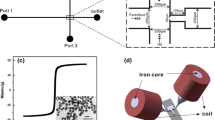
Abstract
A new ferrofluidic droplet generator is demonstrated using an electropermanent magnet to change the viscosity of the ferrofluid oil phase in a flow-focusing junction, which enables control of the aqueous droplet size. Electropermanent magnets are capable of fast switching (< 100 \(\upmu\)s) and have magnetic field strengths comparable to those of permanent magnets. When switched on, the magnetoviscous effect increases the viscosity of the ferrofluid, thus increasing the channel’s fluidic resistance, slowing the flow rate of the oil-based phase and changing the droplet diameter. We have demonstrated on-demand droplet size modulation as large as 44% at speeds fast enough to modulate the size of a single droplet in a stream. Due to compliance in the supply tubing and Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microfluidic channels, the change in droplet size relaxes with a time scale of seconds. An application of droplet size modulation was demonstrated by integrating a passive size-based magnetic droplet sorting stage.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Ahn K, Kerbage C, Hunt TP, Westervelt RM, Link DR, Weitz DA (2006) Dielectrophoretic manipulation of drops for high-speed microfluidic sorting devices. Appl Phys Lett 88(2):024104
Anna SL, Bontoux N, Stone HA (2003) Formation of dispersions using flow focusing in microchannels. Appl Phys Lett 82(3):364–366
Baroud CN, Delville JP, Gallaire F, Wunenburger R (2007) Thermocapillary valve for droplet production and sorting. Phys Rev E 75(4):5
Bremond N, Thiam AR, Bibette J (2008) Decompressing emulsion droplets favors coalescence. Appl Phys Lett 100(2):4
Bringer MR, Gerdts CJ, Song H, Tice JD, Ismagilov RF (2004) Microfluidic systems for chemical kinetics that rely on chaotic mixing in droplets. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser A Math Phys Eng Sci 362(1818):1087–1104
Cheung YN, Qiu HH (2011) Characterization of acoustic droplet formation in a microfluidic flow-focusing device. Phys Rev E 84(6):10
Chong ZZ, Tan SH, Ganan-Calvo AM, Tor SB, Loh NH, Nguyen NT (2016) Active droplet generation in microfluidics. Lab Chip 16(1):35–58
Chou WL, Lee PY, Yang CL, Huang WY, Lin YS (2015) Recent advances in applications of droplet microfluidics. Micromachines 6(9):1249–1271
Duffy DC, Mcdonald JC, Schueller OJA, Whitesides GM (1998) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal Chem 70(23):4974–4984. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac980656z
Fair RB, Khlystov A, Tailor TD, Ivanov V, Evans RD, Srinivasan V, Pamula VK, Pollack MG, Griffin PB, Zhou J (2007) Chemical and biological applications of digital microfluidic devices. Design Test Comput IEEE 24(1):10–24
Gu H, Malloggi F, Vanapalli SA, Mugele F (2008) Electrowetting-enhanced microfluidic device for drop generation. Appl Phys Lett 93(18):3
He P, Kim H, Luo DW, Marquez M, Cheng ZD (2010) Low-frequency ac electro-flow-focusing microfluidic emulsification. Appl Phys Lett 96(17):3
Holtze C, Rowat AC, Agresti JJ, Hutchison JB, Angilè FE, Schmitz CHJ, Köster S, Duan H, Humphry KJ, Scanga RA, Johnson JS, Pisignano D, Weitz DA (2008) Biocompatible surfactants for water-in-fluorocarbon emulsions. Lab Chip 8(10):1632
Ilg P, Hess S (2003) Nonequilibrium dynamics and magnetoviscosity of moderately concentrated magnetic liquids: a dynamic mean-field study. J Phys Sci 58(11):589–600
Katsikis G, Cybulski J, Prakash M (2015) Synchronous universal droplet logic and control. Nat Phys 11(7):588–596
Kim J, Won J, Song S (2014) Dual-mode on-demand droplet routing in multiple microchannels using a magnetic fluid as carrier phase. Biomicrofluidics 8(5):054105
Knaian AN (2010) Electropermanent magnetic connectors and actuators: devices and their application in programmable matter. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Lee CY, Lin YH, Lee GB (2009) A droplet-based microfluidic system capable of droplet formation and manipulation. Microfluid Nanofluidics 6(5):599–610
Link DR, Anna SL, Weitz DA, Stone HA (2004) Geometrically mediated breakup of drops in microfluidic devices. Phys Rev Lett 92(5):4
Link DR, Grasland-Mongrain E, Duri A, Sarrazin F, Cheng ZD, Cristobal G, Marquez M, Weitz DA (2006) Electric control of droplets in microfluidic devices. Angewandte Chemie Int Ed 45(16):2556–2560
Liu J, Tan SH, Yap YF, Ng MY, Nguyen NT (2011) Numerical and experimental investigations of the formation process of ferrofluid droplets. Microfluid Nanofluidics 11(2):177–187
Martsenyuk MA, Raikher YL, Shliomis MI (1974) On the kinetics of magnetization of suspension of ferromagnetic particles. Sov Phys JETP 38(2):413–416
Nguyen NT, Beyzavi A, Ng KM, Huang X (2007) Kinematics and deformation of ferrofluid droplets under magnetic actuation. Microfluid Nanofluidics 3(5):571–579
Odenbach S (2009) Colloidal magnetic fluids: basics, development and application of ferrofluids, vol 763. Lecture notes in physics. Springer, Berlin
Odenbach S, Thurm S (2002) Magnetoviscous Effects in Ferrofluids. In: Odenbach S (ed) Ferrofluids. Lecture Notes in Physics, vol 594. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45646-5_10
Padovani JI, Jeffrey SS, Howe RT (2016) Electropermanent magnet actuation for droplet ferromicrofluidics. Technology 4(2):110–119
Padovani-Blanco JI (2016) Electromagnetic actuation for ferrofluid-based droplet microfluidics. Ph.D. thesis, Stanford University
Rosensweig RE (1985) Ferrohydrodynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Schmid L, Franke T (2013) Saw-controlled drop size for flow focusing. Lab Chip 13(9):1691
Schmid L, Franke T (2014) Acoustic modulation of droplet size in a t-junction. Appl Phys Lett 104(13):133501
Schneider T, Kreutz J, Chiu DT (2013) The potential impact of droplet microfluidics in biology. Anal Chem 85:3476–3482
Seemann R, Brinkmann M, Pfohl T, Herminghaus S (2012) Droplet based microfluidics. Rep Prog Phys 75(1):016601
Simon MG, Lee AP (2012) Microfluidic droplet manipulations and their applications, vol 2. Springer Science and Business Media, Berlin, pp 23–50
Casadevall i Solvas X, deMello A (2011) Droplet microfluidics: recent developments and future applications. Chem Commun 47:1936–1942
Tan SH, Nguyen NT, Yobas L, Kang TG (2010) Formation and manipulation of ferrofluid droplets at a microfluidict-junction. J Micromech Microeng 20(4):045004
Teh SY, Lin R, Hung LH, Lee AP (2008) Droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 8(2):198
Theberge AB, Courtois F, Schaerli Y, Fischlechner M, Abell C, Hollfelder F, Huck WT (2010) Microdroplets in microfluidics: an evolving platform for discoveries in chemistry and biology. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49(34):5846–68
Ward T, Faivre M, Abkarian M, Stone HA (2005) Microfluidic flow focusing: drop size and scaling in pressure versus flow-rate-driven pumping. Electrophoresis 26(19):3716–3724. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200500173
Wu YN, Fu TT, Ma YG, Li HZ (2013) Ferrofluid droplet formation and breakup dynamics in a microfluidic flow-focusing device. Soft Matter 9(41):9792–9798
Yan Q, Xuan S, Ruan X, Wu J, Gong X (2015) Magnetically controllable generation of ferrofluid droplets. Microfluid Nanofluidics 19(6):1377–1384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1652-7
Zhu P, Wang L (2017) Passive and active droplet generation with microfluidics: a review. Lab Chip 17(1):34–75. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6LC01018K
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Karlheinz Merkle for the wire electro-discharge machining of the EPM pole pieces. The microfabrication was performed in the Stanford Nanofabrication Facility, supported by the National Science Foundation under award ECS-1542152.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Code availability
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was supported in part by NIH-P01HG000205 (RTH, JIP) and NIH-R21CA177447 (SSJ).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Padovani, J.I., Ibrahim, A.M., Jeffrey, S.S. et al. Electropermanent magnet-driven droplet size modulation for two-phase ferromicrofluidics. Microfluid Nanofluid 24, 93 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-020-02398-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-020-02398-4