Abstract
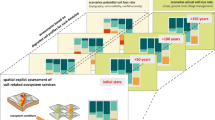
Current spatially explicit approaches to map and assess ecosystem services are often grounded on unreliable proxy data based on land use/cover to derive ecosystem service indicators. These approaches fail to make a distinction between the actual service provision and the underlying ecosystem capacity to provide the service. We present an integrative conceptual framework to estimate the provision of soil erosion prevention by combining the structural impact of soil erosion and the social–ecological processes that allow for its mitigation. The framework was tested and illustrated in the Portel municipality in Southern Portugal, a Mediterranean silvo-pastoral system that is prone to desertification and soil degradation. The results show a clear difference in the spatial and temporal distribution of the capacity for ecosystem service provision and the actual ecosystem service provision. It also shows that although the average actual ecosystem service provision in the region is sufficient to mitigate the existing structural impact, vulnerable areas can be identified where significant soil losses are not mitigated at present. This becomes more significant when comparing different land management intensities. Considering these results, we argue that the general assumption that there is an almost direct relation between the capacity for ecosystem service provision of a given area and the actual ecosystem service provision is wrong. We also discuss how the framework presented here could be used to support land management and policy, and how it can be adapted for other regulating services.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida M, Guerra C, Pinto-Correia T. 2013. Unfolding relations between land cover and farm management: high nature value assessment in complex silvo-pastoral systems. Geogr Tidsskr J Geogr 113:1–12.
Amore E, Modica C, Nearing MA, Santoro VC. 2004. Scale effect in USLE and WEPP application for soil erosion computation from three Sicilian basins. J Hydrol 293:100–14.
Bagstad KJ, Johnson GW, Voigt B, Villa F. 2012. Spatial dynamics of ecosystem service flows: a comprehensive approach to quantifying actual services. Ecosyst Serv 4:117–25.
Bangash RF, Passuello A, Sanchez-Canales M, Terrado M, López A, Elorza FJ, Ziv G, Acuña V, Schuhmacher M. 2013. Ecosystem services in Mediterranean river basin: climate change impact on water provisioning and erosion control. Sci Total Environ 458–460(C):246–55.
Benoît M, Rizzo D, Marraccini E, Moonen AC, Galli M, Lardon S, Rapey H, Thenail C, Bonari E. 2012. Landscape agronomy: a new field for addressing agricultural landscape dynamics. Landsc Ecol 27:1385–94.
Bou Kheir R, Cerdan O, Abdallah C. 2006. Regional soil erosion risk mapping in Lebanon. Geomorphology 82:347–59.
Burger Ja, Kelting DL. 1999. Using soil quality indicators to assess forest stand management. For Ecol Manag 122:155–66.
Burkhard B, Kroll F, Müller F. 2009. Landscapes‘ capacities to provide ecosystem services—a concept for land-cover based assessments. Landsc Online 15:1–22.
Burkhard B, Kroll F, Nedkov S, Müller F. 2012. Mapping ecosystem service supply, demand and budgets. Ecol Indic 21:17–29.
Cardoso JC. 1965. Os solos de Portugal sua classificação, caracterização e génese: 1-A sul do rio tejo. Lisboa: Secretaria de Estado da Agricultura.
Carter MR. 2002. Soil quality for sustainable land management: organic matter and aggregation interactions that maintain soil functions. Agron J 94:38–47.
CBD. 2012. Decision X/2 strategic plan for biodiversity 2011–2020 and the aichi biodiversity targets. Nagoya.
Cerdan O, Govers G, Le Bissonnais Y, Van Oost K, Poesen J, Saby N, Gobin A, Vacca A, Quinton J, Auerswald K, Klik A, Kwaad FJPM, Raclot D, Ionita I, Rejman J, Rousseva S, Muxart T, Roxo MJ, Dostal T. 2010. Rates and spatial variations of soil erosion in Europe: a study based on erosion plot data. Geomorphology 122:167–77.
COM. 2011. Our life insurance, our natural capital: an EU biodiversity strategy to 2020.
Daily GC, Matson Pa. 2008. Ecosystem services: from theory to implementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9455–6.
Daily GC, Polasky S, Goldstein J, Kareiva PM, Mooney HA, Pejchar L, Ricketts TH, Salzman J, Shallenberger R. 2009. Ecosystem services in decision making: time to deliver. Front Ecol Environ 7:21–8.
Diodato N, Bellocchi G. 2010. MedREM, a rainfall erosivity model for the Mediterranean region. J Hydrol 387:119–27.
Eigenbrod F, Armsworth PR, Anderson BJ, Heinemeyer A, Gillings S, Roy DB, Thomas CD, Gaston KJ. 2010. The impact of proxy-based methods on mapping the distribution of ecosystem services. J Appl Ecol 47:377–85.
Erskine WD, Mahmoudzadeh A, Myers C. 2002. Land use effects on sediment yields and soil loss rates in small basins of Triassic sandstone near. Catena 49:271–87.
Fensholt R, Proud SR. 2012. Evaluation of earth observation based global long term vegetation trends—comparing GIMMS and MODIS global NDVI time series. Remote Sens Environ 119:131–47.
Fistikoglu O, Harmancioglu NB. 2002. Integration of GIS with USLE in assessment of soil erosion. Water Resour Manag 16:447–67.
Fritsch S, Machwitz M, Ehammer A, Conrad C, Dech S. 2012. Validation of the collection 5 MODIS FPAR product in a heterogeneous agricultural landscape in arid Uzbekistan using multitemporal RapidEye imagery. Int J Remote Sens 33:37–41.
Fu B, Liu Y, Lü Y, He C, Zeng Y, Wu B. 2011. Assessing the soil erosion control service of ecosystems change in the Loess Plateau of China. Ecol Complex 8:284–93.
Gobin A, Govers G, Jones R, Kirkby M, Kosmas C. 2003. Assessment and reporting on soil erosion.
Grimm M, Jones R, Montanarella L. 2002. Soil Erosion Risk in Europe. Joint Research Center.
Haines-Young R, Potschin M, Kienast F. 2012. Indicators of ecosystem service potential at European scales: mapping marginal changes and trade-offs. Ecol Indic 21:39–53.
Hauck J, Görg C, Varjopuro R, Ratamäki O, Jax K. 2013. Benefits and limitations of the ecosystem services concept in environmental policy and decision making: some stakeholder perspectives. Environ Sci Policy 25:13–21.
Haylock MR, Hofstra N, Klein Tank AMG, Klok EJ, Jones PD, New M. 2008. A European daily high-resolution gridded data set of surface temperature and precipitation for 1950-2006. J Geophys Res 113:D20119.
Herrick JE. 2000. Soil quality: an indicator of sustainable land management? Appl Soil Ecol 15:75–83.
Holling CS. 2001. Understanding the complexity of economic, ecological, and social systems. Ecosystems 4:390–405.
INAG. 2010. Sistema Nacional de Informação de Recursos Hídricos.
INE. 2011. Recenseamento agrícola—análise dos principais resultados: 2009. Lisboa.
Van der Knijff J, Jones R, Montanarella L. 1999. Soil erosion risk assessment in Italy. Joint Research Center.
Van der Knijff J, Jones R, Montanarella L. 2000. Soil erosion risk assessment in Europe. Joint Research Center.
Kouli M, Soupios P, Vallianatos F. 2008. Soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in a GIS framework, Chania, Northwestern Crete, Greece. Environ Geol 57:483–97.
Kumar P. 2010. TEEB Ecological and Economic Foundations. TEEB.
Millennium Assessment (MA). 2005. Ecosystems and human well-being: current status and trends. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Maes J, Egoh B, Willemen L, Liquete C, Vihervaara P, Schägner JP, Grizzetti B, Drakou EG, La Notte A, Zulian G, Bouraoui F, Luisa Paracchini M, Braat L, Bidoglio G. 2012. Mapping ecosystem services for policy support and decision making in the European Union. Ecosyst Serv 1:31–9.
Maes J, Paracchini M, Zulian G. 2011. A European assessment of the provision of ecosystem services: towards an atlas of ecosystem services. JRC Scientific and Technical Reports.
Martín-Fernández L, Martínez-Núñez M. 2011. An empirical approach to estimate soil erosion risk in Spain. Sci Total Environ 409:3114–23.
Metzger MJ, Schröter D, Leemans R, Cramer W. 2008. A spatially explicit and quantitative vulnerability assessment of ecosystem service change in Europe. Reg Environ Chang 8:91–107.
Moore ID, Burch GJ. 1986. Physical basis of the length-slope factor in the universal soil loss equation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:1294.
Morgan RPC. 2005. Soil erosion & conservation. 3rd edn. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing.
Müller F, Burkhard B. 2012. The indicator side of ecosystem services. Ecosyst Serv 1:26–30.
Naidoo R, Balmford A, Costanza R, Fisher B, Green RE, Lehner B, Malcolm TR, Ricketts TH. 2008. Global mapping of ecosystem services and conservation priorities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9495–500.
Nedkov S, Burkhard B. 2011. Flood regulating ecosystem services—mapping supply and demand, in the Etropole municipality, Bulgaria. Ecol Indic 21:67–79.
Ortega M, Guerra C, Honrado JP, Metzger MJ, Bunce RGH, Jongman RHG. 2013. Surveillance of habitats and plant diversity indicators across a regional gradient. Ecol Indic 33:36–44.
Panagos P, Jones A, Bosco C, Kumar PSS. 2011a. European digital archive on soil maps (EuDASM): preserving important soil data for public free access. Int J Digit Earth 4:434–43.
Panagos P, Karydas CG, Gitas IZ. 2011b. Monthly soil erosion monitoring based on remotely sensed biophysical parameters: a case study in Strymonas river basin towards a functional pan-European service. Int J Digit Earth 5(6):461–87.
Pereira H, Ferrier S, Walters M, Geller N, Jongman RHG, Scholes J, Bruford M, Brummitt N, Butchart S, Cardoso A, Coops N, Dulloo E, Faith D, Freyhof J, Gregory R, Heip C, Höft R, Hurtt G, Jetz W, Karp D, McGeoch M, Obura D, Onoda Y, Pettorelli N, Reyers B, Sayre R, Scharlemann J, Stuart N, Turak E, Walpole M, Wegmann M. 2013. Essential biodiversity variables. Science 339(80):277–8.
Pereira PM, Fonseca MP. 2003. Nature vs nurture: the making of the Montado ecosystem. Conserv Ecol 7(3):7.
Pinto-Correia T, Godinho S. 2013. Changing agriculture—changing landscape: what is going on in the high valued Montado landscapes of Southern Portugal? In: Ortiz-Miranda D, Moragues-Faus AM, Arnalte-Alegre E, Eds. Agriculture in Mediterranean Europe between old and new paradigms. Research in Rural Sociology and Development, Vol. 19. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Limited. p 75–90.
Pinto-Correia T, Mascarenhas J. 1999. Contribution to the extensification/intensification debate: new trends in the Portuguese montado. Landsc Urban Plan 46:125–31.
Pinto-Correia T, Ribeiro N, Sá-Sousa P. 2011. Introducing the montado, the cork and holm oak agroforestry system of Southern Portugal. Agrofor Syst 82:99–104.
Pinto-Correia T, Vos W. 2004. Multifunctionality in Mediterranean landscapes-past and future. The new dimensions of the European landscape. Wageningen EU Frontis Series. Dordrecht: Springer. p 135–64.
Plieninger T, Dijks S, Oteros-Rozas E, Bieling C. 2013. Assessing, mapping, and quantifying cultural ecosystem services at community level. Land Use Policy 33:118–29.
Prasannakumar V, Vijith H, Abinod S, Geetha N. 2012. Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous sub-watershed in Kerala, India, using Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geosci Front 3:209–15.
Presbitero AL, Escalante MC, Rose CW, Coughlan KJ, Ciesiolka CA. 1995. Erodibility evaluation and the effect of land management practices on soil erosion from steep slopes in Leyte, the Philippines. Soil Technol 8:205–13.
Purevdorj T, Tateishi R, Ishiyam T, Honda Y. 1998. Relationships between percent vegetation cover and vegetation indices. Int J Remote Sens 19:3519–35.
Rounsevell MDA, Pedroli B, Erb K-H, Gramberger M, Busck AG, Haberl H, Kristensen S, Kuemmerle T, Lavorel S, Lindner M, Lotze-Campen H, Metzger MJ, Murray-Rust D, Popp A, Pérez-Soba M, Reenberg A, Vadineanu A, Verburg PH, Wolfslehner B. 2012. Challenges for land system science. Land Use Policy 29:899–910.
Seppelt R, Dormann CF, Eppink FV, Lautenbach S, Schmidt S. 2011. A quantitative review of ecosystem service studies: approaches, shortcomings and the road ahead. J Appl Ecol 48:630–6.
Surová D, Pinto-Correia T, Marušák R. 2013. Visual complexity and the montado do matter: landscape pattern preferences of user groups in Alentejo Portugal. Ann For Sci . doi:10.1007/s13595-013-0330-8.
Swaffield S, Primdahl J. 2010. Globalisation and local agricultural landscapes: patterns of change, policy dilemmas and research questions. In: Primdahl J, Swaffield S, Eds. Globalisation and agricultural landscapes—change patterns and policy trends in developed countries. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p 245–70.
Van-Camp L, Bujarrabal B, Gentile AR, Jones RJA, Montanarella L, Olazabal C, Selvaradjou S. 2004. Reports of the Technical Working Groups Established under the Thematic Strategy for Soil Protection. Luxembourg.
Vanwalleghem T, Laguna A, Giráldez JV, Jiménez-Hornero FJ. 2010. Applying a simple methodology to assess historical soil erosion in olive orchards. Geomorphology 114:294–302.
Verheijen FGA, Jones RJA, Rickson RJ, Smith CJ. 2009. Tolerable versus actual soil erosion rates in Europe. Earth-Science Rev 94:23–38.
Verheijen FGA, Jones RJA, Rickson RJ, Smith CJ, Bastos AC, Nunes P, Keizer JJ. 2013. Concise overview of European soil erosion research and evaluation. Acta Agric Scand Sect B 62:185–90.
Vicente JR, Pinto AT, Araújo MB, Verburg PH, Lomba A, Randin CF, Guisan A, Honrado JP. 2013. Using life strategies to explore the vulnerability of ecosystem services to invasion by alien plants. Ecosystems 16:678–93.
Vihervaara P, Kumpula T, Tanskanen A, Burkhard B. 2010. Ecosystem services–a tool for sustainable management of human–environment systems. Case study Finnish Forest Lapland. Ecol Complex 7:410–20.
Wallace KJ. 2007. Classification of ecosystem services: problems and solutions. Biol Conserv 139:235–46.
Van Wijnen HJ, Rutgers M, Schouten AJ, Mulder C, de Zwart D, Breure AM. 2012. How to calculate the spatial distribution of ecosystem services—natural attenuation as example from The Netherlands. Sci Total Environ 415:49–55.
Williams L, Kapustka L. 2000. Ecosystem vulnerability: a complex interface with technical components. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:1055–8.
Wischmeier W, Smith D. 1978. Predicting rainfall erosion losses. A guide to conservation planning. Washington DC: Science and Education Administration, U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author contributions
Carlos Guerra, Teresa Pinto-Correia, and Marc J. Metzger designed the study, Performed research, and wrote the paper; Carlos Guerra analyzed data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerra, C.A., Pinto-Correia, T. & Metzger, M.J. Mapping Soil Erosion Prevention Using an Ecosystem Service Modeling Framework for Integrated Land Management and Policy. Ecosystems 17, 878–889 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-014-9766-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-014-9766-4