Abstract
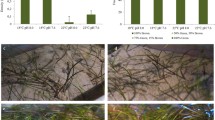
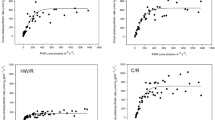
Seagrasses are globally declining and often their loss is due to synergies among stressors. We investigated the interactive effects of eutrophication and burial on the Mediterranean seagrass, Posidonia oceanica. A field experiment was conducted to estimate whether shoot survival depends on the interactive effects of three levels of intensity of both stressors and to identify early changes in plants (i.e., morphological, physiological and biochemical, and expression of stress-related genes) that may serve to detect signals of imminent shoot density collapse. Sediment burial and nutrient enrichment produced interactive effects on P. oceanica shoot survival, as high nutrient levels had the potential to accelerate the regression of the seagrass exposed to high burial (HB). After 11 weeks, HB in combination with either high or medium nutrient enrichment caused a shoot loss of about 60%. Changes in morphology were poor predictors of the seagrass decline. Likewise, few biochemical variables were associated with P. oceanica survival (the phenolics, ORAC and leaf δ34S). In contrast, the expression of target genes had the highest correlation with plant survival: photosynthetic genes (ATPa, psbD and psbA) were up-regulated in response to high burial, while carbon metabolism genes (CA-chl, PGK and GADPH) were down-regulated. Therefore, die-offs due to high sedimentation rate in eutrophic areas can only be anticipated by altered expression of stress-related genes that may warn the imminent seagrass collapse. Management of local stressors, such as nutrient pollution, may enhance seagrass resilience in the face of the intensification of extreme climate events, such as floods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams SM, Greeley MS (2000) Ecotoxicological indicators of water quality: using multi-response indicators to assess the health of aquatic ecosystems. Water Air Soil Pollut 123:103–115
Alcoverro T, Romero J, Duarte CM, López NI (1997) Spatial and temporal variations in nutrient limitation of seagrass Posidonia oceanica growth in the NW Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 146:155–161
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF (2004) Normalization of realtime quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Can Res 64:5245–5250
Ashraf M, Harris PJC (2013) Photosynthesis under stressful environments: an overview. Photosynthetica 51(2):163–190
Bellwood DR, Hughes TP, Folke C, Nyström M (2004) Confronting the coral reef crisis. Nature 429:827–833
Bockelmann AC, Beining K, Reusch TBH (2011) Widespread occurrence of endophytic Labyrinthula spp. in northern European eelgrass Zostera marina beds. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 445:109–116
Boettiger C, Hastings A (2013) From patterns to predictions. Nature 493:157–158
Booker FL, Miller JE (1998) Phenylpropanoid metabolism and phenolic composition of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] leaves following exposure to ozone. J Exp Bot 49:1191–1202
Borum J, Pedersen O, Greve TM, Frankovich TA, Zieman JC, Fourqurean JW et al (2005) The potential role of plant oxygen and sulphide dynamics in die-off events of the tropical seagrass, Thalassia testudinum. J Ecol 93:148–158
Bulthuis DA (1983) Effects of in situ light reduction on density and growth of the seagrass Heterozostera tasmanica (Martens ex Aschers.) den Hartog in Western Port, Victoria, Australia. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 67:91–103
Burkholder JM, Tomasko DA, Touchette BW (2007) Seagrasses and eutrophication. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 350:46–72
Cabaço S, Santos R (2014) Human-induced changes of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa in Ria Formosa lagoon (Southern Portugal) after a decade. Cahier de Biologie Marine 55:101–108
Cabaço S, Santos R, Duarte CM (2008) The impact of sediment burial and erosion on seagrasses: a review. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 79(3):354–366
Carpenter J (2011) May the best analyst win. Science 331:698–699
Costa M, Barrote I, Silva J, Olivé I, Costa MM (2015) Epiphytes modulate Posidonia oceanica photosynthetic production, energetic balance, antioxidant mechanisms and oxidative damage. Front Mar Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2015.00111
Costanza R, d’Arge R, de Groot R, Farber S, Grasso M, Hannon B, Limburg K, Naeem S, O’Neill RV, Paruelo J, Raskin RG, Sutton P, Van den Belt M (1997) The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 387:253–260
Crain CM, Kroeker K, Halpern BS (2008) Interactive and cumulative effects of multiple human stressors in marine systems. Ecol Lett 11:1304–1315
Danovaro R, Fabiano M, Boyer M (1994) Seasonal changes of benthic bacteria in a seagrass bed (Posidonia oceanica) of the Ligurian Sea in relation to origin, composition and fate of the sediment organic matter. Mar Biol 119:489–500
Dattolo E, Ruocco M, Brunet C, Lorenti M, Lauritano C, Sanges R, De Luca P, Procaccini G (2014) Response of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica to different light environments: insight from a combined molecular and photo-physiological study. Mar Environ Res 101:225–236
Dattolo E, Marín-Guirao L, Ruiz J, Procaccini G (2017) Long-term acclimation to reciprocal light conditions reveals depth-related selection in the marine foundation species Posidonia oceanica. Ecol Evol. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.2731
Delgado O, Ruiz J, Perez M, Romero R, Ballesteros E (1999) Effects of fish farming on seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) in a Mediterranean bay: seagrass decline after organic loading cessation. Oceanol Acta 22:109–117
Erftemeijer PLA, Lewis RRR (2006) Environmental impacts of dredging on seagrasses: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 52:1553–1572
Falkenberg LJ, Connell BD, Russel SD (2010) Disrupting the effects of synergies between stressors: improved water quality dampens the effects of future CO2 on a marine habitat. J Appl Ecol 50:51–58
Fonseca MS, Cahalan JA (1992) A preliminary evaluation of wave attenuation by four species of seagrass. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 35:565–576
Fonseca MS, Koehl MAR (2006) Flow in Seagrass canopies: the influence of patch width. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 67:1–9
Fourqurean JW, Robblee MB (1999) Florida Bay: a recent history of ecological changes. Estuaries 22:345–357
Frederiksen MS, Holmer M, Diaz-Almela E, Marba N, Duarte CM (2007) Sulfide invasion in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica at Mediterranean fish farms: assessment using stable sulphur isotopes. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 345:93–104
Garcia R, Holmer M, Duarte CM, Marbà N (2013) Global warming enhances sulphide stress in a key seagrass species (NW Mediterranean). Glob Change Biol 19:3629–3639
Garcìa-Sanz T, Ruiz-Fernandez JM, Ruiz M, Garcia R, Gonzalez MN, Perez M (2010) An evaluation of a macroalgal bioassay tool for assessing the spatial extent of nutrient release from offshore fish farms. Mar Environ Res 70:189–200
Gera A, Pagès JF, Arthur R, Farina S, Roca G, Romero J, Alcoverro T (2014) The effect of a centenary storm on the long-lived seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Limnol Oceanogr 59:1910–1918
Giakoumi S, Halpern BS, Michel LN, Gobert S, Sini M, Boudouresque CF, Gambi MC, Katsanevakis S, Lejeune P, Montefalcone M, Pergent G, Pergent-Martini C, Sanchez-Jerez P, Velimirov B, Vizzini S, Abadie A, Coll M, Guidetti P, Micheli F, Possingham HP (2015) Towards a framework for assessment and management of cumulative human impacts on marine food webs. Conserv Biol 29(4):1228–1234
Gobert S, Sartoretto S, Rico-Raimondino V, Andral B, Chery A, Lejeune P, Boissery P (2009) Assessment of the ecological status of Mediterranean French coastal waters as required by the water framework directive using the Posidonia oceanica Rapid Easy Index, PREI. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1727–1733
Govers LL, de Brouwer JHF, Suykerbuyk W, Bouma TJ, Lamersc LPM, Smolders AJP, van Katwijk MM (2014) Toxic effects of increased sediment nutrient and organic matter loading on the seagrass Zostera noltii. Aquat Toxicol 155:253–260
Griffen BD, Belgrad BA, Cannizzo ZJ, Knotts ER, Hancock ER (2016) Rethinking our approach to multiple stressor studies in marine environments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 543:273–281
Gromping U (2006) Relative importance for linear regression in R: the package relaimpo. J Stat Softw 17(1):1–27
Heck KL, Hays C, Orth RJ (2003) A critical evaluation of the nursery role hypothesis for seagrass meadows. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 253:123–136
Hemminga MA, Duarte CM (2000) Seagrass ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Holmer M, Argyrou M, Dalsgaard T, Danovaro R, Diaz-Almela E, Duarte CM, Frederiksen M, Grau A, Karakassis I, Marbà N, Mirto S, Pérez M, Pusceddu A, Tsapakis M (2008) Effects of fish farm waste on Posidonia oceanica meadows: synthesis and provision of monitoring and management tools. Mar Pollut Bull 56:1618–1629
Huang D, Ou B, Hampsch-Woodill M, Flanagan JA, Prior RL (2002) High-throughput assay of oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) using a multichannel liquid handling system coupled with a microplate fluorescence reader in 96-well format. J Agric Food Chem 50:4437–4444
Hughes AR, Stachowicz JJ (2004) Genetic diversity enhances the resistance of a seagrass ecosystem to disturbance. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:8998–9002
Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (2006) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Dordrecht
Lauritano C, Ruocco M, Dattolo E, Buia MC, Silva J, Santos R, Olivé I, Costa MM, Procaccini G (2015) Response of key stress-related genes of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica in the vicinity of submarine volcanic vents. Biogeosciences 12:4185–4194
Lindeman RH, Merenda PF, Gold RZ (1980) Introduction to bivariate and multivariate analysis. Scott, Foresman
Macreadie PI, Baird ME, Trevathan-Tackett SM, Larkum AWD, Ralph PJ (2014) Quantifying and modelling the carbon sequestration capacity of seagrass meadows—a critical assessment. Mar Pollut Bull 83:430–439
Manzanera M, Alcoverro T, Tomas F, Romero J (2011) Response of Posidonia oceanica to burial dynamics. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 423:47–56
Marbá N, Santiago R, Díaz-Almela E, Álverez E, Duarte CM (2006) Seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) vertical growth as an early indicator of fish farm-derived stress. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 67:475–483
Marbà N, Duarte CM, Díaz-Almela E, Terrados J, Álvarez E, Martínez R, Santiago R, Gacia E, Grau AM (2005) Direct evidence of imbalanced seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) shoot population dynamics along the Spanish Mediterranean. Estuaries 28:53–62
Marín-Guirao L, Ruiz JM, Dattolo E, Garcia-Munoz R, Procaccini G (2016) Physiological and molecular evidence of differential short-term heat tolerance in Mediterranean seagrasses. Sci Rep 6:28615
Mazzuca S, Bjork M, Beer S, Felisberto P, Gobert S, Procaccini G, Runcie J, Silva J, Borges AV, Brunet C, Buapet P, Champenois W, Costa MM, D’Esposito D, Gullstrom M, Lejeune P, Lepoint G, Olive I, Rasmusson M, Richir J, Ruocco M, Serra IA, Spadafora A, Santos R (2013) Establishing research strategies, methodologies and technologies to link genomics and proteomics to seagrass productivity, community metabolism, and ecosystem carbon fluxes. Front Plant Sci 4:38
McMahon K, Collier C, Lavery PS (2013) Identifying robust bioindicators of light stress in seagrasses: a meta-analysis. Ecol Ind 30:7–15
Migliore L, Rotini A, Randazzo D, Albanese NN, Giallongo A (2007) Phenols content and 2-D electrophoresis protein pattern: a promising tool to monitor Posidonia meadows health state. BMC Ecol 7:6
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Montefalcone M (2009) Ecosystem health assessment using the Mediterranean sea- grass Posidonia oceanica: a review. Ecol Ind 9:595–604
Moshe A, Gorovits R, Liu Y, Czosnek H (2016) Tomato plant cell death induced by inhibition of HSP90 is alleviated by Tomato yellow leaf curl virus infection. Mol Plant Pathol 17:247–260
Munkes B (2005) Eutrophication, phase shift, the delay and the potential return in the Greifswalder Bodden, Baltic Sea. Aquat Sci 67:372–381
Nishizawa-Yokoi A, Tainaka H, Yoshida E, Tamoi M, Yabuta Y, Shigeoka S (2010) The 26S Proteasome function and Hsp90 activity involved in the regulation of HsfA2 expression in Response to oxidative stress. Plant Cell Physiol 51:486–496
NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) (2016) Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature (ERSST.v4). National Centers for Environmental Information. http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/data-access/marineocean-data/extended-reconstructed-sea-surface-temperature-ersst. Accessed March 2016
Oliva S (2012) Seagrass systems under human pressure: responses and assessment tools. PhD Thesis Universitat de Barcelona (Spain)
Oliva S, Mascaró O, Llagostera I, Pérez M, Romero J (2012) Selection of metrics based on the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa and development of a biotic index (CYMOX) for assessing ecological status of coastal and transitional waters. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 114:7–17
Orth RJ, Moore KA (1983) Chesapeake Bay: an unprecedented decline in submerged aquatic vegetation. Science 222:51–53
Orth RJ, Carruthers TJB, Dennison WC, Duarte CM, Fourqurean JW, Heck KL Jr, Hughes AR, Kendrick GA, Kenworthy WJ, Olyarnik S, Short FT, Waycott M, Williams SL (2006) A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 56:987–996
Pace ML, Carpenter SR, Cole JJ (2015) With and without warning: managing ecosystems in a changing world. Front Ecol Environ 13:460–467
Pergent G, Boudouresque CF, Dumay O, Pergent-Martini C, Wyllie-Echeverria S (2008) Competition between the invasive macrophyte Caulerpa taxifolia and the seagrass Posidonia oceanica: contrasting strategies. BMC Ecol 8:20
Perry CT, Morgan KM (2017) Bleaching drives collapse in reef carbonate budgets and reef growth potential on southern Maldives reefs. Sci Rep 7:40581. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40581
Piazzi L, Balata D, Ceccherelli G (2016) Epiphyte assemblages of the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica: an overview. Mar Ecol 37:3–41
Prado P, Alcoverro T, Romero J (2008) Seasonal response of Posidonia oceanica epiphyte assemblages to nutrient increase. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 359:89–98
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Biol Med 26:1231–1237
Roca G, Alcoverro T, Krause-Jensen D, Balsby TJS, van Katwijk MM, Marbà N, Santos R, Arthur R, Mascaró O, Fernández-Torquemada Y, Pérez M, Duarte CM, Romero J (2016) Response of seagrass indicators to shifts in environmental stressors: a global review and management synthesis. Ecol Ind 63:310–323
Rotini A, Belmonte A, Barrote I, Micheli C, Peirano A, Santos RO, Silva J, Migliore L (2013) Effectiveness and consistency of a suite of descriptors to assess the ecological status of seagrass meadows (Posidonia oceanica L. Delile). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 130:252–259
Ruíz JM, Pérez M, Romero J (2001) Effects of fish farm loadings on seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) distribution, growth and photosynthesis. Mar Pollut Bull 42(9):749–760
Russell BD, Connell SD (2012) Origins and consequences of global and local stressors: incorporating climatic and non-climatic phenomena that buffer or accelerate ecological change. Mar Biol 159(11):2633–2639
Serra IA, Lauritano C, Dattolo E, Puoti A, Nicastro S, Innocenti AM, Procaccini G (2012) Reference genes assessment for the seagrass Posidonia oceanica in different salinity, pH and light conditions. Mar Biol 159:1269–1282
Short FT, Wyllie-Echeverria S (1996) Natural and human-induced disturbance of seagrasses. Environ Conserv 23:17–27
Tamburello L, Benedetti-Cecchi L, Ghedini G, Bulleri F (2012) Variation in the structure of subtidal landscapes in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 457:29–41
Telesca L, Belluscio A, Criscoli A, Ardizzone G, Apostolaki ET, Fraschetti S, Gristina M, Knittweis L, Martin CS, Pergent G, Alagna A, Badalamenti F, Garofalo G, Gerakaris V, Pace ML, Pergent-Martini C, Salomidi M (2015) Seagrass meadows (Posidonia oceanica) distribution and trajectories of change. Sci Rep 5:12505
Terrados J, Duarte CM, Kamp-Nielsen L, Agawin NSR, Gacia E, Lacap D, Fortes MD, Borum J, Lubanski M, Greve T (1999) Are seagrass growth and survival affected by reducing conditions in the sediment? Aquat Bot 65:175–197
Underwood AJ (1997) Experiments in ecology: their logical design and interpretation using analysis of variance. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Unsworth RKF, Collier CJ, Waycott M, Mckenzie LJ, Cullen-Unsworth LC (2015) A framework for the resilience of seagrass ecosystems. Mar Pollut Bull 100:34–46
Van Katwijk MM, Van der Welle MEW, Lucassen ECHET, Vonk JA, Christianen MJA, Kiswara W, Inayat al Hakim I, Arifin A, Bouma TJ, Roelofs JGM, Lamerset LPM (2011) Early warning indicators for river nutrient and sediment loads in tropical seagrass beds: a benchmark from a near-pristine archipelago in Indonesia. Mar Pollut Bull 62:1512–1520
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT–PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3(0034):1
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern applied statistics with S, 4th edn. Springer, New York
Walker DI, Kendrick GA, McComb AJ (2006) Decline and recovery of seagrass ecosystems-the dynamics of change. In: Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 551–565
Waycott M, Duarte CM, Carruthers TJB, Orth RJ, Dennison WC, Olyarnik S, Calladine A, Fourqurean JW, Heck KL, Hughes AR, Kendrick GA, Kenworthy WJ, Short FT, Williams SL (2009) Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:12377–12381
Whitham TG, Bailey JK, Schweitzer JA, Shuster SM, Bangert RK, LeRoy CJ, Lonsdorf EV, Allan GJ, DiFazio SP, Potts BM, Fischer DG, Gehring CA, Lindroth RL, Marks JC, Hart SC, Wimp GM, Wooley SC (2006) A framework for community and ecosystem genetics: from genes to ecosystems. Nat Rev Genet 7:510–523
Williams SL (2007) Introduced species in seagrass ecosystems: status and concerns. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 350:89–110
Zuur AF, Ieno EN, Elphick CS (2010) A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems. Methods Ecol Evol 1:3–14
Acknowledgements
Analyses were performed at the Servizos de Apoio á Investigación-Universidade da Coruña (Leaf N, Leaf C, and corresponding isotopic signatures), Iso-Analytical Ltd (Leaf S and leaf δ34S). We are grateful to Capo Caccia-Isola Piana MPA administration for facilitating the samplings within their domains. This research was supported by MIUR, the Italian Ministry of Education and Research, (TETRIS Grant 2011–2015) and by Fondazione di Sardegna (EIMS Grant 2016–2019). PG acknowledges the support of S. Porrello and E. Persia at ISPRA laboratories for water nutrient analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GC, SO, and LP conceived and designed the experiments. GC, SO, SP and LP performed the experiments. GP, LMG, ED, RG, PG, MMC, IB, JS analysed the sampled material, FB analysed the data. GC and FB led the writing of the ms. All authors contributed critically to the drafts and gave final approval for publication.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by James Fourqurean.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ceccherelli, G., Oliva, S., Pinna, S. et al. Seagrass collapse due to synergistic stressors is not anticipated by phenological changes. Oecologia 186, 1137–1152 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-018-4075-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-018-4075-9