Abstract
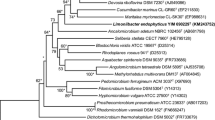
A white bacterial strain, designated EGI 650022T, was isolated from the roots of Salsola affinis C. A. Mey, collected from Urumqi City, Xinjiang, north-western China. The strain was found to be aerobic, Gram-stain positive, oxidase-positive and catalase-positive. Cells were non-motile and irregular rods. Growth occurred at NaCl concentrations between 0 and 7 % (w/v), temperatures between 5 and 45 °C, and pH 6.0–9.0. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequence indicated that strain EGI 650022T belongs to a clade with the genera Okibacterium and Plantibacter in the family Microbacteriaceae. The novel strain EGI 650022T showed highest levels of 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity with members of the genera Okibacterium and Plantibacter (97.2–98.0 %). The cell-wall peptidoglycan contained glutamate, homoserine, glycine, alanine and lysine. The predominant menaquinones (MKs) were MK-11, MK-12 and MK-12 (H4). The polar lipid pattern comprised phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, two unknown glycolipids and two unknown phospholipids. The major fatty acids were anteiso-C15:0 and anteiso-C17:0. The DNA G+C content was 66.0 mol%. The DNA–DNA relatedness values of strain EGI 650022T with Okibacterium fritillariae DSM 12584T, Plantibacter flavus DSM 14012T and Plantibacter auratus DSM 19586T were 39.7, 19.7 and 22.0 %. Based on phylogenetic, phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and DNA–DNA hybridization data, strain EGI 650022T is considered to represent a novel species of the genus Okibacterium, for which the name Okibacterium endophyticum sp. nov. is proposed; the type strain is EGI 650022T (=JCM 30086T = KCTC 29492T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behrendt U, Ulrich A, Schumann P, Naumann D, Suzuki K-l (2002) Diversity of grass-associated Microbacteriaceae isolated from the phyllosphere and litter layer after mulching the sward; polyphasic characterization of Subtercola pratensis sp. nov., Curtobacterium herbarum sp. nov. and Plantibacter flavus gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1441–1454
Christensen H, Angen O, Mutters R, Olsen JE, Bisgaard M (2000) DNA–DNA hybridization determined in micro-wells using covalent attachment of DNA. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1095–1102
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and Corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230
Evtushenko LL, Dorofeeva LV, Krausova VL, Gavrish EY, Yashina SG, Takeuchi M (2002) Okibacterium fritillariae gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel genus of the family Microbacteriaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:987–993
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid–deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in micro-dilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Gonzalez C, Gutierrez C, Ramirez C (1978) Halobacterium vallismortis sp. nov., an amylolytic and carbohydrate-metabolizing, extremely halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol 24:710–715
Goodfellow M (1986) Genus Rhodococcus Zopf 1891, 28 AL. In: Sneath PHA, Mair NS, Sharpe NE, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 2. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1472–1481
Kelly KL (1964) Color-name charts illustrated with centroid colors. Inter-Society Color Council-National Bureau of Standards, Chicago (Published in US)
Kim SJ, Lee SS (2011) Amnibacterium kyonggiense gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Microbacteriaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:155–159
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Komagata K, Suzuki K-I (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. In: Colwell RR, Grigorova R (eds) Methods in microbiology. Academic Press, Orlando
Kroppenstedt RM (1982) Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase (RP18) and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases. J Liq Chromatogr 5:2359–2387
Lee KC, Kim KK, Eom MK, Kim MJ, Lee JS (2001) Fontibacillus panacisegetis sp. nov., isolated from soil of a ginseng field. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:369–374
Li WJ, Xu P, Schumann P, Zhang YQ, Pukall R, Xu LH, Stackebrandt E, Jiang CL (2007) Georgenia ruanii sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from forest soil in Yunnan (China) and emended description of the genus Georgenia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1424–1428
Lin YC, Yokota A (2006) Plantibacter auratus sp. nov., in the family Microbacteriaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2337–2339
MacFaddin JF (1980) Biochemical tests for identification of medical bacteria, 2nd edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin DE, Alshamaony L, Goodfellow M (1975) Differentiation of Mycobacterium, Nocardia, and related taxa by thin-layer chromatographic analysis of whole-organism methanolysates. J Gen Microbiol 88:200–204
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal K, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Qin S, Wang HB, Chen HH, Zhang YQ, Jiang CL, Xu LH, Li WJ (2008) Glycomyces endophyticus sp. nov., an endophytic actinomycete isolated from the root of Carex baccans Nees. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2525–2528
Qin S, Li J, Chen HH, Zhao GZ, Zhu WY, Jiang CL, Xu LH, Li WJ (2009) Isolation, diversity, and antimicrobial activity of rare actinobacteria from medicinal plants of tropical rain forests in Xishuangbanna, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6176–6186
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic tree. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI technical note 101. Microbial ID, Inc., Newark
Shirling EB, Gottlieb D (1966) Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 16:313–340
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tang SK, Wang Y, Chen Y, Lou K, Cao LL, Xu LH, Li WJ (2009) Zhihengliuella alba sp. nov., and emended description of the genus Zhihengliuella. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2025–2033
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Xu P, Li WJ, Tang SK, Zhang YQ, Chen GZ, Chen HH, Xu LH, Jiang CL (2005) Naxibacter alkalitolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family ‘Oxalobacteraceae’ isolated from China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1149–1153
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Prof. Dr. Aharon Oren (The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel) for his kind help with the Latin etymology for the new species, Prof. Hans-Peter Klenk (DSMZ, Germany) and Prof. Takuji Kudo (JCM, Japan) for their kindly providing reference type strains. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81102806, 31200008 and 31400009). The Hundred Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, the High-level Talents Program of Xinjiang Autonomous Region and the West Light Foundation of Chinese Academy of Sciences. WNH and W-J L extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding the work through the research group project no. RGP-205. W-J Li was also supported by Guangdong Province Higher Vocational Colleges & Schools Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HF., Zhang, YG., Li, L. et al. Okibacterium endophyticum sp. nov., a novel endophytic actinobacterium isolated from roots of Salsola affinis C. A. Mey. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107, 835–843 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0376-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0376-0