Abstract
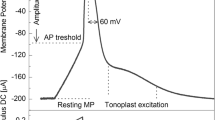
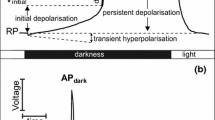
The effect of nickel (Ni) on the generation of plant bioelectrical signals was evaluated in Nitellopsis obtusa, a Characean model organism. Conventional glass-microelectrode technique and K+-anaesthesia method in current-clamp and voltage-clamp modes were used for the measurement and analysis of electrical parameters. Ni2+ treatment rapidly influenced the action potential (AP) parameters namely, excitation threshold, AP peak and duration, membrane potential at various voltages and dynamics of ion currents. We conclude that altered electrical signaling pathway in the test organism constituted the early target for Ni toxicity imposition. The observed Ni interference could be ascribed to disturbed [Ca2+]cyt content, impaired Cl− and K+ channels activity resulting in decreased excitability and repolarization rate in generated AP.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Khazaaly S, Beilby MJ (2012) Zinc ions block H+/OH− channels in Chara australis. Plant Cell Environ 35:1380–1392
Beilby MJ (2007) Action potential in charophytes. Int Rev Cytol 257:43–82
Berestovsky G, Kataev A (2005) Voltage-gated calcium and Ca2+-activated chloride channels and Ca2+ transients: voltage-clamp studies of perfused and intact cells of Chara. Eur Biophys J 34:973–986
De Vos CHR, Schat H, De Waal MAM, Vooijs R, Ernst WHO (1991) Increased resistance to copper-induced damage of the root cell plasmalemma in copper tolerant Silene cucubalus. Physiol Plant 82:523–528
Demidchik V, Sokolik A, Yurin V (1997) The effect of Cu2+ on ion transport systems of the plant cell plasmalemma. Plant Physiol 114:1313–1325
Djebali W, Zarrouk M, Brouquisse R, El Kahoui S, Limam F, Ghorbel MH, Chaïbi W (2005) Ultrastructure and lipid alterations induced by cadmium in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) chloroplast membranes. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 7:358–368
Elzenga JTM, Prins HBA, Vanvolkenburgh E (1995) Light-induced membrane-potential changes of epidermal and mesophyll-cells in growing leaves of pisum–sativum. Planta 197:127–134
Felle HH, Zimmermann MR (2007) Systemic signalling in barley through action potentials. Planta 226:203–214
Fisahn J, Herde O, Willmitzer L, Pena-Cortes H (2004) Analysis of the transient increase in cytosolic Ca2+ during the action potential of higher plants with high temporal resolution: requirement of Ca2+ transients for induction of jasmonic acid biosynthesis and PINII gene expression. Plant Cell Physiol 45:456–459
Fromm J, Lautner S (2007) Electrical signals and their physiological significance in plants. Plant Cell Environ 30:249–257
Gajewska E, Bernat P, Długoński J, Skłodowska M (2012) Effect of nickel on membrane integrity, lipid peroxidation and fatty acid composition in wheat seedlings. J Agron Crop Sci 198:286–294
Gradogna A, Scholz-Starke J, Gutla PVK, Carpaneto A (2009) Fluorescence combined with excised patch: measuring calcium currents in plant cation channels. Plant J 58:175–182
Homann U, Thiel G (1994) Cl− and K+ channel currents during the action-potential in chara: simultaneous recording of membrane voltage and patch currents. J Membr Biol 141:297–309
Janicka-Russak M, Kabala K, Burzynski M, Klobus G (2008) Response of plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase to heavy metal stress in Cucumis sativus roots. J Exp Bot 59:3721–3728
Kisnieriene V, Sakalauskas V, Pleskaciauskas A, Yurin V, Ruksenas O (2009) The combined effect of Cd2+ and ACh on action potentials of Nitellopsis obtusa cells. Cent Eur J Biol 4:343–350
Kisnieriene V, Ditchenko TI, Kudryashov AP, Sakalauskas V, Yurin VM, Ruksenas O (2012) The effect of acetylcholine on Characeae K+ channels at rest and during action potential generation. Cent Eur J Biol 7:1066–1075
Kisnieriene V, Burneika J, Lapeikaite I, Sevriukova O, Daktariunas A (2014) Investigation of membrane potential changes in Nitellopsis obtusa cells induced by blue and red light stimulation. Biologija 60:71–78
Kurtyka R, Burdach Z, Karcz W (2011) Effect of cadmium and lead on the membrane potential and photoelectric reaction of Nitellopsis obtusa cells. Gen Physiol Biophys 30:52–58
Llamas A, Sanz A (2008) Organ-distinctive changes in respiration rates of rice plants under nickel stress. Plant Growth Regul 54:63–69
Lunevsky VZ, Zherelova OM, Vostrikov IY, Berestovsky GN (1983) Excitation of characeae cell-membranes as a result of activation of calcium and chloride channels. J Membr Biol 72:43–58
Manusadzianas L, Maksimov G, Darginaviciene J, Jurkoniene S, Sadauskas K, Vitkus R (2002) Response of the charophyte Nitellopsis obtusa to heavy metals at the cellular, cell membrane, and enzyme levels. Environ Toxicol 17:275–283
Mimura T (1995) Physiological-characteristics and regulation mechanisms of the H+ pumps in the plasma-membrane and tonoplast of characean cells. J Plant Res 108:249–256
Moran N, Fox D, Satter RL (1990) Interaction of the depolarization-activated K+ channel of Samanea–Saman with inorganic-ions: a patch-clamp study. Plant Physiol 94:424–431
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
Nishida S, Aisu A, Mizuno T (2012) Induction of IRT1 by the nickel-induced iron-deficient response in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 7:329–331
Opritov VA, Pyatygin SS, Vodeneev VA (2002) Direct coupling of action potential generation in cells of a higher plant (Cucurbita pepo) with the operation of an electrogenic pump. Russ J Plant Physiol 49:142–147
Polacco JC, Mazzafera P, Tezotto T (2013) Opinion: nickel and urease in plants—still many knowledge gaps. Plant Sci 199200:79–90
Pyatygin SS, Opritov VA, Vodeneev VA (2008) Signaling role of action potential in higher plants. Russ J Plant Physiol 55:285–291
Rubio MI, Escrig I, Mart_Łnez-Cortina C, Lopez-Benet FJ, Sanz A (1994) Cadmium and nickel accumulation in rice plants. Effects on mineral nutrition and possible interactions of abscisic and gibberellic acids. Plant Growth Regul 14:151–157
Sanz A, Llamas A, Ullrich CI (2009) Distinctive phytotoxic effects of Cd and Ni on membrane functionality. Plant Signal Behav 4:980–982
Seregin IV, Kozhevnikova AD (2006) Physiological role of nickel and its toxic effects on higher plants. Russ J Plant Physiol 53:257–277
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2009) The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci 14:43–50
Shepherd V, Beilby M, Shimmen T (2002) Mechanosensory ion channels in charophyte cells: the response to touch and salinity stress. Eur Biophys J 31:341–355
Shimmen T, Mimura T, Kikuyama M, Tazawa M (1994) Characean cells as a tool for studying electrophysiological characteristics of plant-cells. Cell Struct Funct 19:263–278
Sreekanth TVM, Nagajyothi PC, Lee KD, Prasad TNVK (2013) Occurrence, physiological responses and toxicity of nickel in plants. J Environ Sci Technol 10:1129–1140
Sukhov V, Nerush V, Lova LO, Vodeneev V (2011) Simulation of action potential propagation in plants. J Theor Biol 291:47–55
Thakur S, Sharma S (2015) Characterization of seed germination, seedling growth, and associated metabolic responses of Brassica juncea L. cultivars to elevated nickel concentrations. Protoplasma. doi:10.1007/s00709-015-0835-0
Thiel G, Homann U, Plieth C (1997) Ion channel activity during the action potential in Chara: new insights with new techniques. J Exp Bot 48:609–622
Trebacz K, Simonis W, Schonknecht G (1997) Effects of anion channel inhibitors on light-induced potential changes in the liverwort Conocephalum conicum. Plant Cell Physiol 38:550–557
Tsutsui I, Ta Ohkawa, Nagai R, Kishimoto U (1987) Role of calcium ion in the excitability and electrogenic pump activity of theChara corallina membrane: I. Effects of La3+, verapamil, EGTA, W-7, and TFP on the action potential. J Membrain Biol 96:65–73
Van Assche F, Clijsters H (1990) Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ 13:195–206
Volkov AG, Ranatunga DR (2006) Plants as environmental biosensors. Plant Signal Behav 1:105–115
Woolhouse HW (1983) Toxicity and tolerance in the responses of plants to metals. In: Lange OL, Nobel PS, Osmond CB, Ziegler H (eds) Physiological plant ecology III, Ed 12/C. Springer, Berlin, pp 245–300
Yusuf M, Fariduddin Q, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2011) Nickel: an overview of uptake, essentiality and toxicity in plants. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:1–17
Zamponi GW, Bourinet E, Snutch TP (1996) Nickel block of a family of neuronal calcium channels: subtype- and subunit-dependent action at multiple sites. J Membr Biol 151:77–90
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Vidmantas Sakalauskas (Vilnius University) for technical support and Prof. Shanti S. Sharma (Department of Biosciences, Himachal Pradesh University, Shimla, India) for helpful discussion and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kisnieriene, V., Lapeikaite, I., Sevriukova, O. et al. The effects of Ni2+ on electrical signaling of Nitellopsis obtusa cells. J Plant Res 129, 551–558 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-016-0794-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-016-0794-3