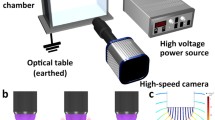
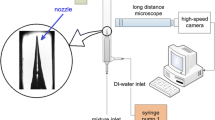
Abstract
The possibility of controlled droplet motion (droplet addressing) mediated by DC electric field in aqueous two-phase systems (ATPS) is here reported for the first time. Three ATPS of polyethylene glycol (PEG)/salt type, namely PEG/phosphate, PEG/sulphate, and PEG/carbonate, were selected for this study. We observed fast motion of salty droplets dispersed in PEG continuous phase induced by electric field of relative low strength. Hence, three fluidic systems with separated electrode chambers for the evaluation of electrophoretic mobilities and for addressing experiments were fabricated. Electrophoretic mobilities of salty droplets always exceeded the value of \(1\times 10^{-7}\, \hbox {m}^2\hbox {V}^{-1}\hbox {s}^{-1}\), which is about by one magnitude higher value than those typically measured in water–oil droplet systems. The electrophoretic mobilities in systems with free surface are the same or even smaller than in closed microfluidic structures, which is accounted mainly to the fact that a significant part of salty droplets is exposed to air and does not contribute to droplet forcing. Series of addressing and merging experiments in a microfluidic chip shows that DC electric field can be used as a powerful tool for smart manipulation of droplets in microfluidic systems with PEG/salt ATPS.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn B, Lee K, Panchapakesan R, Oh KW (2011) On-demand electrostatic droplet charging and sorting. Biomicrofluidics 5(2):024113. doi:10.1063/1.3604393
Asenjo J, Mistry S, Andrews B, Merchuk J (2002) Phase separation rates of aqueous two-phase systems: correlation with system properties. Biotechnol Bioeng 79(2):217–223. doi:10.1002/bit.10273
Banik R, Santhiagu A, Kanari B, Sabarinath C, Upadhyay S (2003) Technological aspects of extractive fermentation using aqueous two-phase systems. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 19(4):337–348. doi:10.1023/A:1023940809095
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2001) Electrochemical methods: fundemantals and applications. Wiley, Hoboken
Beranek P, Flittner R, Hrobar V, Ethgen P, Pribyl M (2014) Oscillatory motion of water droplets in kerosene above co-planar electrodes in microfluidic chips. AIP Adv 4(6):067103. doi:10.1063/1.4881675
Brooks D, Sharp K, Bamberger S, Tamblyn C, Seaman G, Walter H (1984) Electrostatic and electrokinetic potentials in 2 polymer aqueous phase systems. J Colloid Interface Sci 102(1):1–13. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(84)90195-4
Campos CDM, Park JK, Neuzil P, da Silva JAF, Manz A (2014) Membrane-free electroextraction using an aqueous two-phase system. RSC Adv 4(90):49485–49490. doi:10.1039/c4ra09246e
Cao J, Koehler JM (2015) Droplet-based microfluidics for microtoxicological studies. Eng Life Sci 15(3, SI):306–317. doi:10.1002/elsc.201400074
Choi YH, Song YS, Kim DH (2010) Droplet-based microextraction in the aqueous two-phase system. J Chromatogr A 1217(24):3723–3728. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2010.04.015
Deen W (1998) Analysis of transport phenomena. Oxford University Press, New York
Frampton JP, Lai D, Sriram H, Takayama S (2011) Precisely targeted delivery of cells and biomolecules within microchannels using aqueous two-phase systems. Biomed Microdevices 13(6):1043–1051. doi:10.1007/s10544-011-9574-y
Grilo AL, Raquel Aires-Barros M, Azevedo AM (2016) Partitioning in aqueous two-phase systems: fundamentals. Appl Trends Sep Purif Rev 45(1):68–80. doi:10.1080/15422119.2014.983128
Hahn T, Hardt S (2011) Concentration and size separation of DNA samples at liquid–liquid interfaces. Anal Chem 83(14):5476–5479. doi:10.1021/ac201228v
Hardt S, Hahn T (2012) Microfluidics with aqueous two-phase systems. Lab Chip 12(3):434–442. doi:10.1039/c1lc20569b
Hase M, Watanabe SN, Yoshikawa K (2006) Rhythmic motion of a droplet under a dc electric field. Phys Rev E 74:046301. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.74.046301
Huang Y, Meng T, Guo T, Li W, Yan W, Li X, Wang S, Tong Z (2014) Aqueous two-phase extraction for bovine serum albumin (BSA) with co-laminar flow in a simple coaxial capillary microfluidic device. Microfluid Nanofluid 16(3):483–491. doi:10.1007/s10404-013-1245-2
Huh YS, Jeong CM, Chang HN, Lee SY, Hong WH, Park TJ (2010) Rapid separation of bacteriorhodopsin using a laminar-flow extraction system in a microfluidic device. Biomicrofluidics 4(1):014103. doi:10.1063/1.3298608
Im DJ, Noh J, Moon D, Kang IS (2011) Electrophoresis of a charged droplet in a dielectric liquid for droplet actuation. Anal Chem 83(13):5168–5174. doi:10.1021/ac200248x
Jacinto MJ, Soares RRG, Azevedo AM, Chu V, Tover A, Conde JP, Aires-Barros MR (2015) Optimization and miniaturization of aqueous two phase systems for the purification of recombinant human immunodeficiency virus-like particles from a CHO cell supernatant. Sep Purif Technol 154:27–35. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2015.09.006
Jung YM, Oh HC, Kang IS (2008) Electrical charging of a conducting water droplet in a dielectric fluid on the electrode surface. J Colloid Interface Sci 322(2):617–623. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2008.04.019
Link DR, Grasland-Mongrain E, Duri A, Sarrazin F, Cheng ZD, Cristobal G, Marquez M, Weitz DA (2006) Electric control of droplets in microfluidic devices. Angew Chem Int Edit 45(16):2556–2560. doi:10.1002/anie.200503540
Madhusudhan MC, Chethana S, Raghavarao KSMS (2011) Electrokinetic demixing of polymer/salt systems containing biomolecules. Sep Sci Technol 46(5):727–733. doi:10.1080/01496395.2010.529098
Matsumoto S (1998) Proteins and sugars in water/oil/water emulsions. In: Ohshima H, Furusawa K (eds) Electrical phenomena at interfaces, vol 32. Marcel Dekker, New York, p 600
Munchow G, Hardt S, Kutter JP, Drese KS (2007) Electrophoretic partitioning of proteins in two-phase microflows. Lab Chip 7(1):98–102. doi:10.1039/b612669n
Munchow G, Schoenfeld F, Hardt S, Graf K (2008) Protein diffusion across the interface in aqueous two-phase systems. Langmuir 24(16):8547–8553. doi:10.1021/la800956j
Nagaraj N, Chethana S, Raghavarao K (2005) Electrokinetic demixing of aqueous two-phase polymer/salt systems. Electrophoresis 26(1):10–17. doi:10.1002/elps.200406122
Novak U, Lakner M, Plazl I, Znidarsic-Plazl P (2015) Experimental studies and modeling of alpha-amylase aqueous two-phase extraction within a microfluidic device. Microfluid Nanofluid 19(1):75–83. doi:10.1007/s10404-015-1550-z
Ohshima H (1998a) Electric double layer. In: Ohshima H, Furusawa K (eds) Electrical phenomena at interfaces, vol 1. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–18
Ohshima H (1998b) Interfacial electrokinetic phenomena. In: Ohshima H, Furusawa K (eds) Electrical phenomena at interfaces, vol 2. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 38–39
Pfennig A, Schwerin A, Gaube J (1998) Consistent view of electrolytes in aqueous two-phase systems. J Chromatogr B 711(1–2):45–52. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(97)00593-8
Powell BD, Alexander AE (1952) The mobility of oil droplets, interfacial tension measurements, and gegen ion adsorption in soap solutions. Can J Chem 30(12):1044–1055. doi:10.1139/v52-123
Raghavarao K, Stewart R, Rudge S, Todd P (1998) Electrokinetic demixing of aqueous two-phase systems. 3. Drop electrophoretic mobilities and demixing rates. Biotechnol Prog 14(6):922–930. doi:10.1021/bp9800889
Rao K, Stewart R, Todd P (1991) Electrokinetic demixing of 2-phase aqueous polymer systems.2. Separation rates of polyethylene-glycol maltodextrin mixtures. Sep Sci Technol 26(2):257–267. doi:10.1080/01496399108050470
Seemann R, Brinkmann M, Pfohl T, Herminghaus S (2012) Droplet based microfluidics. Rep Prog Phys 75(1):016601. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/75/1/016601
Silva DFC, Azevedo AM, Fernandes P, Chu V, Conde JP, Aires-Barros MR (2012) Design of a microfluidic platform for monoclonal antibody extraction using an aqueous two-phase system. J Chromatogr A 1249:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.05.089
Slouka Z, Pribyl M, Snita D, Postler T (2007) Transient behavior of an electrolytic diode. Phys Chem Chem Phys 9(39):5374–5381. doi:10.1039/b707197c
Soares RRG, Novo P, Azevedo AM, Fernandes P, Aires-Barros MR, Chu V, Conde JP (2014) On-chip sample preparation and analyte quantification using a microfluidic aqueous two-phase extraction coupled with an immunoassay. Lab Chip 14(21):4284–4294. doi:10.1039/c4lc00695j
Song YS, Choi YH, Kim DH (2007) Microextraction in a tetrabutylammonium bromide/ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase system and electrohydrodynamic generation of a micro-droplet. J Chromatogr A 1162(2):180–186. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.06.032
Svoboda M, Slouka Z, Schrott W, Cervenka P, Pribyl M, Snita D (2010) Fabrication of plastic microchips with gold microelectrodes using techniques of sacrificed substrate and thermally activated solvent bonding. Microelectron Eng 87(5–8):1590–1593. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2009.11.010
Taylor AJ, Wood FW (1957) The electrophoresis of hydrocarbon droplets in dilute solutions of electrolytes. Trans Faraday Soc 53:523–529. doi:10.1039/TF9575300523
Teh SY, Lin R, Hung LH, Lee AP (2008) Droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 8:198–220. doi:10.1039/B715524G
Tucek J, Beranek P, Vobecka L, Slouka Z, Pribyl M (2016) Electric field driven addressing of oil-in-water droplets in the presence of gradients of ionic and nonionic surfactants. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 52(5):4337–4344. doi:10.1109/TIA.2016.2563391
Wei D, Zhu J, Cao X (2002) Enzymatic synthesis of cephalexin in aqueous two-phase systems. Biochem Eng J 11(2–3):95–99. doi:10.1016/S1369-703X(02)00032-3
Wu Y, Zhu Z, Mei L (1996) Interfacial tension of poly(ethylene glycol) plus salt plus water systems. J Chem Eng Data 41(5):1032–1035. doi:10.1021/je960044g
Yang CG, Xu ZR, Wang JH (2010) Manipulation of droplets in microfluidic systems. Trac Trends Anal Chem 29(2):141–157. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2009.11.002
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Czech Science Foundation (grant no. 14-01781S) and Ministry of Education Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic: CENTEM PLUS (LO1402) for financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vobecká, L., Khafizova, E., Stragier, T. et al. Electric field driven addressing of ATPS droplets in microfluidic chips. Microfluid Nanofluid 21, 51 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1891-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1891-x