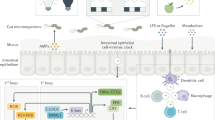
Abstract
The human microbiome is intimately associated with human health, with a role in obesity, metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, and divergent diseases such as cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. The microbiome can be changed by diet, probiotics, and faecal transplants, which has flow-on effects to health outcomes. Photobiomodulation has a therapeutic effect on inflammation and neurological disorders (amongst others) and has been reported to influence metabolic disorders and obesity. The aim of this study was to examine the possibility that PBM could influence the microbiome of mice. Mice had their abdomen irradiated with red (660 nm) or infrared (808 nm) low-level laser, either as single or multiple doses, over a 2-week period. Genomic DNA extracted from faecal pellets was pyrosequenced for the 16S rRNA gene. There was a significant (p < 0.05) difference in microbial diversity between PBM- and sham-treated mice. One genus of bacterium (Allobaculum) significantly increased (p < 0.001) after infrared (but not red light) PBM by day 14. Despite being a preliminary trial with small experimental numbers, we have demonstrated for the first time that PBM can alter microbiome diversity in healthy mice and increase numbers of Allobaculum, a bacterium associated with a healthy microbiome. This change is most probably a result of PBMt affecting the host, which in turn influenced the microbiome. If this is confirmed in humans, the possibility exists for PBMt to be used as an adjunct therapy in treatment of obesity and other lifestyle-related disorders, as well as cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. The clinical implications of altering the microbiome using PBM warrants further investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raza GS, Putaala H, Hibberd AA, Alhoniemi E, Tiihonen K, Mäkelä KA, Herzig K-H (2017) Polydextrose changes the gut microbiome and attenuates fasting triglyceride and cholesterol levels in Western diet fed mice. Sci Rep 7(1):5294
Kau AL, Ahern PP, Griffin NW, Goodman AL, Gordon JI (2011) Human nutrition, the gut microbiome, and immune system: envisioning the future. Nature 474(7351):327
Tilg H, Kaser A (2011) Gut microbiome, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction. J Clin Invest 121(6):2126–2132. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI58109
Tang WW, Kitai T, Hazen SL (2017) Gut microbiota in cardiovascular health and disease. Circ Res 120(7):1183–1196
de la Fuente-Nunez C, Meneguetti BT, Franco OL, Lu TK (2018) Neuromicrobiology: how microbes influence the brain. ACS Chem Neurosci 9:141–150
Turnbaugh PJ, Gordon JI (2009) The core gut microbiome, energy balance and obesity. J Physiol 587(Pt 17):4153–4158. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2009.174136
Montagner A, Korecka A, Polizzi A, Lippi Y, Blum Y, Canlet C, Tremblay-Franco M, Gautier-Stein A, Burcelin R, Yen Y-C, Je HS, Maha A-A, Mithieux G, Arulampalam V, Lagarrigue S, Guillou H, Pettersson S, Wahli W (2016) Hepatic circadian clock oscillators and nuclear receptors integrate microbiome-derived signals. Sci Rep 6:20127. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20127
Lozupone CA, Stombaugh JI, Gordon JI, Jansson JK, Knight R (2012) Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 489(7415):220
Nguyen TLA, Vieira-Silva S, Liston A, Raes J (2015) How informative is the mouse for human gut microbiota research? Dis Model Mech 8(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.017400
Everard A, Lazarevic V, Gaia N, Johansson M, Stahlman M, Backhed F, Delzenne NM, Schrenzel J, Francois P, Cani PD (2014) Microbiome of prebiotic-treated mice reveals novel targets involved in host response during obesity. ISME J 8(10):2116–2130. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.45
Avci P, Nyame TT, Gupta GK, Sadasivam M, Hamblin MR (2013) Low-level laser therapy for fat layer reduction: a comprehensive review. Lasers Surg Med 45(6):349–357. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.22153
Chung H, Dai T, Sharma S, Huang Y-Y, Carroll J, Hamblin M (2012) The nuts and bolts of low-level laser (light) therapy. Ann Biomed Eng 40(2):516–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10439-011-0454-7
Hamblin MR (2017) Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation. AIMS Biophys 4(3):337–361. https://doi.org/10.3934/biophy.2017.3.337
Wang X, Tian F, Soni SS, Gonzalez-Lima F, Liu H (2016) Interplay between up-regulation of cytochrome-c-oxidase and hemoglobin oxygenation induced by near-infrared laser. Sci Rep 6:30540
Hamblin MR (2018) Mechanisms and mitochondrial redox signaling in photobiomodulation. Photochem Photobiol 94(2):199–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12864
Liebert AD, Chow RT, Bicknell BT, Varigos E (2016) Neuroprotective effects against POCD by photobiomodulation: evidence from assembly/disassembly of the cytoskeleton. J Exp Neurosci 10:1
Yoshimura TM, Sabino CP, Ribeiro MS (2016) Photobiomodulation reduces abdominal adipose tissue inflammatory infiltrate of diet-induced obese and hyperglycemic mice. J Biophotonics 9(11–12):1255–1262. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbio.201600088
Silva G, Ferraresi C, de Almeida RT, Motta ML, Paixão T, Ottone VO, Fonseca IA, Oliveira MX, Rocha-Vieira E, Dias-Peixoto MF (2017) Infrared photobiomodulation (PBM) therapy improves glucose metabolism and intracellular insulin pathway in adipose tissue of high-fat fed mice. Lasers Med Sci 33(3):559–571
da Silveira Campos RM, Dâmaso AR, Masquio DCL, Duarte FO, Sene-Fiorese M, Aquino AE, Savioli FA, Quintiliano PCL, Kravchychyn ACP, Guimarães LI (2018) The effects of exercise training associated with low-level laser therapy on biomarkers of adipose tissue transdifferentiation in obese women. Lasers Med Sci 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-018-2465-1
Johnstone D, El Massri N, Moro C, Spana S, Wang X, Torres N, Chabrol C, De Jaeger X, Reinhart F, Purushothuman S (2014) Indirect application of near infrared light induces neuroprotection in a mouse model of parkinsonism–an abscopal neuroprotective effect. Neuroscience 274:93–101
Liebert A, Krause A, Goonetilleke N, Bicknell B, Kiat H (2017) A role for photobiomodulation in the prevention of myocardial ischemic reperfusion injury: a systematic review and potential molecular mechanisms. Sci Rep 7
Liebert A, Bicknell B, Adams R (2014) Protein conformational modulation by photons: a mechanism for laser treatment effects. Med Hypotheses 82(3):275–281
Neves LM, Gonçalves EC, Cavalli J, Vieira G, Laurindo LR, Simões RR, Coelho IS, Santos AR, Marcolino AM, Cola M (2017) Photobiomodulation therapy improves acute inflammatory response in mice: the role of cannabinoid receptors/ATP-sensitive K+ channel/p38-MAPK signalling pathway. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0792-z
Boulangé CL, Neves AL, Chilloux J, Nicholson JK, Dumas M-E (2016) Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Med 8(1):42
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335
Mandal S, Van Treuren W, White RA, Eggesbø M, Knight R, Peddada SD (2015) Analysis of composition of microbiomes: a novel method for studying microbial composition. Microb Ecol Health Dis 26. https://doi.org/10.3402/mehd.v26.27663
Agababova A, Movsesyan H (2011) Change of gut microflora of healthy rats under the low energy laser irradiation. Doklady Akademii Nauk Armenii 111:372–378
Liang X, Bushman FD, FitzGerald GA (2015) Rhythmicity of the intestinal microbiota is regulated by gender and the host circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(33):10479–10484. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1501305112
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Xu J, Xue Z, Zhang M, Pang X, Zhang X, Zhao L (2015) Modulation of gut microbiota by berberine and metformin during the treatment of high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats. 5:14405. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14405. https://www.nature.com/articles/srep14405#supplementary-information
Joensen J, Demmink JH, Johnson MI, Iversen VV, Lopes-Martins RÁB, Bjordal JM (2011) The thermal effects of therapeutic lasers with 810 and 904 nm wavelengths on human skin. Photomed Laser Surg 29(3):145–153
dos Santos Grandinétti V, Miranda EF, Johnson DS, de Paiva PRV, Tomazoni SS, Vanin AA, Albuquerque-Pontes GM, Frigo L, Marcos RL, de Carvalho PDTC (2015) The thermal impact of phototherapy with concurrent super-pulsed lasers and red and infrared LEDs on human skin. Lasers Med Sci 30(5):1575–1581
Wang X, Reddy DD, Nalawade SS, Pal S, Gonzalez-Lima F, Liu H (2017) Impact of heat on metabolic and hemodynamic changes in transcranial infrared laser stimulation measured by broadband near-infrared spectroscopy. Neurophotonics 5(1):011004
Cowan CS, Hoban AE, Ventura-Silva AP, Dinan TG, Clarke G, Cryan JF (2018) Gutsy moves: the amygdala as a critical node in microbiota to brain signaling. BioEssays 40(1)
Sharon G, Sampson TR, Geschwind DH, Mazmanian SK (2016) The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. Cell 167
Pascal V, Pozuelo M, Borruel N, Casellas F, Campos D, Santiago A, Martinez X, Varela E, Sarrabayrouse G, Machiels K (2017) A microbial signature for Crohn's disease. Gut 66(5):813–822
Sherwin E, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2017) Recent developments in understanding the role of the gut microbiota in brain health and disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
Tremlett H, Bauer KC, Appel-Cresswell S, Finlay BB, Waubant E (2017) The gut microbiome in human neurological disease: a review. Ann Neurol
Sampson TR, Debelius JW, Thron T, Janssen S, Shastri GG, Ilhan ZE, Challis C, Schretter CE, Rocha S, Gradinaru V (2016) Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 167(6):1469–1480.e1412
O'Mahony SM, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2017) The gut microbiota as a key regulator of visceral pain. Pain 158:S19–S28
Gonzalez A, Hyde E, Sangwan N, Gilbert JA, Viirre E, Knight R (2016) Migraines are correlated with higher levels of nitrate-, nitrite-, and nitric oxide-reducing oral microbes in the American gut project cohort. mSystems 1(5). https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00105-16
Arora HC, Eng C, Shoskes DA (2017) Gut microbiome and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Ann Transl Med 5(2):30
Hamblin M (2010) Introduction to experimental and clinical studies using low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT). Lasers Surg Med 42:447–449
Hamblin MR (2016) Shining light on the head: photobiomodulation for brain disorders. BBA Clin 6:113–124
Duarte FO, Sene-Fiorese M, de Aquino Junior AE, da Silveira Campos RM, Masquio DCL, Tock L, de Oliveira Duarte ACG, Dâmaso AR, Bagnato VS, Parizotto NA (2015) Can low-level laser therapy (LLLT) associated with an aerobic plus resistance training change the cardiometabolic risk in obese women? A placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 153:103–110
Ucero AC, Sabban B, Benito-Martin A, Carrasco S, Joeken S, Ortiz A (2013) Laser therapy in metabolic syndrome-related kidney injury. Photochem Photobiol 89(4):953–960
Houser MC, Tansey MG (2017) The gut-brain axis: is intestinal inflammation a silent driver of Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis? NPJ Parkinsons Dis 3(1):3
Johnstone D, Massri N, Moro C, Spana S, Wang S, Torres N, Chabrol C, De Jaeger X, Reinhart F, Purushothuman S, Benabid A, Stone J, Mitrofanis J (2014) Indirect application of near infrared light induces neuroprotection in a mouse model of parkinsonism - an abscopal neuoroprotective effect. Neuroscience 274:93–101
Kim B, Mitrofanis J, Stone J, Johnstone DM (2018) Remote tissue conditioning is neuroprotective against MPTP insult in mice. IBRO Rep 4:14–17
Stone J, Johnstone D, Mitrofanis J (2013) The helmet experiment in Parkinson's disease: an observation of the mechanism of neuroprotection by near infra-red light. In: 9th WALT Congress (Gold Coast, QLD)
Blivet G, Meunier J, Roman FJ, Touchon J (2018) Neuroprotective effect of a new photobiomodulation technique against Aβ25–35 peptide–induced toxicity in mice: novel hypothesis for therapeutic approach of Alzheimer’s disease suggested. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 4:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2017.12.003
Tetel MJ, de Vries GJ, Melcangi RC, Panzica G, O'Mahony SM (2017) Steroids, stress, and the gut microbiome-brain Axis. J Neuroendocrinol
Mayer EA, Tillisch K, Gupta A (2015) Gut/brain axis and the microbiota. J Clin Invest 125(3):926–938
Kelly JR, Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Clarke G, Hyland NP (2015) Breaking down the barriers: the gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders. Front Cell Neurosci 9:392
Purkayastha S, Cai D (2013) Neuroinflammatory basis of metabolic syndrome. Mol Metab 2(4):356–363
Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, Buffa JA, Org E, Sheehy BT, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Li L (2013) Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med 19(5):576–585
Seyedsadjadi N, Berg J, Bilgin AA, Tung C, Grant R (2017) Significant relationships between a simple marker of redox balance and lifestyle behaviours; relevance to the Framingham risk score. PLoS One 12(11):e0187713. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187713
Cong X, Henderson WA, Graf J, McGrath JM (2015) Early life experience and gut microbiome: the brain-gut-microbiota signaling system. Adv Neonatal Care 15(5):314
Hueston CM, Cryan JF, Nolan YM (2017) Stress and adolescent hippocampal neurogenesis: diet and exercise as cognitive modulators. Transl Psychiatry 7(4):e1081
Bonder MJ, Kurilshikov A, Tigchelaar EF, Mujagic Z, Imhann F, Vila AV, Deelen P, Vatanen T, Schirmer M, Smeekens SP (2016) The effect of host genetics on the gut microbiome. Nat Genet 48(11):1407
Spor A, Koren O, Ley R (2011) Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol 9(4):279
Mukherjee S, Maitra SK (2015) Gut melatonin in vertebrates: chronobiology and physiology. Front Endocrinol 6(112). https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2015.00112
Anderson G, Vaillancourt C, Maes M, Reiter RJ (2017) Breastfeeding and the gut-brain axis: is there a role for melatonin? Biomol Concepts 8(3–4):185–195
Tomazoni SS, Leal-Junior ECP, Pallotta RC, Teixeira S, de Almeida P, Lopes-Martins RÁB (2017) Effects of photobiomodulation therapy, pharmacological therapy, and physical exercise as single and/or combined treatment on the inflammatory response induced by experimental osteoarthritis. Lasers Med Sci 32(1):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-2091-8
Wang Q, Liu D, Song P, Zou M-H (2015) Deregulated tryptophan-kynurenine pathway is linked to inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune activation pathway in cardiovascular diseases. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 20:1116–1143
Owe-Young R, Webster NL, Mukhtar M, Pomerantz RJ, Smythe G, Walker D, Armati PJ, Crowe SM, Brew BJ (2008) Kynurenine pathway metabolism in human blood–brain–barrier cells: implications for immune tolerance & neurotoxicity. J Neurochem 105(4):1346–1357
Mbongue JC, Nicholas DA, Torrez TW, Kim N-S, Firek AF, Langridge WH (2015) The role of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase in immune suppression and autoimmunity. Vaccines 3(3):703–729
Tomaz de Magalhães M, Núñez SC, Kato IT, Ribeiro MS (2016) Light therapy modulates serotonin levels and blood flow in women with headache. A preliminary study. Exp Biol Med 241(1):40–45
Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Clarke G (2017) Kynurenine pathway metabolism and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Neuropharmacology 112:399–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.07.002
Summa KC, Turek FW (2014) Chronobiology and obesity: interactions between circadian rhythms and energy regulation. Adv Nutr 5(3):312S–319S
Leone V, Gibbons SM, Martinez K, Hutchison AL, Huang EY, Cham CM, Pierre JF, Heneghan AF, Nadimpalli A, Hubert N (2015) Effects of diurnal variation of gut microbes and high-fat feeding on host circadian clock function and metabolism. Cell Host Microbe 17(5):681–689
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Elvis Freeman-Acquah who assisted with the PBM treatments and collection of faeces and Lyudmyla Arshynnikova who translated manuscripts in the Russian language.
Funding
DJ was supported by the Early Career Fellowship from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) of Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BB, AL, and DJ—design and implementation the study; BB and DJ—acquisition of data; BB—analysis and interpretation; BB, AL, and HK—drafting of manuscript; all authors—revision and approval.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
BB is an agent for Spectro Analytic Irradia AB, the company that manufactures the Irradia laser products supplied for this experiment. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of University of Sydney (Protocol Number: 2017/1128).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bicknell, B., Liebert, A., Johnstone, D. et al. Photobiomodulation of the microbiome: implications for metabolic and inflammatory diseases. Lasers Med Sci 34, 317–327 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-018-2594-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-018-2594-6