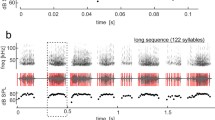
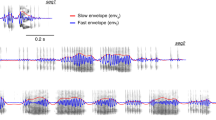
Abstract
Empirical evidence suggests that, in the auditory cortex (AC), the phase relationship between spikes and local-field potentials (LFPs) plays an important role in the processing of auditory stimuli. Nevertheless, unlike the case of other sensory systems, it remains largely unexplored in the auditory modality whether the properties of the cortical columnar microcircuit shape the dynamics of spike–LFP coherence in a layer-specific manner. In this study, we directly tackle this issue by addressing whether spike–LFP and LFP–stimulus phase synchronization are spatially distributed in the AC during sensory processing, by performing laminar recordings in the cortex of awake short-tailed bats (Carollia perspicillata) while animals listened to conspecific distress vocalizations. We show that, in the AC, spike–LFP and LFP–stimulus synchrony depend significantly on cortical depth, and that sensory stimulation alters the spatial and spectral patterns of spike–LFP phase-locking. We argue that such laminar distribution of coherence could have functional implications for the representation of naturalistic auditory stimuli at a cortical level.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnal LH, Giraud AL (2012) Cortical oscillations and sensory predictions. Trends Cogn Sci 16:390–398
Atilgan H, Town SM, Wood KC, Jones GP, Maddox RK, Lee AKC, Bizley JK (2018) Integration of visual information in auditory cortex promotes auditory scene analysis through multisensory binding. Neuron 97(640–655):e644
Barczak A, O’Connell MN, McGinnis T, Ross D, Mowery T, Falchier A, Lakatos P (2018) Top-down, contextual entrainment of neuronal oscillations in the auditory thalamocortical circuit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E7605–E7614
Bastos AM, Usrey WM, Adams RA, Mangun GR, Fries P, Friston KJ (2012) Canonical microcircuits for predictive coding. Neuron 76:695–711
Beltramo R, D’Urso G, Dal Maschio M, Farisello P, Bovetti S, Clovis Y, Lassi G, Tucci V, De Pietri Tonelli D, Fellin T (2013) Layer-specific excitatory circuits differentially control recurrent network dynamics in the neocortex. Nat Neurosci 16:227–234
Berens P (2009) CircStat: a MATLAB toolbox for circular statistics. J Stat Softw 31:1–21
Bokil H, Andrews P, Kulkarni JE, Mehta S, Mitra PP (2010) Chronux: a platform for analyzing neural signals. J Neurosci Methods 192:146–151
Buffalo EA, Fries P, Landman R, Buschman TJ, Desimone R (2011) Laminar differences in gamma and alpha coherence in the ventral stream. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:11262–11267
Buzsaki G, Wang XJ (2012) Mechanisms of gamma oscillations. Annu Rev Neurosci 35:203–225
Buzsaki G, Anastassiou CA, Koch C (2012) The origin of extracellular fields and currents—EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:407–420
Creutzfeldt O, Hellweg FC, Schreiner C (1980) Thalamocortical transformation of responses to complex auditory stimuli. Exp Brain Res 39:87–104
De Martino F, Moerel M, Ugurbil K, Goebel R, Yacoub E, Formisano E (2015) Frequency preference and attention effects across cortical depths in the human primary auditory cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:16036–16041
Doelling KB, Assaneo MF, Bevilacqua D, Pesaran B, Poeppel D (2019) An oscillator model better predicts cortical entrainment to music. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:10113–10121
Douglas RJ, Martin KA (2004) Neuronal circuits of the neocortex. Annu Rev Neurosci 27:419–451
Einevoll GT, Kayser C, Logothetis NK, Panzeri S (2013) Modelling and analysis of local field potentials for studying the function of cortical circuits. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:770–785
Esser KH, Eiermann A (1999) Tonotopic organization and parcellation of auditory cortex in the FM-bat Carollia perspicillata. Eur J Neurosci 11:3669–3682
Farahani ED, Goossens T, Wouters J, van Wieringen A (2017) Spatiotemporal reconstruction of auditory steady-state responses to acoustic amplitude modulations: potential sources beyond the auditory pathway. Neuroimage 148:240–253
Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC (1991) Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 1:1–47
Francis NA, Elgueda D, Englitz B, Fritz JB, Shamma SA (2018) Laminar profile of task-related plasticity in ferret primary auditory cortex. Sci Rep 8:16375
Fries P (2009) Neuronal gamma-band synchronization as a fundamental process in cortical computation. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:209–224
Fries P (2015) Rhythms for cognition: communication through coherence. Neuron 88:220–235
Fries P, Reynolds JH, Rorie AE, Desimone R (2001) Modulation of oscillatory neuronal synchronization by selective visual attention. Science 291:1560–1563
Gao X, Wehr M (2015) A coding transformation for temporally structured sounds within auditory cortical neurons. Neuron 86:292–303
Gao L, Kostlan K, Wang Y, Wang X (2016) Distinct subthreshold mechanisms underlying rate-coding principles in primate auditory cortex. Neuron 91:905–919
García-Rosales F, Beetz MJ, Cabral-Calderin Y, Kössl M, Hechavarria JC (2018a) Neuronal coding of multiscale temporal features in communication sequences within the bat auditory cortex. Commun Biol 1:200
García-Rosales F, Martin LM, Beetz MJ, Cabral-Calderin Y, Kossl M, Hechavarria JC (2018b) Low-frequency spike-field coherence is a fingerprint of periodicity coding in the auditory cortex. iScience 9:47–62
Giraud AL, Poeppel D (2012) Cortical oscillations and speech processing: emerging computational principles and operations. Nat Neurosci 15:511–517
Gross J, Hoogenboom N, Thut G, Schyns P, Panzeri S, Belin P, Garrod S (2013) Speech rhythms and multiplexed oscillatory sensory coding in the human brain. PLoS Biol 11:e1001752
Haegens S, Handel BF, Jensen O (2011) Top-down controlled alpha band activity in somatosensory areas determines behavioral performance in a discrimination task. J Neurosci 31:5197–5204
Haider B, Schulz DP, Hausser M, Carandini M (2016) Millisecond coupling of local field potentials to synaptic currents in the awake visual cortex. Neuron 90:35–42
Hansen BJ, Dragoi V (2011) Adaptation-induced synchronization in laminar cortical circuits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:10720–10725
Harris KD, Mrsic-Flogel TD (2013) Cortical connectivity and sensory coding. Nature 503:51–58
Hechavarria JC, Beetz MJ, Macias S, Kossl M (2016a) Distress vocalization sequences broadcasted by bats carry redundant information. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 202:503–515
Hechavarria JC, Beetz MJ, Macias S, Kossl M (2016b) Vocal sequences suppress spiking in the bat auditory cortex while evoking concomitant steady-state local field potentials. Sci Rep 6:39226
Henry MJ, Obleser J (2012) Frequency modulation entrains slow neural oscillations and optimizes human listening behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:20095–20100
Herdman AT, Lins O, Van Roon P, Stapells DR, Scherg M, Picton TW (2002) Intracerebral sources of human auditory steady-state responses. Brain Topogr 15:69–86
Hyafil A, Fontolan L, Kabdebon C, Gutkin B, Giraud AL (2015) Speech encoding by coupled cortical theta and gamma oscillations. Elife 4:e06213
Joris PX, Schreiner CE, Rees A (2004) Neural processing of amplitude-modulated sounds. Physiol Rev 84:541–577
Kayser C, Petkov CI, Logothetis NK (2008) Visual modulation of neurons in auditory cortex. Cereb Cortex 18:1560–1574
Kayser C, Montemurro MA, Logothetis NK, Panzeri S (2009) Spike-phase coding boosts and stabilizes information carried by spatial and temporal spike patterns. Neuron 61:597–608
Kayser C, Ince RA, Panzeri S (2012) Analysis of slow (theta) oscillations as a potential temporal reference frame for information coding in sensory cortices. PLoS Comput Biol 8:e1002717
Konig P, Engel AK, Singer W (1995) Relation between oscillatory activity and long-range synchronization in cat visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:290–294
Lakatos P, Shah AS, Knuth KH, Ulbert I, Karmos G, Schroeder CE (2005) An oscillatory hierarchy controlling neuronal excitability and stimulus processing in the auditory cortex. J Neurophysiol 94:1904–1911
Lakatos P, Chen CM, O’Connell MN, Mills A, Schroeder CE (2007) Neuronal oscillations and multisensory interaction in primary auditory cortex. Neuron 53:279–292
Lakatos P, Musacchia G, O’Connel MN, Falchier AY, Javitt DC, Schroeder CE (2013) The spectrotemporal filter mechanism of auditory selective attention. Neuron 77:750–761
Levy JM, Zold CL, Namboodiri VMK, Hussain Shuler MG (2017) The timing of reward-seeking action tracks visually cued theta oscillations in primary visual cortex. J Neurosci 37:10408–10420
Linden JF, Schreiner CE (2003) Columnar transformations in auditory cortex? A comparison to visual and somatosensory cortices. Cereb Cortex 13:83–89
Luo H, Poeppel D (2007) Phase patterns of neuronal responses reliably discriminate speech in human auditory cortex. Neuron 54:1001–1010
Luo H, Liu Z, Poeppel D (2010) Auditory cortex tracks both auditory and visual stimulus dynamics using low-frequency neuronal phase modulation. PLoS Biol 8:e1000445
Manita S, Suzuki T, Homma C, Matsumoto T, Odagawa M, Yamada K, Ota K, Matsubara C, Inutsuka A, Sato M et al (2015) A top-down cortical circuit for accurate sensory perception. Neuron 86:1304–1316
Molinaro N, Lizarazu M (2018) Delta(but not theta)-band cortical entrainment involves speech-specific processing. Eur J Neurosci 48:2642–2650
Mountcastle VB (1997) The columnar organization of the neocortex. Brain 120(Pt 4):701–722
Ng BSW, Schroeder T, Kayser C (2012) A precluding but not ensuring role of entrained low-frequency oscillations for auditory perception. J Neurosci 32:12268–12276
Nourski KV, Brugge JF (2011) Representation of temporal sound features in the human auditory cortex. Rev Neurosci 22:187–203
O’Connell MN, Barczak A, Schroeder CE, Lakatos P (2014) Layer specific sharpening of frequency tuning by selective attention in primary auditory cortex. J Neurosci 34:16496–16508
O’Connell MN, Barczak A, Ross D, McGinnis T, Schroeder CE, Lakatos P (2015) Multi-scale entrainment of coupled neuronal oscillations in primary auditory cortex. Front Hum Neurosci 9:655
Panzeri S, Brunel N, Logothetis NK, Kayser C (2010) Sensory neural codes using multiplexed temporal scales. Trends Neurosci 33:111–120
Park H, Ince RA, Schyns PG, Thut G, Gross J (2015) Frontal top-down signals increase coupling of auditory low-frequency oscillations to continuous speech in human listeners. Curr Biol 25:1649–1653
Percival DB, Walden AT (1993) Spectral analysis for physical applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Reimann MW, Anastassiou CA, Perin R, Hill SL, Markram H, Koch C (2013) A biophysically detailed model of neocortical local field potentials predicts the critical role of active membrane currents. Neuron 79:375–390
Romano J, Kromrey JD, Coraggio J, Skowronek J (2006) Appropriate statistics for ordinal level data: Should we really be using t-test and Cohen’s d for evaluating group differences on the NSSE and other surveys. Paper presented at: annual meeting of the Florida Association of Institutional Research
Romanski LM, LeDoux JE (1993) Organization of rodent auditory cortex: anterograde transport of PHA-L from MGv to temporal neocortex. Cereb Cortex 3:499–514
Rutishauser U, Ross IB, Mamelak AN, Schuman EM (2010) Human memory strength is predicted by theta-frequency phase-locking of single neurons. Nature 464:903–907
Sakata S, Harris KD (2009) Laminar structure of spontaneous and sensory-evoked population activity in auditory cortex. Neuron 64:404–418
Sanchez-Vives MV, McCormick DA (2000) Cellular and network mechanisms of rhythmic recurrent activity in neocortex. Nat Neurosci 3:1027–1034
Schaefer MK, Hechavarria JC, Kossl M (2015) Quantification of mid and late evoked sinks in laminar current source density profiles of columns in the primary auditory cortex. Front Neural Circuits 9:52
Schaefer MK, Kossl M, Hechavarria JC (2017) Laminar differences in response to simple and spectro-temporally complex sounds in the primary auditory cortex of ketamine-anesthetized gerbils. PLoS One 12:e0182514
Schroeder CE, Lakatos P (2009) Low-frequency neuronal oscillations as instruments of sensory selection. Trends Neurosci 32:9–18
Schroeder CE, Lakatos P, Kajikawa Y, Partan S, Puce A (2008) Neuronal oscillations and visual amplification of speech. Trends Cogn Sci 12:106–113
Spyropoulos G, Bosman CA, Fries P (2018) A theta rhythm in macaque visual cortex and its attentional modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E5614–E5623
Stefanics G, Hangya B, Hernadi I, Winkler I, Lakatos P, Ulbert I (2010) Phase entrainment of human delta oscillations can mediate the effects of expectation on reaction speed. J Neurosci 30:13578–13585
Szymanski FD, Rabinowitz NC, Magri C, Panzeri S, Schnupp JW (2011) The laminar and temporal structure of stimulus information in the phase of field potentials of auditory cortex. J Neurosci 31:15787–15801
Tang J, Suga N (2008) Modulation of auditory processing by cortico-cortical feed-forward and feedback projections. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:7600–7605
Teng X, Tian X, Rowland J, Poeppel D (2017) Concurrent temporal channels for auditory processing: oscillatory neural entrainment reveals segregation of function at different scales. PLoS Biol 15:e2000812
Tiesinga P, Sejnowski TJ (2009) Cortical enlightenment: are attentional gamma oscillations driven by ING or PING? Neuron 63:727–732
van Atteveldt N, Murray MM, Thut G, Schroeder CE (2014) Multisensory integration: flexible use of general operations. Neuron 81:1240–1253
van Kerkoerle T, Self MW, Dagnino B, Gariel-Mathis MA, Poort J, van der Togt C, Roelfsema PR (2014) Alpha and gamma oscillations characterize feedback and feedforward processing in monkey visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:14332–14341
van Wassenhove V, Grant KW, Poeppel D (2005) Visual speech speeds up the neural processing of auditory speech. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1181–1186
von Stein A, Chiang C, Konig P (2000) Top-down processing mediated by interareal synchronization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:14748–14753
Winer JA, Lee CC (2007) The distributed auditory cortex. Hear Res 229:3–13
Womelsdorf T, Fries P (2007) The role of neuronal synchronization in selective attention. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17:154–160
Womelsdorf T, Schoffelen JM, Oostenveld R, Singer W, Desimone R, Engel AK, Fries P (2007) Modulation of neuronal interactions through neuronal synchronization. Science 316:1609–1612
Zion Golumbic EM, Poeppel D, Schroeder CE (2012) Temporal context in speech processing and attentional stream selection: a behavioral and neural perspective. Brain Lang 122:151–161
Zion Golumbic E, Cogan GB, Schroeder CE, Poeppel D (2013) Visual input enhances selective speech envelope tracking in auditory cortex at a “cocktail party”. J Neurosci 33:1417–1426
Zoefel B, Heil P (2013) Detection of near-threshold sounds is independent of eeg phase in common frequency bands. Front Psychol 4:262
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the German Research Council (DFG) (Grant no. HE 7478/1-1, to JCH). The authors would like to thank Gisa Prange for providing support with the histological approaches.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FGR and JCH designed the study. FGR, KW, MR and YHL collected the data. FGR analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. FGR, DR, KW, MR, YHL, YCC, MK, and JCH discussed, interpreted the results, and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interests.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Ethical statement
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All experimental procedures were in compliance with current European regulations on animal experimentation, and were approved by the Regierungspräsidium Darmstadt (experimental permit #FU-1126).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Rosales, F., Röhrig, D., Weineck, K. et al. Laminar specificity of oscillatory coherence in the auditory cortex. Brain Struct Funct 224, 2907–2924 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01944-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01944-3