Abstract
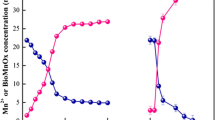
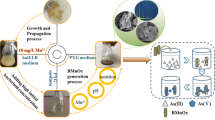
Biogenic manganese oxides (BioMnOx) have been found all over the world, and most of them were formed by Mn(II)-oxidizing bacteria (MnOB). In this study, a MnOB designated as FF-1 was isolated from marine surface sediments in the Bohai Sea, China. This strain was identified as Bacillus sp. and can tolerate more than 5% salinity. It can grow in the presence of 0–7 mM Mn(II) and pH range from 5.0 to 7.0. When the initial Mn(II) was 5 mM, the percentage of Mn(II) oxidation reached the highest value of 16% after 10 days of incubation. The initial pH (5.0 to 7.0) affected the percentage of Mn(II) oxidation, but the ability of the strain FF-1 to self-regulate pH resulted in the final pH being almost 7.6. The removal of Mn(II) by the strain FF-1 involves extracellular and intracellular adsorption as well as Mn(II) oxidation. Intracellular Mn adsorption contributed a small part to the total Mn removal, and extracellular adsorption was dominant in the initial stage of Mn removal. The solid products after Mn removal were a mixture of MnOx and MnCO3. The layered MnOx formed in the extracellular space could be easily collected and used for adsorption and oxidation of pollutants.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BioMnOx :
-
Biogenic manganese oxides
- EDS:
-
Energy dispersion analysis
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- ICP-MS:
-
Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry
- LBB:
-
Leucoberbelin blue
- MnOB:
-
Mn(II)-oxidizing bacteria
- MnOM:
-
Mn(II)-oxidizing microbes
- MnOx:
-
Manganese oxides (1 < x < 2)
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscope
- XANES:
-
X-ray adsorption near edge spectroscopy
- XPS:
-
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
Akob DM, Bohu T, Beyer A, Schäffner F, Händel M, Johnson CA, Merten D, Büchel G, Totsche KU, Küsel K, Lovell CR (2014) Identification of Mn(II)-oxidizing bacteria from a low-pH contaminated former uranium mine. Appl Environ Microb 80:5086–5097. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01296-14
Andeer PF, Learman DR, McIlvin M, Dunn JA, Hansel CM (2015) Extracellular haem peroxidases mediate Mn(II) oxidation in a marine Roseobacter bacterium via superoxide production. Environ Microbiol 17:3925–3936. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12893
Barboza NR, Amorim SS, Santos PA, Reis FD, Cordeiro MM, Guerra-Sá R, Leão VA, Fan X (2015) Indirect manganese removal by Stenotrophomonas sp. and Lysinibacillus sp. isolated from Brazilian mine water. Biomed Res Int 925972. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/925972
Bargar JR, Tebo BM, Villinski JE (2000) In situ characterization of Mn(II) oxidation by spores of the marine Bacillus sp. strain SG-1. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 64:2775–2778. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00368-9
Bargar JR, Tebo BM, Bergmann U, Webb SM, Glatzel P, Chiu VQ, Villalobos M (2005) Biotic and abiotic products of Mn(II) oxidation by spores of the marine Bacillus sp. strain SG-1. Am Mineral 90:143–154. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2005.1557
Cömert S, Tepe O (2020) Production and characterization of biogenic manganese oxides by manganese-adapted Pseudomonas putida NRRL B-14878. Geomicrobiol J 37:753–763. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2020.1770900
Dhami NK, Reddy MS, Mukherjee A (2014) Synergistic role of bacterial urease and carbonic anhydrase in carbonate mineralization. Appl Biochem Biotech 172:2552–2561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0694-0
Forrez I, Carballa M, Verbeken K, Vanhaecke L, Michael S, Ternes T, Boon N, Verstraete W (2010) Diclofenac oxidation by biogenic manganese oxides. Environ Sci Technol 44:3449–3454. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9027327
Francis CA, Tebo BM (2002) Enzymatic manganese(II) oxidation by metabolically dormant spores of diverse Bacillus species. Appl Environ Microb 68:874–880. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.2.874-880.2002
Furuta S, Ikegaya H, Hashimoto H, Ichise S, Kohno T, Miyata N, Takada J (2015) Formation of filamentous Mn oxide particles by the Alphaproteobacterium Bosea sp. Strain BIWAKO-01. Geomicrobiol J 32:666–676.https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2014.982837
Gao B, Zhu S, Gu J, Liu Y, Yi X, Zhou H (2022) Superoxide radical mediated Mn (III) formation is the key process in the activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) by Mn-incorporated bacterial-derived biochar. J Hazard Mater 431:128549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128549
Hansel CM, Zeiner CA, Santelli CM, Webb SM (2012) Mn (II) oxidation by an ascomycete fungus is linked to superoxide production during asexual reproduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:12621–12625. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1203885109
Katsoyiannis IA, Zouboulis AI (2004) Biological treatment of Mn(II) and Fe(II) containing groundwater: kinetic considerations and product characterization. Water Res 38:1922–1932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.01.014
Klueglein N, Zeitvogel F, Stierhof YD, Floetenmeyer M, Konhauser KO, Kappler A, Obst M (2014) Potential role of nitrite for abiotic Fe (II) oxidation and cell encrustation during nitrate reduction by denitrifying bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:1051–1061. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03277-13
Liang J, Bai Y, Hu C, Qu J (2016) Cooperative Mn(II) oxidation between two bacterial strains in an aquatic environment. Water Res 89:252–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.062
Liang DH, Hu Y, Cheng J, Chen Y (2021) Enhanced performance of sulfamethoxazole degradation using Achromobacter sp. JL9 with in-situ generated biogenic manganese oxides. Bioresource Technol 333:125089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125089
Liao S, Zhou J, Wang H, Chen X, Wang H, Wang G (2013) Arsenite oxidation using biogenic manganese oxides produced by a deep-sea manganese-oxidizing bacterium, Marinobacter sp. MnI7–9. Geomicrobiol J 30:150–159.https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2011.654379
Miletto M, Wang X, Planavsky NJ, Luther GW, Lyons TW, Tebo BM (2021) Marine microbial Mn(II) oxidation mediates Cr(III) oxidation and isotope fractionation. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 297:101–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2021.01.008
Naik-Samant S, Furtado I (2019) Formation of rhodochrosite by Haloferax alexandrinus GUSF-1. J Clust Sci 30:1435–1441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01586-9
Parikh SJ, Chorover J (2005) FTIR spectroscopic study of biogenic Mn-oxide formation by Pseudomonas putida GB-1. Geomicrobiol J 22:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490450590947724
Romano CA, Zhou M, Song Y, Wysocki VH, Dohnalkova AC, Kovarik L, Paša-Tolić L, Tebo BM (2017) Biogenic manganese oxide nanoparticle formation by a multimeric multicopper oxidase Mnx. Nat Commun 8:746. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00896-8
Tu J, Yang Z, Hu C, Qu J (2014) Characterization and reactivity of biogenic manganese oxides for ciprofloxacin oxidation. J Environ Sci-China 26:1154–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(13)60505-7
Wang R, Wang S, Tai Y, Tao R, Dai Y, Guo J, Yang Y, Duan S (2017) Biogenic manganese oxides generated by green algae Desmodesmus sp. WR1 to improve bisphenol A removal. J Hazard Mater 339:310–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.06.026
Wang G, Liu Y, Wu M, Zong W, Yi X, Zhan J, Liu L, Zhou H (2019) Coupling the phenolic oxidation capacities of a bacterial consortium and in situ-generated manganese oxides in a moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR). Water Res 166:115047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115047
Wang Q, Wei H, Liu W, Zhai J (2021) Carbamazepine removal by the synergistic effect of manganese-oxidizing microalgae and biogenic manganese oxides. J Hazard Mater 419:126530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126530
Zhang S, Zhao L, Wu Y, Pang Y, Yue X, Li B, Li Q, Zhang J (2019a) Controllable synthesis of hierarchical nanoporous ε-MnO2 crystals for the highly effective oxidation removal of formaldehyde. Cryst Eng Comm 21:3863–3872. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CE00466A
Zhang Y, Tang Y, Qin Z, Luo P, Ma Z, Tan M, Kang H, Huang Z (2019b) A novel manganese oxidizing bacterium-Aeromonas hydrophila strain DS02: Mn(II) oxidization and biogenic Mn oxides generation. J Hazard Mater 367:539–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.01.012
Zhao X, Wang X, Liu B, Xie G, Xing D (2018) Characterization of manganese oxidation by Brevibacillus at different ecological conditions. Chemosphere 205:553–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.130
Zhou H, Fu C (2020) Manganese-oxidizing microbes and biogenic manganese oxides: characterization, Mn(II) oxidation mechanism and environmental relevance. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 19:489–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09541-1
Zhu S, Xiao P, Wang X, Liu Y, Yi X, Zhou H (2022) Efficient peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation by visible-light-driven formation of polymorphic amorphous manganese oxides. J Hazard Mater 427:127938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127938
Funding
The authors are financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41977197), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (DUT20JC49), Xingliao Talent Plan Projects in Liaoning province (XLYC1907109), and Dalian Municipal Outstanding Youth Science And Technology Talent Project (2019RJ09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain studies involving animals conducted by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
The authors state that they consent to publication.
Additional declarations for articles in bioscience journals reporting the results of studies with humans and/or animals
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Kang, F., Wang, Z. et al. Manganese removal and product characteristics of a marine manganese-oxidizing bacterium Bacillus sp. FF-1. Int Microbiol 25, 701–708 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-022-00254-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-022-00254-9