Abstract
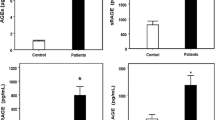
Activation of the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) has been implicated in the development of diabetic vascular complications. Soluble RAGE (sRAGE) could act as a decoy for the RAGE ligands and may thus exert a cytoprotective effect. Since RAGE is upregulated by advanced glycation end products (AGEs), the same could be implied for sRAGE. We aimed to investigate the role of sRAGE as a marker of early diabetic nephropathy. Forty-eight type 2 diabetic patients, further subdivided into group 1 without renal affection (10 patients), group 2 with microalbuminuria (25 patients), and group 3 with proteinuria (13 patients), and age-matched control group 4 (17 subjects) were included. Serum sRAGE, urea, creatinine, plasma glycated hemoglobin (HBA1c), and urinary albumin excretion (albumin/creatinine ratio) were measured. sRAGE levels were significantly higher in groups 2 and 3when compared to groups 1 and 4. No significant difference was found on comparing groups 2 and 3 together or on comparing groups 1 and 4. There was a significant positive correlation between sRAGE level and all the studied parameters (p < 0.05) as well as a significant association between the sRAGE positivity within the three diabetic groups and the degree of proteinuria. Although sRAGE level was found to be significantly higher in the microalbuminuria group when compared to both the control and diabetics with normal kidney groups, the absolute value did not differ significantly from the proteinuria group. So we say that sRAGE can be used as a marker of diabetic nephropathy; however, its absolute level cannot be used to distinguish different degrees of renal affection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed N (2005) Advanced glycation endproducts – role in pathology of diabetic complications. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 67:3–21
American Diabetes Association (2012) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 35(Suppl 1):S64–71
Bucciarelli LG, Wendt T, Rong L, Lalla E, Hofmann MA, Goova MT, Taguchi A, Yan SF, Yan SD, Stern DM, Schmidt AM (2002) RAGE is a multiligand receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily: implications for homeostasis and chronic disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 59(7):1117–1128
Challier M, Jacqueminet S, Benabdesselam O, Grimaldi A, Beaudeux JL (2005) Increased serum concentrations of soluble receptor for advanced glycation endproducts in patients with type 1 diabetes. Clin Chem 51(9):1749–1750
Geroldi D, Falcone C, Emanuele E (2006) Soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products: from disease marker to potential therapeutic target. Curr Med Chem 13(17):1971–1978
Gohda T, Tanimoto M, Moon JY, Gotoh H, Aoki T, Matsumoto M, Shibata T, Ohsawa I, Funabiki K, Tomino Y (2008) Increased serum endogenous secretory receptor for advanced glycation end-product (esRAGE) levels in type 2 diabetic patients with decreased renal function. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 81(2):196–201
Grossin N, Wautier MP, Meas T, Guillausseau PJ, Massin P, Wautier JL (2008) Severity of diabetic microvascular complications is associated with a low soluble RAGE level. Diabetes Metab 34(4Pt 1):392–5
Hanford LE, Enghild JJ, Valnickova Z, Petersen SV, Schaefer LM, Schaefer TM, Reinhart TA, Oury TD (2004) Purification and characterization of mouse soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE). J Biol Chem 279(48):50019–50024
Hudson BI, Harja E, Moser B, Schmidt AM (2005) Soluble levels of receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (sRAGE) and coronary artery disease: the next C-reactive protein? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(5):879–882
Humpert PM, Kopf S, Djuric Z, Wendt T, Morcos M, Nawroth PP, Bierhaus A (2006) Plasma sRAGE is independently associated with urinary albumin excretion in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 29(5):1111–1113
Humpert PM, Djuric Z, Kopf S, Rudofsky G, Morcos M, Nawroth PP, Bierhaus A (2007) Soluble RAGE but not endogenous secretory RAGE is associated with albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 6:9
Katakami N, Matsuhisa M, Kaneto H, Matsuoka TA, Sakamoto K, Nakatani Y, Ohtoshi K, Hayaishi-Okano R, Kosugi K, Hori M, Yamasaki Y (2005) Decreased endogenous secretory advanced glycation end product receptor in type 1 diabetic patients: its possible association with diabetic vascular complications. Diabetes Care 28(11):2716–2721
Kislinger T, Fu C, Huber B, Qu W, Taguchi A, Du Yan S, Hofmann M, Yan SF, Pischetsrieder M, Stern D, Schmidt AM (1999) N(epsilon)-(carboxymethyl)lysine adducts of proteins are ligands for receptor for advanced glycation end products that activate cell signaling pathways and modulate gene expression. J Biol Chem 274(44):31740–31749
Knapp RG, Miller MC (1992) Describing the performance of a diagnostic test. In: Knapp RG, Miller MC (eds) Clinical epidemiology and biostatistics, 1st edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 41–42
Koyama H, Shoji T, Yokoyama H, Motoyama K, Mori K, Fukumoto S, Emoto M, Shoji T, Tamei H, Matsuki H, Sakurai S, Yamamoto Y, Yonekura H, Watanabe T, Yamamoto H, Nishizawa Y (2005) Plasma level of endogenous secretory RAGE is associated with components of the metabolic syndrome and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(12):2587–93
Koyama H, Shoji T, Fukumoto S, Shinohara K, Shoji T, Emoto M, Mori K, Tahara H, Ishimura E, Kakiya R, Tabata T, Yamamoto H, Nishizawa Y (2006) Low circulating endogenous secretory receptor for AGEs predicts cardiovascular mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27(1):147–53
Pullerits R, Bokarewa M, Dahlberg L, Tarkowski A (2005) Decreased levels of soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products in patients with rheumatoid arthritis indicating deficient inflammatory control. Arthritis Res Ther 7(4):R817–24
Rowe DJ, Dawnay A, Watts GF (1990) Microalbuminuria in diabetes mellitus: review and recommendations for the measurement of albumin in urine. Ann Clin Biochem 27:297–312
Stern DM, Yan SD, Yan SF, Schmidt AM (2002) Receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) and the complications of diabetes. Ageing Res Rev 1:1–15
Tan KC, Shiu SW, Chow WS, Leng L, Bucala R, Betteridge DJ (2007) Association between serum levels of soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products and circulating advanced glycation end products in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev Jul 23(5):368–71
World Medical Association (2008) Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects, the 59th WMA general assembly, Seoul, South Korea
Yonekura H, Yamamoto Y, Sakurai S, Petrova RG, Abedin MJ, Li H, Yasui K, Takeuchi M, Makita Z, Takasawa S, Okamoto H, Watanabe T, Yamamoto H (2003) Novel splice variants of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products expressed in human vascular endothelial cells and pericytes, and their putative roles in diabetes-induced vascular injury. Biochem J 370(Pt 3):1097–1109
Yu JY, An XF, Liu JS, Ten SC, Wang X, Zhao Y, Huang S, Gu WJ, Gao F (2010) Plasma sRAGE is not associated with urinary microalbumin excretion in type 2 diabetic nephropathy at the early stage. Diabetes Res Clin Pract Feb 87(2):157–60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeyada, R., Osman, N.A. Increased serum level of soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE) in type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Comp Clin Pathol 22, 845–849 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-012-1487-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-012-1487-5