Abstract
Purpose
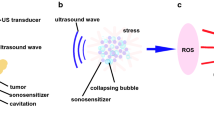
Although sanazole has been used as a hypoxic radiosensitizer, we recently reported on its ability to sensitize U937 cells to hyperthermia and X-irradiation under aerobic conditions, enhancing apoptotic cell death following the combined treatment. The current study was undertaken to evaluate the effect of sanazole as a sonosensitizer under previously studied acoustic conditions of different pulse repetition frequencies, using two cell lines representative of solid tumours and haematopoietic cancers.
Methods
Cells were treated with different doses of sanazole. Flow-cytometric analysis and DNA fragmentation assay were carried out at different times, and morphological features were also inspected. For ultrasound treatment, cells were pre-incubated with a non-cytotoxic dose of sanazole for 30 min before exposure. Evaluation of cell killing and a parallel examination of intracellular oxidative stress levels in both cell lines were performed using flow cytometry.
Results
Sanazole alone displayed selective cytotoxic effects towards solid tumour-derived cancer cells, resulting in complete cell death after 24 h of treatment, and enhanced the ultrasound-induced cell killing 6 h post-treatment. The enhancement seemed to be mediated by an additive increase in intracellular oxidative stress levels.
Conclusion
Sanazole seems to be an efficient cytotoxic agent for the treatment of solid tumours and a promising sonosensitizer under aerobic conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shibamoto Y, Sakano K, Kimura R, Nishidai T, Nishimoto S, Ono K, Kagiya T, Abe M. Radiosensitization in vitro and in vivo by 3-nitrotriazoles. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986;12:1063.
Dobrowsky W, Huigol NG, Jayatilake RS, Kizilbash NI, Okkan S, Kagiya TV, Tatsuzaki H. AK-2123 (Sanazol) as a radiation sensitizer in the treatment of stage III cancer cervix: initial results of an IAEA multicentre randomized trial. J Cancer Res Ther. 2005;1:75.
Dobrowsky W, Huigol NG, Jayatilake RS, Kizilbash NI, Okkan S, Kagiya VT, Tatsuzaki H. AK-2123 (Sanazol) as a radiation sensitizer in the treatment of stage III cervical cancer: results of an IAEA multicentre randomised trial. Radiother Oncol. 2007;82:24.
Ullal SD, Shenoy KK, Pai MR, Chowta MN, Adiga SM, Dinesh M, Kamath A, Kotian MS, Pai DK. Safety and radiosensitizing efficacy of sanazole (AK 2123) in oropharyngeal cancers: randomized controlled double blind clinical trial. Indian J Cancer. 2006;43:151.
Konovalova NP, Volkova LM, Tatyanenko LV, Kotelnikova RA, Yakushchenko TN, Kagiya TV. Inhibitory effect of radiosensitizer AK-2123 on experimental hepatic metastases and Ca2+ active transport. Neoplasma. 1997;44:361.
Konovalova NP, Diatchkovskaya RF, Volkova LM, Kagiya TV. Radiosensitizer AK-2123 as modulating agent in the chemotherapy of experimental metastases. Neoplasma. 1995;42:119.
Mitsuhashi N, Sakurai H, Takahashi T, Akimoto T, Higuchi K, Matsumoto H, Ebara T, Nozaki M, Niibe H. Does AK-2123 (Senazole) have sensitizing effects on radiation, cisplatin and hyperthermia under aerobic conditions in vitro? Anticancer Res. 1998;18:3463.
Sugie C, Shibamoto Y, Ito M, Ogino H, Suzuki H, Uto Y, Nagasawa H, Hori H. Reevaluation of the radiosensitizing effects of sanazole and nimorazole in vitro and in vivo. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 2005;46:453.
Feril LB Jr, Kondo T. Biological effects of low intensity ultrasound: the mechanism involved, and its implications on therapy and on biosafety of ultrasound. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 2004;45:479.
Yoshida T, Kondo T, Ogawa R, Feril LB Jr, Zhao QL, Watanabe A, Tsukada K. Combination of doxorubicin and low-intensity ultrasound causes a synergistic enhancement in cell killing and an additive enhancement in apoptosis induction in human lymphoma U937 cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008;61:559.
Kondo T, Yoshida T, Ogawa R, Hassan MA, Furusawa Y, Zhao QL, Watanabe A, Morii A, Feril LB Jr, Tachibana K, Kitagawa H, Tabuchi Y, Takasaki I, Shehata M, Kudo N, Tsukada K. Low-intensity ultrasound adjuvant therapy: enhancement of doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity and the acoustic mechanisms involved. J Med Ultrasonics. 2009;36:61.
Hassan MA, Campbell P, Kondo T. The role of Ca2+ in ultrasound-elicited bioeffects: progress, perspectives, and prospects. Drug Discov Today. 2010;15:892.
Honda H, Kondo T, Zhao QL, Feril LB Jr, Kitagawa H. Role of intracellular calcium ions and reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induced by ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2004;30:683.
Buldakov MA, Hassan MA, Zhao QL, Feril LB Jr, Kudo N, Kondo T, Litvyakov NV, Bolshakov MA, Rostov VV, Cherdyntseva NV, Riesz P. Influence of changing pulse repetition frequency on chemical and biological effects induced by low-intensity ultrasound in vitro. Ultrason Sonochem. 2009;16:392.
Hassan MA, Buldakov MA, Ogawa R, Zhao QL, Furusawa Y, Kudo N, Kondo T, Riesz P. Modulation control over ultrasound-mediated gene delivery: evaluating the importance of standing waves. J Control Release. 2010;141:70.
Feril LB Jr, Kondo T. Major factors involved in the inhibition of ultrasound-induced free radical production and cell killing by pre-sonication incubation or by high cell density. Ultrason Sonochem. 2005;12:353.
Furusawa Y, Zhao QL, Hassan MA, Tabuchi Y, Takasaki I, Wada S, Kondo T. Ultrasound-induced apoptosis in the presence of sonazoid and associated alterations in gene expression levels: a possible therapeutic application. Cancer Lett. 2010;288:107.
Wada S, Cui ZG, Kondo T, Zhao QL, Ogawa R, Shoji M, Arai T, Makino K, Furuta I. A hydrogen peroxide-generating agent, 6-formylpterin, enhances heat-induced apoptosis. Int J Hyperthermia. 2005;21:231.
Li M, Kondo T, Zhao QL, Li FJ, Tanabe K, Arai Y, Zhou ZC, Kasuya M. Apoptosis induced by cadmium in human lymphoma U937 cells through Ca2+-calpain and caspase-mitochondria-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:39702.
Yoshihisa Y, Honda A, Zhao QL, Makino T, Abe R, Matsui K, Shimizu H, Miyamoto Y, Kondo T, Shimizu T. Protective effects of platinum nanoparticles against UV-light-induced epidermal inflammation. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19:1000–6.
Li FJ, Kondo T, Zhao QL, Tanabe K, Ogawa R, Li M, Arai Y. Enhancement of hyperthermia-induced apoptosis by a free radical initiator, 2,2′-azobis (2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride, in human histiocytic lymphoma U937 cells. Free Radic Res. 2001;35:281.
Ahmed K, Zhao QL, Matsuya Y, Yu DY, Feril LB Jr, Nemoto H, Kondo T. Rapid and transient intracellular oxidative stress due to novel macrosphelides trigger apoptosis via Fas/caspase-8-dependent pathway in human lymphoma U937 cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2007;170:86.
Yu DY, Zhao QL, Wei ZL, Shehata M, Kondo T. Enhancement of hyperthermia-induced apoptosis by sanazole in human lymphoma U937 cells. Int J Hyperthermia. 2009;25:364.
Yu DY, Zhao QL, Wei ZL, Nomura T, Kashiwakura I, Kagiya TV, Kondo T. Enhancement of radiation-induced apoptosis of human lymphoma U937 cells by sanazole. Apoptosis. 2009;14:655.
Ohnuma T, Arkin H, Holland JF. Effects of cell density on drug-induced cell kill kinetics in vitro (inoculum effect). Br J Cancer. 1986;54:415.
Smrz D, Draberova L, Draber P. Non-apoptotic phosphatidylserine externalization induced by engagement of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:10487.
Yan B, Wang H, Peng Y, Hu Y, Wang H, Zhang X, Chen Q, Bedford JS, Dewhirst MW, Li CY. A unique role of the DNA fragmentation factor in maintaining genomic stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:1504.
Kim G, Lee YE, Xu H, Philbert MA, Kopelman R. Nanoencapsulation method for high selectivity sensing of hydrogen peroxide inside live cells. Anal Chem. 2010;82:2165.
Miller DL, Dou C. Induction of apoptosis in sonoporation and ultrasonic gene transfer. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009;35:144.
Imamura M, Edgren M, Murata T, Imamura M, Nagata K, Isoda H, Akagi K, Revesz L, Tanaka Y. Radiosensitization with a 3-nitrotriazole (AK-2123). Int J Oncol. 1995;6:841.
Ingber DE. Cellular mechanotransduction: putting all the pieces together again. FASEB J. 2006;20:811.
Rojkind M, Dominguez-Rosales JA, Nieto N, Greenwel P. Role of hydrogen peroxide and oxidative stress in healing responses. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002;59:1872.
Kapoor S, Mathew R, Huilgol NG, Kagiya TV, Nair CK. Redox reactions of sanazole (AK-2123) in aqueous solutions: a pulse radiolysis study. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 2000;41:355.
Sukhanov GT, Sukhanova AG, Ilyasova YV. Reactions of 3-nitro-1,2,4-triazoles with alkylating agents. 3. Alkylation of a neutral heterocycle by diethyl sulfate. Chem Heterocycl Comp. 2006;42:1197.
Alam A, Rapthap CC, Singha LI, Sharan RN, Singh V. Radiomodulatory effect of liposome encapsulated AK-2123 on tumor in mice exposed to hepatocarcinogen. Mol Cell Biochem. 2005;271:139.
Acknowledgments
Part of this work was supported by the Research and Development Committee Program of the Japan Society of Ultrasonics in Medicine, and by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (No. 20590765) (to MM) from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, M.A., Furusawa, Y., Zhao, QL. et al. Differential cytotoxicity and sonosensitization by sanazole: effect of cell type and acoustic parameters. J Med Ultrasonics 38, 65–72 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-010-0295-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-010-0295-2