilz DR, Gray RW, Dominguez JH, Lemann J Jr (1979) Plasma 1,25-(OH)2-vitamin D concentrations and net intestinal calcium, phosphate, and magnesium absorption in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 32:2052–2060
Wolf MT, Zalewski I, Martin FC, Ruf R, Muller D, Hennies HC, Schwarz S, Panther F, Attanasio M, Acosta HG, Imm A, Lucke B, Utsch B, Otto E, Nurnberg P, Nieto VG, Hildebrandt F (2005) Mapping a new suggestive gene locus for autosomal dominant nephrolithiasis to chromosome 9q33.2-q34.2 by total genome search for linkage. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:909–914
Worcester EM, Coe FL (2008) Nephrolithiasis. Prim Care 35:369–391, vii
Wrong OM, Norden AG, Feest TG (1994) Dent’s disease; a familial proximal renal tubular syndrome with low-molecular-weight proteinuria, hypercalciuria, nephrocalcinosis, metabolic bone disease, progressive renal failure and a marked male predominance. Qjm 87:473–493
Yamamoto T, Michigami T, Aranami F, Segawa H, Yoh K, Nakajima S, Miyamoto K, Ozono K (2007) Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria: a study for the phosphate transporter gene type IIc and osteoblastic function. J Bone Miner Metab 25:407–413
Yamazaki Y, Okazaki R, Shibata M, Hasegawa Y, Satoh K, Tajima T, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Nakahara K, Yamashita T, Fukumoto S (2002) Increased circulatory level of biologically active full-length FGF-23 in patients with hypophosphatemic rickets/osteomalacia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:4957–4960
Yan X, Yokote H, Jing X, Yao L, Sawada T, Zhang Y, Liang S, Sakaguchi K (2005) Fibroblast growth factor 23 reduces expression of type IIa Na+/Pi co-transporter by signaling through a receptor functionally distinct from the known FGFRs in opossum kidney cells. Genes Cells 10:489–502
Yu Y, Sanderson SR, Reyes M, Sharma A, Dunbar N, Srivastava T, Jüppner H, Bergwitz C (2012) Novel NaPi-IIc mutations causing HHRH and idiopathic hypercalciuria in several unrelated families: long-term follow-up in one kindred. Bone 50:1100–1106
Acknowledgements
We thank Wenzhen Zhao, B.C. candidate for editorial help.
Funding
This work was in part supported by the Yale O’Brien Center (Pilot grant to C.B., NIH P30DK079310).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the special issue on Phosphate transport in Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergwitz, C., Miyamoto, KI. Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria: pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and therapy. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 471, 149–163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-018-2184-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-018-2184-2