Abstract
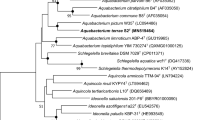
An aerobic, Gram-stain negative, short rod-shaped, asporogenous, non-motile bacterium designated strain NK8T was isolated from a chlorobenzoate contaminated soil in China. Strain NK8T was observed to grow optimally at pH 7.0, 30 °C and in the absence of NaCl in LB medium. The G + C content of the total DNA of strain NK8T was found to be 65.5 mol%. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain NK8T showed high similarity to that of Aquamicrobium aerolatum Sa14T (97.3%), followed by Aquamicrobium lusatiense S1T (96.7%) and Mesorhizobium sangali SCAU7T (96.6%). The DNA–DNA relatedness between strain NK8T and A. aerolatum Sa14T was 35.5 ± 0.9%. The major fatty acids of strain NK8T were determined to be C19:0 cyclo ω8c (45.6%), C18:1 ω7c (33.4%) and C16:0 (8.4%). The respiratory quinone was found to be ubiquinone Q-10. The major polyamine was found to be spermidine. The polar lipid profile include the major compounds phosphatidylcholine and diphosphatidylglycerol, and moderate amounts of phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylmonomethylethanolamine, aminolipid and phospholipid. Based on the differential biochemical and physiological characteristics, the geno-, chemo- and phenotypic characteristics, strain NK8T is proposed to represent a novel species of the genus Aquamicrobium, Aquamicrobium soli sp. nov. The type strain is NK8T (=KCTC 52165T=CCTCC AB2016045T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bambauer A, Rainey FA, Stackebrandt E, Winter J (1988) Characterization of Aquamicrobium defluvii gen. nov. sp. nov., a thiophene-2-carboxylate-metabo-lizing bacterium from activated sludge. Arch Microbiol 169:293–302
Bertani G (1951) Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 62:293–300
Beveridge TJ, Lawrence JR, Murray RGE (2007) Sampling and staining for light microscopy. In: Reddy CA, Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf GA, Schmidt TM, Snyder RL (eds) Methods for general and molecular 208 microbiology, 3rd edn. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 19–33
Busse HJ, Auling G (1988) Polyamine pattern as a chemotax-onomic marker within the Proteobacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 11:1–8
Busse HJ, Bunka S, Hensel A, Lubitz W (1997) Discrimination of members of the family Pasteurellaceae based on poly-amine patterns. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:698–708
Dadáková E, Křıžek M, Pelikánová T (2009) Determination of biogenic amines in foods using ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). Food Chem 116:365–370
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Fritsche K, Auling G, Andreesen JR, Lechner U (1999) Defluvibacter lusatiensis corrig, sp. nov. in validation of publication of new names and new combinations previously effectively published outside the IJSB, List no. 71. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:1325–1326
Gaunt MW, Turner SL, Rigottier-Gois L, Lloyd-Macgilp SA, Young JPW (2001) Phylogenies of atpD and recA support the small subunit rRNA-based classification of rhizobia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2037–2048
Gomori G (1955) Preparation of buffers for use in enzyme studies. In: Colowick SP, Kaplan NO (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 138–146
He L, Li W, Huang Y, Wang L, Liu Z, Lanoot B, Vancanneyt M, Swings J (2005) Streptomyces jietaisiensis sp. nov., isolated from soil in northern China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1939–1944
Hyun MJ, Kim JM, Jeon CO (2013) Aquamicrobium aestuarii sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from a tidal flat. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:4012–4017
Kämpfer P, Martin E, Lodders N, Jäckel U (2009) Transfer of Defluvibacter lusatiensis to the genus Aquamicrobium as Aquamicrobium lusatiense comb. nov. and description of Aquamicrobium aerolatum sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2468–2470
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes thatrepresent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kluge AG, Farris FS (1969) Quantitative phyletics and the evolution of anurans. Syst Zool 18:1–32
Kuykendall LD, Roy MA, O’Neill JJ, Devine TE (1988) Fatty acids, antibiotic resistance, and deoxyribonucleic acid homology groups of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:358–361
Lane DL (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt ER, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Lechner U, Baumbach R, Becker D, Kitunen V, Auling G, Salkinoja-Salonen M (1995) Degradation of 4-chloro-2-methylphenol by an activated sludge isolate and its taxonomic description. Biodegradation 6:83–92
Lipski A, Kämpfer P (2012) Aquamicrobium ahrensii sp. nov. and Aquamicrobium segne sp. nov., isolated from experimental biofilters. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2511–2516
Liu XM, Chen K, Meng C, Zhang L, Zhu JC, Huang X, Li SP, Jiang JD (2014) Pseudoxanthobacter liyangensis sp. nov., isolated from dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane-contaminated soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3390–3394
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G + C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Miller LT (1982) Single derivatization method for routine analysis of bacterial whole-cell fatty acid methyl esters, including hydroxy acids. J Clin Microbiol 16:584–586
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tel-Zur N, Abbo S, Myslabodski D, Mizrahi Y (1999) Modified CTAB procedure for DNA isolation from epiphytic cacti of the genera Hylocereus and Selenicereus (Cactaceae). Plant Mol Biol Rep 17:249–254
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tindall BJ (1990a) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130
Tindall BJ (1990b) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 66:199–202
Tindall BJ, Sikorski J, Smibert RM, Kreig NR (2007) Phenotypic characterization and the principles of comparative systematics. In: Reddy CA, Beveridge TJ, Marzluf JA, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (eds) Methods for general and molecular microbiology, 3rd edn. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 330–393
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE (1987) International committee on systematic bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Wu ZG, Wang F, Gu CG, Zhang YP, Yang ZZ, Wu XX, Jiang X (2014) Aquamicrobium terrae sp. nov., isolated from the polluted soil near a chemical factory. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 105:1131–1137
Zhang J, Gu T, Zhou Y, He J, Zheng LQ, Li WJ, Huang X, Li SP (2012) Terrimonas rubra sp. nov., isolated from a polluted farmland soil and emended description of the genus Terrimonas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2593–2597
Zhang L, Song M, Cao Q, Wu S, Zhao Y, Huang JW, Chen K, Li SP, Xia ZY, Jiang JD (2015) Camelimonas fluminis sp. nov., a cyhalothrin-degrading bacterium isolated from river water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:3109–3114
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYZ201422), the Outstanding Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20130029) and the Scientific Foundation from Yunnan Tobacco Company (2014YN08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain NK8T is KU877213.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, CF., Zhang, L., Huang, JW. et al. Aquamicrobium soli sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from a chlorobenzoate-contaminated soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 305–312 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0800-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0800-8