Summary.
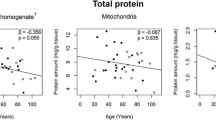
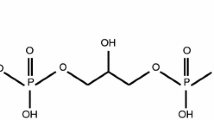
Breakdown of cellular membranes is a characteristic feature of neuronal degeneration in acute (stroke) and chronic (senile dementia) neurological disorders. The present review summarizes recent experimental and clinical work which concentrated on changes of choline-containing phospholipids as indicators of neuronal membrane breakdown. Experimental studies identified glutamate release, calcium influx, and activation of cellular phospholipase A2 (PLA2) as important steps initiating membrane breakdown in cultured neurons or brain slices under hypoxic or ischemic conditions. Proton NMR studies have shown an elevation of choline-containing compounds in the brain of Alzheimer patients while neurochemical studies in post mortem-brain demonstrated increases of the catabolic metabolite, glycerophosphocholine, an indicator of PLA2 activation. In contrast, studies of cerebrospinal fluid, phosphorus NMR studies, and measurements of phospholipases in post mortem Alzheimer brain gave ambiguous results which may be explained by methodical limitations. The finding that, in experimental studies, choline was a rate-limiting factor for phospholipid biosynthesis has stimulated clinical studies aimed at counteracting phospholipid breakdown, e.g. by combinations of choline and cytidine. Future experimental approaches should clarify whether loss of membrane phospholipids is cause or consequence of the neurodegenerative disease process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received October 2, 1999; accepted February 29, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klein, J. Membrane breakdown in acute and chronic neurodegeneration: focus on choline-containing phospholipids. J Neural Transm 107, 1027–1063 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020070051
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020070051