Abstract
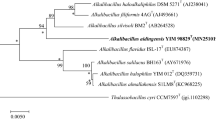
A novel Gram-stain positive, short rod, forming sub-terminal endospores of ellipsoidal shape, halophilic, alkaliphilic and aerobic bacterium, designated strain KQ-12T, was isolated from a saline–alkaline lake in China, and characterised by a polyphasic taxonomic approach. The isolate grew at 4–40 °C (optimum, 25 °C), at pH 8.0–10.0 (pH 9.0) and in the presence of 0–16% (w/v) NaCl (8%). 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity of KQ-12T to species in the genera Salipaludibacillus ranged from 96.6 to 98.1%. Phylogenetic trees indicated that the strain should be assigned to the genus Salipaludibacillus. The polar lipids of KQ-12T were diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, and an unidentified phospholipid and its major cellular fatty acids were anteiso-C15:0, anteiso-C17:0, iso-C15:0, and C16:0. The isoprenoid quinone was MK-7. These key chemotaxonomic properties also confirmed the affiliation of the strain to the genus Salipaludibacillus. However, some physiological, biochemical properties, low average nucleotide identity and low digital DNA–DNA hybridization relatedness values enabled the strain to be differentiated from closely related species of the genus Salipaludibacillus. Thus, KQ-12T can be classified as a novel species in the genus Salipaludibacillus, for which the name Salipaludibacillus keqinensis sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is KQ-12T ( = ACCC 60430T = KCTC 33935T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoozegar MA, Shahinpei A, Makzum S, Rafieyan S, Moshtaghi Nikou M et al (2018) Salipaludibacillus halalkaliphilus sp. nov., a moderately haloalkaliphilic bacterium from a coastal-marine wetland. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68(7):2214–2219. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002814
Cappuccino JG, Sherman N (2002) Microbiology: a laboratory manual, 6th edn. Pearson Education, Inc. and Benjamin Cummings, San Francisco
Chen YG, Zhang YQ, Wang YX, Liu ZX, Klenk HP et al (2009) Bacillus neizhouensis sp. nov., a halophilic marine bacterium isolated from a sea anemone. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:3035–3039. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.009522-0
Collins MD (1985) Analysis of isoprenoid quinones. Methods Microbiol 18:329–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70480-X
Dong XZ, Cai MY (2001) Determination of biochemical properties. In: Dong XZ, Cai MY (eds) Manual for the systematic identification of general bacteria. Science Press, Beijing, pp 370–398 (in Chinese)
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734359
Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN, Nester EW, Wood WA et al (1981) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 25–29
Gregersen T (1978) Rapid method for distinction of gram-negative from gram-positive bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 5:123–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00498806
Hasegawa T, Takizawa M, Tanida S (1983) A rapid analysis for chemical grouping of aerobic actinomycetes. J Gen Appl Microbiol 29:319–322. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.29.319
Kämpfer P, Kroppenstedt RM (1996) Numerical analysis of fatty acid patterns of coryneform bacteria and related taxa. Can J Micobiol 42:989–1005. https://doi.org/10.1139/m96-128
Kelly KL (1964) Inter-society colour council-national bureau of standards colour-name charts illustrated with centroid colours published in US. US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Kim M, Oh HS, Park SC, Chun J (2014) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:346–351. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.064931-0
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581
Kuenen JG, Muyzer G (2011) The microbial sulfur cycle at extremely haloalkaline conditions of soda lakes. Front Microbiol 2:44. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2011.00044
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M et al (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbbiol Methods 2:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7012(84)90018-6
Nielsen P, Fritze D, Priest FG (1995) Phenetic diversity of alkaliphilic bacillus strains: proposal for nine new species. Microbiology 141:1745–1761. https://doi.org/10.1099/13500872-141-7-1745
Ohta H, Hattori T (1983) Agromonas oligotrophica gen. nov., sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing oligotrophic bacterium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 49:429–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399322
Pettersson B, Lembke F, Hammer P, Stackebrandt E, Priest FG (1996) Bacillus sporothermodurans, a new species producing highly heat-resistant endospores. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:759–764. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-46-3-759
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Rosselló-Móra R, Trujillo ME, Sutcliffe IC (2017) Introducing a digital protologue: a timely move towards a database-driven systematics of archaea and bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:455–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0841-7
Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1992) A simple method for estimating and testing minimum-evolution trees. Mol Biol Evol 9:945. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040771
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.moldev.a040454
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 607–654
Sultanpuram VR, Mothe T (2016) Salipaludibacillus aurantiacus gen. nov., sp. nov. a novel alkali tolerant bacterium, reclassification of Bacillus agaradhaerens as Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens comb. nov. and Bacillus neizhouensis as Salipaludibacillus neizhouensis comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:2747–2753. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001117
Wang H, Zhang X, Wang S, Zhao B, Lou K et al (2018) Massilia violaceinigra sp. nov., a novel purple-pigmented bacterium isolated from glacier permafrost. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68(7):2271–2278. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002826
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O et al (1987) International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb01872.x
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y et al (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Zhang S, Li Z, Yan Y, Zhang C, Li J et al (2016) Bacillus urumqiensis sp. nov., a moderately haloalkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:2305–2312. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001028
Zhao B, Yan Y, Chen S (2014) How could haloalkaliphilic microorganisms contribute to biotechnology? Can J Microbiol 60:717–727. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2014-0233
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31300101) and Fundamental Research Funds for Central Non-profit Scientific Institution (Grant No. 1610042018005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WS, WH and WK wrote the main manuscript text. WH and WK designed the experiments. WS., DL and XS carried out the experiments. WH, ZB and ZX analyzed the data. All authors approved and read the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
No specific ethical or institutional permits were required to conduct sampling and the experimental studies did not involve endangered or protected species.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Dong, L., Zhao, B. et al. Salipaludibacillus keqinensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a saline–alkaline lake. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 112, 897–903 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-01224-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-01224-w