Abstract
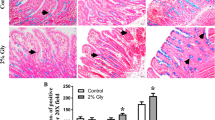
Tempeh, a well-known Indonesian fermented food made from soybeans, results from mixed-culture fermentation using a diverse group of microorganisms. The presence of many nonviable microorganisms in cooked tempeh may trigger responses in the immune system. Thirty female Sprague-Dawley rats were fed a standard diet supplemented with either non-fermented soybeans or tempeh (uncooked or cooked), for 28 days. Gene expression of intestinal immunoglobulin A (IgA) was analyzed using semi-quantitative real-time PCR, and intestinal IgA was further quantified from the ileum wash using ELISA. There was no significant (p>0.05) difference in IgA gene expression between animals groups receiving feed supplemented with cooked or uncooked tempeh. However, a significant (p<0.05) difference was observed between animals receiving feed supplemented with tempeh and with non-fermented soybeans. Microbial cells in tempeh might increase IgA protein secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
FAO/WHO. Report of a joint FAO/WHO expert consultation on guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. World Health of the United Nations Organization and Food and Agriculture Organization, London, Canada (2002)
Kataria J, Li N, Wynn JL, Neu J. Probiotic microbes: Do they need to be alive to be beneficial? Nutr. Rev. 67: 546–550 (2009)
Adams CA. The probiotic paradox: Live and dead cells are biological response modifiers. Nutr. Res. Rev. 23: 37–46 (2010)
Taverniti V, Guglielmetti S. The immunomodulatory properties of probiotic microorganisms beyond their viability (ghost probiotics: proposal of paraprobiotic concepts). Genes Nutr. 6: 261–274 (2011)
Harris NL, Spoerri I, Schopfer JF, Nembrini C, Merky P, Massacand J, Urban JF Jr, Lamarre A, Burki K, Odermatt B, Zinkernagel RM, Macpherson AJ. Mechanisms of neonatal mucosal antibody protection. J. Immunol. 177: 6256–6262 (2006)
Maynard CL, Elson CO, Hatton RD, Weaver CT. Reciprocal interactions of the intestinal microbiota and immune system. Nature 489: 231–241 (2012)
Kaetzel CS, Mostov K. Immunoglobulin transport and the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. Vol. 1, pp. 211–250. In: Mucosal Immunology. Mestechky J, Lam JT, Strober W, Bienenstock J, McGee DW, Mayer L (eds). Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands (2005)
Okada N. Role of microorganisms in tempeh manufacture-Isolation of vitamin B12 producing bacteria. JARQ- Jpn. Agr. Res. Q. 22: 310–316 (1989)
Astuti M, Meliala A, Dalais FS, Wahlqvist ML. tempeh, a nutritious and healthy food from Indonesia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 9: 322–325 (2000)
Babu PD, Bhakyaraj R, Vidhyalakshmi R. A low cost nutritional food “tempeh”- A review. World J. Dairy Food Sci. 4: 22–27 (2009)
Dixit AK, Antony JIX, Sharma NK, Tiwari RK. Soybean constituents and their functional benefits. pp. 367–383. In: Opportunity, Challenge and Scope of Natural Products in Medicinal Chemistry. Tiwari VK, Mishra BB (eds.) Research Signpost, Kerala, India (2011)
Barus T, Suwanto A, Wahyudi AT, Wijaya H. Role of bacteria in tempe bitter taste formation: Microbiological and molecular biological analysis based on 16S rRNA gene. Microbiol. Indones. 2: 17–21 (2008)
Seumahu CA, Suwanto A, Rusmana I, Solihin DD. Comparison of DNA extraction methods for microbial community analysis in Indonesian tempe employing amplified ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis. HAYATI J. Biosci. 19: 93–98 (2012)
Perez-Cano FJ, Ramírez-Santana C, Molero-Luís M, Castell M, Rivero M, Castellote C, Franch A. Mucosal IgA increase in rats by continuous CLA feeding during suckling and early infancy. J. Lipid Res. 50: 467–476 (2009)
Massot-Cladera M, Pérez-Berezo T, Franch A, Castell M, Pérez-Cano FJ. Cocoa modulatory effect on rat faecal microbiota and colonic crosstalk. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 527: 105–112 (2012)
Dréau D, Lallès JP, Philouze-Romé V, Toullec R, Salmon H. Local and systemic immune responses to soybean protein ingestion in early-weaned pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 72: 2090–2098 (1994)
Lallès JP, Dréau D, Huet A, Toullec R. Systemic and local gutspecific antibody responses in pre-ruminant calves sensitive to soya. Res. Vet. Sci. 59: 56–60 (1995)
Mowat AM. Anatomical basis of tolerance and immunity to intestinal antigens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3: 331–341 (2003)
Cerutti A, Chen K, Chomy A. Immunoglobulin responses at the mucosal interface. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 29: 273–293 (2011)
Reyna-Garfias H, Miliar A, Jarillo-Luna A, Rivera-Aguilar V, Pacheco-Yepez J, Baeza I, Campos-Rodriguez R. Repeated restraint stress increases IgA concentration in rat small intestine. Brain Behav. Immun. 24: 110–118 (2010)
Schrenzenmeir J, de Vrese M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics: Approaching a definition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 73: 361–364 (2001)
Philpott DJ, Girardin SE. The role of Toll-like receptors and Nod proteins in bacterial infection. Mol. Immunol. 41: 1099–1108 (2004)
Sakai Y, Tsukahara T, Matsubara N, Ushida K. A cell wall preparation of Enterococcus faecalis strain EC-12 stimulates β-defensin expression in newly hatched broiler chicks. Anim. Sci. J. 78: 92–97 (2007)
Marin ML, Lee JH, Murtha J, Ustunol Z, Pestka JJ. Differential cytokine production in clonal macrophage and T-cell lines cultured with bifidobacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 80: 2713–2720 (1997)
Torii A, Torii S, Fujiwara S, Tanaka H, Inagaki N, Nagai H. Lactobacillus acidophilus strain L-92 regulates the production of Th1 cytokine as well as Th2 cytokines. Allergol. Int. 56: 293–301 (2007)
Taverniti V, Guglielmetti S. The immunomodulatory properties of probiotic microorganisms beyond their viability (ghost probiotics: proposal of paraprobiotic concepts). Genes Nutr. 6: 261–274 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soka, S., Suwanto, A., Sajuthi, D. et al. Impact of tempeh supplementation on mucosal immunoglobulin A in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Sci Biotechnol 24, 1481–1486 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0191-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0191-z