Abstract
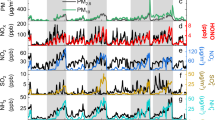
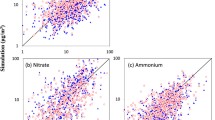
Heterogeneous reactions involving aerosol water, i.e., haze chemistry, are responsible for high aerosol concentrations observed during severe haze events in Chinese megacities. Attempts were made to incorporate these reactions into air quality models, by using reactive uptake coefficients for gaseous precursors of secondary aerosols. Nonetheless, the revised models were most frequently evaluated using bulk particle concentrations, mainly due to the lack of observational constraints on aerosol compositions. Here, we tested such a revised model using data from primary and secondary aerosol components measured during the winter of 2019‒2020 in Harbin, an unexplored megacity located in the severe cold climate region in Northeast China. We studied reasons for discrepancies between observed and modeled results. Our findings show that despite the reasonable consistency between the observed and simulated aerosol concentrations, large discrepancies occur for sulfate and secondary-organic-carbon under humid conditions, e.g., with average overprediction of ~ 20 μg/m3 for sulfate, and underprediction of ~ 10 μgC/m3 for secondary-organic-carbon. These discrepancies point to improper simulation of heterogeneous reactions. Therefore, we suggest that previous modeling has exaggerated the role of sulfate in haze formation over Chinese megacities.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data are available from the corresponding author upon request (jiumengliu@hit.edu.cn).
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Cheng YF, Zheng GJ, Wei C et al (2016) Reactive nitrogen chemistry in aerosol water as a source of sulfate during haze events in China. Sci Adv 2:e1601530. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1601530
Elser M, Huang RJ, Wolf R et al (2016) New insights into PM2.5 chemical composition and sources in two major cities in China during extreme haze events using aerosol mass spectrometry. Atmos Chem Phys 16:3207–3225. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-3207-2016
Hu JL, Chen JJ, Ying Q et al (2016) One-year simulation of ozone and particulate matter in China using WRF/CMAQ modeling system. Atmos Chem Phys 16:10333–10350. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-10333-2016
Kuang Y, He Y, Xu WY et al (2020) Photochemical aqueous-phase reactions induce rapid daytime formation of oxygenated organic aerosol on the North China Plain. Environ Sci Technol 54:3849–3860. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06836
Liu JM, Wang PF, Zhang HL et al (2020) Integration of field observation and air quality modeling to characterize Beijing aerosol in different seasons. Chemosphere 242:125195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125195
Liu TY, Chan AWH, Abbatt JPD (2021) Multiphase oxidation of sulfur dioxide in aerosol particles: implications for sulfate formation in polluted environments. Environ Sci Technol 8:4227–4242. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c06496
Su H, Cheng YF, Pöschl U (2020) New multiphase chemical processes influencing atmospheric aerosols, air quality, and climate in the Anthropocene. Acc Chem Res 53:2034–2043. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00246
Wang YX, Zhang QQ, Jiang JK et al (2014) Enhanced sulfate formation during China’s severe winter haze episode in January 2013 missing from current models. J Geophys Res Atmos 119:10425–10440. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JD021426
Wang JF, Li JY, Ye JH et al (2020a) Fast sulfate formation from oxidation of SO2 by NO2 and HONO observed in Beijing haze. Nat Commun 11:2844. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16683-x
Wang PF, Chen KY, Zhu SQ et al (2020b) Severe air pollution events not avoided by reduced anthropogenic activities during COVID-19 outbreak. Resour Conserv Recy 158:104814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.104814
Wang JF, Ye JH, Zhang Q et al (2021a) Aqueous production of secondary organic aerosol from fossil-fuel emissions in winter Beijing haze. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118:e2022179118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2022179118
Wang WG, Liu MY, Wang TT et al (2021b) Sulfate formation is dominated by manganese-catalyzed oxidation of SO2 on aerosol surfaces during haze events. Nat Commun 12:1993. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22091-6
Ying Q, Li JY, Kota SH (2015) Significant contributions of isoprene to summertime secondary organic aerosol in eastern United States. Environ Sci Technol 49:7834–7842. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02514
Zhang Q, Zheng YX, Tong D et al (2019) Drivers of improved PM2.5 air quality in China from 2013 to 2017. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:24463–24469. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1907956116
Zheng B, Zhang Q, Zhang Y et al (2015a) Heterogeneous chemistry: a mechanism missing in current models to explain secondary inorganic aerosol formation during the January 2013 haze episode in North China. Atmos Chem Phys 15:2031–2049. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-2031-2015
Zheng GJ, Duan FK, Su H et al (2015b) Exploring the severe winter haze in Beijing: the impact of synoptic weather, regional transport and heterogeneous reactions. Atmos Chem Phys 15:2969–2983. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-2969-2015
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Zhen-yu Du and Lin-lin Liang for their help in sample analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41805097), the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (YQ2019D004) and Heilongjiang Touyan Team.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YC contributed to conceptualization, methodology and writing—Original Draft; XC, SZ, SW and QY involved in investigation; JL, HZ, QZ and KH contributed to methodology, validation and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Cao, Xb., Liu, Jm. et al. Overestimated role of sulfate in haze formation over Chinese megacities due to improper simulation of heterogeneous reactions. Environ Chem Lett 20, 2745–2750 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01464-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01464-3