Abstract
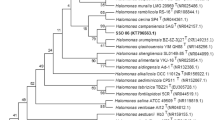
A moderately halophilic bacteria designed strain NY-011T was isolated from the high salt culture of Dunaliella salina in Chengdu of Sichuan Province, China. The isolate was Gram-negative, nonmotile, rod-shaped and 12.5–21.6 μm in length. Colonies on solid media are circular, wet, smooth and cream. The strain grew optimally at 37 °C, pH 7.0 and in the presence of 8 % NaCl. Acid was produced from glycerol, d-arabinose, glucose, trehalose, inositol, mannose, mannitol, sucrose, maltose and sorbitol. Catalase is produced but not oxidase. The major fatty acids are C18: 1ω7c (37.59 %), C19: 0 cyclo ω8c (18.29 %), C16: 0 (16.05 %) and C6: 0 (12.43 %). The predominant respiratory lipoquinone found in strain NY-011T is ubiquinone with nine isoprene units (Q-9). The genomic DNA G + C content of strain NY-011T was 62.7 mol%. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that strain NY-011T belonged to the genus Halomonas. The highest levels of 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity were found between the strain NY-011T and H. pantelleriensis (sequence similarity 98.43 %). However, the levels of DNA–DNA relatedness between them were only 23.1 %. In addition, the strain NY-011T had a phenotypic profile that readily distinguished it from H. pantelleriensis. The strain NY-011T therefore represents a new species of the genus Halomonas, for which the name Halomonas socia sp. nov. is proposed, with NY-011T (=CCTCC AB 2011033T = KCTC 23671T) as the type strain.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arahal DR, Ventosa A (2006) The family Halomonadaceae. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The Prokaryotes A handbook on the biology of bacteria, vol. 6, 3rd edn. Springer, New York, pp 811–835
Arahal DR, Vreeland RH, Litchfield CD, Mormile MR, Tindall BJ, Oren A, Bejar V, Quesada E, Ventosa A (2007) Recommended minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Halomonadaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2436–2446
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230
Cui XL, Mao PH, Tseng M, Li WJ, Zhang LP, Xu LH, Jiang CL (2001) Streptomonospora salina gen. nov., a new member of the family Nocardiopsaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:357–363
De la Haba RR, Arahal DR, Márquez MC, Ventosa A (2010) Phylogenetic relationships within the family Halomonadaceae based on comparative 23S and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:737–748
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Dobson SJ, Franzmann PD (1996) Unification of the genera Deleya (Baumann et al. 1983), Halomonas (Vreeland et al. 1980), and Halovibrio (Fendrich 1988) and the species Paracoccus halodenitrificans (Robinson and Gibbons, 1952) into a single genus, Halomonas, and placement of the genus Zymobacter in the family Halomonadaceae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:550–558
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–789
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Franzmann PD, Wehmeyer U, Stackebrandt E (1988) Halomonadaceae fam. nov., a new family of the class Proteobacteria to accommodate the genera Halomonas and Deleya. Syst Appl Microbiol 11:16–19
Grant WD, Kamekura M, McGenity TJ, Ventosa A (2001) Class III Halobacteria class. nov. In: Boone DR, Castenholz RW, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol. 1, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 294–334
Groth I, Schumann P, Rainey FA, Martin K, Schuetze B, Augsten K (1997) Demetria terragena gen. nov., sp. nov., a new genus of actinomycetes isolated from compost soil. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:1129–1133
Guan TW, Xiao J, Zhao K, Luo XX, Zhang XP, Zhang LL (2010) Halomonas xinjiangensis sp. nov., a halotolerant bacterium isolated from a salt lake in Xinjiang. China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:349–352
Huss V, Festl H, Schleifer KH (1983) Studies on the spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:184–192
Jahnke KD (1992) BASIC computer program for evaluation of spectroscopic DNA renaturation data from Gilford System 2600 spectrophotometer on a PC/XT/AT type personal computer. J Microbiol Methods 15:61–73
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9:299–306
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–218
Mata JA, Martínez-Cánovas MJ, Quesada E, Béjar V (2002) A detailed phenotypic characterisation of the type strains of Halomonas species. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:360–375
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G + C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrate procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Okamoto T, Taguchi H, Nakamura K, Ikenaga H, Kuraishi H, Yamasato K (1993) Zymobacter palmae gen. nov., sp. nov., a new ethanol-fermenting peritrichous bacterium isolated from palm sap. Arch Microbiol 160:333–337
Pick U, Karni L, Avron M (1986) Determination of ion content and ion fluxes in the halotolerant alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol 81:92–96
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic tree. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI technical note 101. IDI Inc., Newyork
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tindall BJ, Rosselló-Móra R, Busse HJ, Ludwig W, Kämpfer P (2010) Notes on the characterization of prokaryote strains for taxonomic purposes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:249–266
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:504–544
Vreeland RH, Litchfield CD, Martin EL, Elliot E (1980) Halomonas elongata, a new genus and species of extremely salt-tolerant bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 30:485–495
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE (1987) International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the College of Life Sciences, Zhejiang University, and Dr. Agata Gambacorta for providing the reference strains. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.: 30500006, 30970043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Oren.
Jiao Cao and Huai-Yuan Ma are co-first authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Ma, HY., Li, HY. et al. Halomonas socia sp. nov., isolated from high salt culture of Dunaliella salina . Extremophiles 17, 663–668 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-013-0549-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-013-0549-1