Summary
Background
Histamine intolerance (HIT) is characterized by an imbalance between histamine intake and the capacity for histamine degradation. The main enzyme for metabolizing ingested histamine is diamine oxidase (DAO). Determining DAO activity in serum may be useful in diagnosing HIT.
Methods
Over a period of 3.5 years we recruited 316 subjects with clinically suspected HIT and 55 healthy controls. Serum DAO activity was measured with a quantitative enzyme immunoassay. Twenty patients with highly reduced DAO activity went on a histamine-free diet for 6–12 months. Afterwards, their DAO activity was determined again.
Results
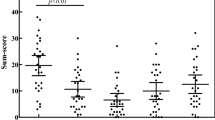
We found that DAO activity was significantly lower in patients than in healthy control subjects (P < 0.0001). Furthermore, 54 patients had highly reduced serum DAO activity (< 40 HDU/ml). Their main symptoms involved the skin, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, and eyes. In all the 20 patients with highly reduced DAO activity, the main clinical symptoms typical of histamine intolerance disappeared after they adopted a histamine-free diet. Furthermore, the serum DAO activity values measured increased significantly (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Our results suggest that determining DAO activity in serum is a useful tool in diagnosing HIT. Furthermore, our results showed the benefit of a histamine-free diet because after the diet the majority of symptoms disappeared and the serum DAO activity significantly increased.
Zusammenfassung
Einleitung
Die Histaminintoleranz (HIT) ist ein Ungleichgewicht zwischen aufgenommenen Histamin und Histaminabbau. Das wichtigste Enzym für den Abbau von aufgenommenen Histamin ist Diaminooxidase (DAO). Die Bestimmung der Aktivität von DAO vermag sich als hilfreich erweisen bei der HIT-Diagnose.
Methoden
Über einen Zeitraum von 3,5 Jahre haben wir 316 Probanden mit klinischem HIT-Verdacht und 55 gesunde Versuchspersonen angeworben. Die Aktivität von DAO im Serum wurde per Enzymimmunoassay quantitiv bestimmt. Zwanzig Patienten mit einer stark reduzierten DAO-Aktivität wurden auf eine histaminfreie Diät gesetzt über einen Zeitraum von 6 bis 12 Monaten. Danach wurde deren DAO-Aktivität erneut gemessen.
Ergebnisse
Wir haben festgestellt, dass die DAO-Aktivität in diesen Patienten signifikant niedriger war als in den gesunden Versuchspersonen (P < 0,0001). Desweiteren hatten 54 Patienten eine stark reduzierte DAO-Aktivität im Serum (< 40 HDU/ml). Deren Hauptsymtome betrafen die Haut, den Magen-Darm-Trakt, die Atemwege und Augen. In allen 20 Patienten mit stark reduzierter DAO-Aktivität verschwanden die typischen klinischen Symptome bei Histaminintoleranz nach Durchführung der histaminfreien Diät. Zudem stieg DAO-Aktivität im Serum signifikant an (P < 0,0001).
Ergebnisse
Unsere Ergebnisse lassen darauf schließen, dass die Bestimmung der Aktivität von Diaminooxidase in Serum dienlich ist als Diagnostiktest auf HIT Desweiteren zeigen unsere Ergebnisse die Vorteile einer histaminfreien Diät, da die Mehrheit der Symptome verschwunden sind während die DAO-Aktivität im Serum signifikant anstieg.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jarisch R. Histamin-Intoleranz [Histamine intolerance]. Aerztemagazin. 2004;8:1–4.
Maintz L, Bieber T, Novak N. Histamine intolerance in clinical practice. Dtsch Arttebl. 2006;103(102–103):3477–83.
Maintz L, Novak N. Histamine and histamine intolerance. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;85:1185–96.
Schwelberger HG. Histamine intolerance: overestimated or underestimated? Inflamm Res. 2009;58(S1):51–2.
Schwelberger HG. Histamine intolerance: a metabolic disease? Inflamm Res. 2010;59(S2):219–21.
Komericki P, Klein G, Reider N, Hawranek T, Strimitzer T, Lang R, Kranzelbinder B, Aberer W. Histamine intolerance: lack of reproducibility of single symptoms by oral provocation with histamine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over study. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2011;123(1–2):15–20.
Tufvesson G, Tryding N. Determination of diamine oxidase activity in normal human blood serum. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969;24:163–8.
Mayer I, Missbichler A, Wantke F, Focke M, Reichl H, Winter M, Jarisch R. Optimierter Radioextraktionsassay zur quantitativen Bestimmung der Aktivität von Diaminooxidase (DAO) in humanem Serum und Plasma [Optimized radioextraction assay for the quantitative measurement of the activity of diamine oxidase (DAO) in human serum and plasma]. Allergologie. 2005;28:1–8.
Steinbrecher I, Jarisch R. Histamin und Kopfschmerz [Histamine and headache]. Allergologie. 2005;28:84–91.
Töndury B, Wüthrich B, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Seifert B, Ballmer-Weber BK. Histaminintoleranz: Wie sinnvoll ist die Bestimmung der Diaminoxidase-Aktivität im Serum in der alltäglichen klinischen Praxis? [Histamine intolerance: is the determination of diamine oxidase activity in the serum useful in routine clinical practice?]. Allergologie. 2008;31:350–6.
Kofler H, Aberer W, Deibi M, Hawranek T, Kleih G, Reider N, Fellner N. Diamine oxidase (DAO) serum activity: not a useful marker for diagnosis of histamine intolerance. Allergologie. 2009;32:105–9.
Kanny G, Gerbaux V, Olszewski A, Fremont S, Empereur F, Nabet F, Cabanis JC, Moneret-Vautrin DA. No correlation between wine intolerance and histamine content of wine. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:375–8.
Wöhrl S, Hemmer W, Focke M, Rappersberger K, Jarisch R. Histamine intolerance-like symptoms in healthy volunteers after oral provocation with liquid histamine. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2004;25:305–11.
Stolze I, Peters KP, Herbst RA. Histaminintoleranz imitiert Anorexia nervosa [Histamine intolerance mimics anorexia nervosa]. Hautarzt. 2010;6:776–8.
Wantke F, Götz M, Jarisch R. Die histaminfreie Diät [The histamine-free diet]. Hautarzt. 1993;44:512–6.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mušič, E., Korošec, P., Šilar, M. et al. Serum diamine oxidase activity as a diagnostic test for histamine intolerance. Wien Klin Wochenschr 125, 239–243 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-013-0354-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-013-0354-y