Abstract
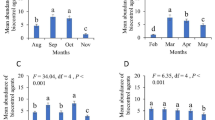
Rhynocoris marginatus (F.) (Reduviidae: Hemiptera:) is an efficient biocontrol agent in the management of multiple insect pests. The study aimed to assess the life table and demographic parameters of R. marginatus feeding on two lepidopterous insect pests, Spodoptera litura (Fab.) (Noctuidae) and Pieris brassicae (Linn.) (Pieridae). The developmental period of all life stages of R. marginatus was shorter when S. litura larvae were provided. The net reproductive rate (R0) was higher (411.4 offspring per individual) on S. litura, while it was 112.4 offspring per individual on P. brassicae. Mean generation time (T) of R. marginatus was shorter (93.28 d) on S. litura than on P. brassicae (105.90 d). Values of the intrinsic rate of increase (0.064 d−1) and finite rate of increase (1.066 d−1) for R. marginatus fed on S. litura were found higher than on P. brassicae (0.044 d−1 and 1.045 d−1, respectively). Age-stage–specific survival rate and age-stage-specific fecundity of R. marginatus were higher feeding on S. litura compared to P. brassicae larvae. The S. litura was the most suitable prey as compared to P. brassicae for R. marginatus. Our study suggests R. marginatus as a useful biocontrol agent against S. litura pest.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Raw data are available upon request.
References
Abbas N, Shad SA, Razaq M (2012) Fitness cost, cross resistance and realized heritability of resistance to imidacloprid in Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pestic Biochem Physiol 103:181–188
Abdullah A, Ullah MI, Raza ABM, Arshad M, Afzal M (2019) Host plant selection affects biological parameters in Armyworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pak J Zool 51(6):2117–2123
Ahmad M, Arif MI, Ahmad M (2007) Occurrence of insecticide resistance in field populations of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Pakistan. Crop Prot 26:809–817
Ahmad M, Ghaffar A, Rafiq M (2013) Host plants of leaf worm, Spodoptera litura (Fabricius)(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Pakistan. Asian J Agric Biol 1:23–28
Ahmadi K, Sengonca C, Blaeser P (2007) Effect of two different temperatures on the biology of predatory flower bug Orius similis Zheng (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae) with two different aphid species as prey. Turk J Entomol 31:253–268
Aljetlawi AA, Sparrevik E, Leonardsson K (2004) Prey–predator size-dependent functional response: derivation and rescaling to the real world. J Anim Ecol 73:239–252
Ambrose DP (1987) Biological behavioral and morphological tools in the biosystematics of Reduviidae (Insecta: Heteroptera: Reduviidae). Proc Anim Sci 96(5):449–508
Ambrose DP, Rajan XJS, Nagarajan K, Singh VJ, Krishnan SS (2009) Biology, behaviour and functional response of Sphedanolestes variabilis Distant (Insecta: Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Harpactorinae), a potential predator of lepidopteran pests. Entomol Croat 13(2):33–44
Amer MES, Fu Y, Niu L (2018) Biological aspects of Orius similis Zheng reared on two preys at three constant temperatures. J Agric Sci Technol 8:350–363
Aragón-Sánchez M, Román-Fernández LR, Martínez-García H, Aragón-García A, Pérez-Moreno I, Marco-Mancebón VS (2018) Rate of consumption, biological parameters, and population growth capacity of Orius laevigatus fed on Spodoptera exigua. BioControl 63:785–794
Atlihan R, Chi H (2008) Temperature-dependent development and demography of Scymnus subvillosus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) reared on Hyalopterus pruni (Homoptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 101(2):325–333
Awadallah KT, Tawfik MFS, El-Husseins MM, Afifi AL (1986) Bio cycle of the anthocorid predator Xylocoris avipes in association with rearing on major pests of stored drug materials. Bull Soc Entomol Egypt 66:27–33
Azher F, Khan MM, Bilal M, Asghar I, Rasheed MA, Ali S (2019) The development of Antilochus coquebertii Fabr. (Heteroptera: Pyrrhocoridae) on different artificial diets. J Kansas Entomol Soc 91:192–208
Bailey R, Chang NT, Lai PY (2011) Two-sex life table and predation rate of Cybocephalus flavocapitis Smith (Coleoptera: Cybocephalidae) reared on Aulacaspis yasumatsui Takagi (Hemiptera: Diaspididae). Taiwan J Asia-Pac Entomol 14(4):433–439
Barbosa L, Santos F, Soliman E, Rodrigues A, Wilcken C, Campos J, Zanuncio A, Zanuncio J (2019) Biological parameters, life table and thermal requirements of Thaumastocoris peregrinus (Heteroptera: Thaumastocoridae) at different temperatures. Sci Rep 9:10174
Bellows TS Jr, van Driesche RG, Elkinton JS (1992) Life table construction and analysis in the evaluation of natural enemies. Annu Rev Entomol 37:587–614
Bonte J, De Ro M, Conlong D, De Clercq P (2012) Thermal biology of the predatory bugs Orius thripoborus and O. naivashae (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Environ Entomol 41:989–996
Butt A, Talib R, Khan MX (2019) Effects of insecticides on the functional response of spider Oxyopes javanus against aphid Sitobion avenae. Int J Agric Biol 22:503–509
Calixto A, Bueno V, Montes F, Silva A, van Lenteren J (2013) Effect of different diets on reproduction, longevity and predation capacity of Orius insidiosus (Say) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Biocontrol Sci Technol 23:1245–1255
Chelliah SL (1985) The tobacco cutworm, Spodoptera litura: problems and prospects of management. Integrated pest and diseases management. Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, pp 139–159
Chi H (1988) Life-table analysis incorporating both sexes and variable development rates among individuals. Environ Entomol 17:26–34
Chi H (2016) TWO SEX-MSChart: computer program for age stage, two-sex life table analysis. http://140.120.197.173/Ecology/prod02.htm
Chi H (2018) TWOSEX-MSChart: a computer program for the age-stage, two-sex life table analysis. National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan, (http://140.120.197.173/Ecology/prod02.htm)
Chi H, Liu H (1985) Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bull Inst Zool Acad Sin 24:225–240
Chi H, Su HY (2006) Age-stage, two-sex life tables of Aphidius gifuensis (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and its host Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae) with mathematical proof of the relationship between female fecundity and the net reproductive rate. Environ Entomol 35:10–21
Chi H, You MS, Atlıhan R, Smith CL, Kavousi A, Özgökçe MS, Güncan A, Tuan SJ, Fu JW, Xu YY, Zheng FQ, Ye BH, Chu D, Yu Y, Gharekhani G, Saska P, Gotoh T, Schneider MI, Bussaman P, Gökçe A, Liu TX (2020) Age-stage, two-sex life table: an introduction to theory, data analysis, and application. Entomol Gen 40(2):103–124
De Clercq P, Bonte M, Van Speybroeck K, Bolckmans K, Deforce K (2005) Development and reproduction of Adalia bipunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on eggs of Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Phycitidae) and pollen. Pest Manag Sci 61(11):1129–1132
Efron B, Tibshirani RJ (1993) An introduction to the bootstrap. Monographs on statistics and applied probability, Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, London, New York, Washington, D.C.
El-Basha NA, Salman M, Osman M (2012) Functional response of Orius albidipennis (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) to the two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). J Entomol 9:248–256
EPPO (2013) PQR database: European and Mediterranean plant protection organization, Paris, France. https://www.eppo.int/DATABASES/pqr/pqr.htm. Accessed 28 April 2014
Firake DM, Lytan D, Behere GT, Thakur NSA (2012) Host plants alter the reproductive behavior of Pieris brassicae (Lepidoptera: Pieridae) and its solitary larval endo-parasitoid, Hyposoter ebeninus (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) in a cruciferous ecosystem. Fla Entomol 95(4):905–913
Garrad R, Booth D, Furlong M (2016) The effect of rearing temperature on development, body size, energetics and fecundity of the diamondback moth. Bull Entomol Res 106:175–181
George PJE, Seenivasagan R, Kannan S (1998) Influence of prey species on the development and reproduction of Acanthaspis siva Distant (Heteroptera: Reduviidae). Entomon 23(4):313–319
Godin JGJ, McDonough HE (2003) Predator preference for brightly colored males in the guppy: a viability cost for a sexually selected trait. Behav Ecol 14:194–200
Guz N, Dageri A (2017) Sequence analysis of insecticide resistance and detoxification related genes in Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Agrofor Int J 2(1):144–153
Hasan F, Ansari MS (2011) Population growth of Pieris brassicae (L.) (Lepidoptera: Pieridae) on different cole crops under laboratory conditions. J Pest Sci 84(2):179–186
Hiltunen T, Kaitala V, Laakso J, Becks L (2017) Evolutionary contribution to coexistence of competitors in microbial food webs. Proc R Soc Biol Sci 284:20170415
Honek A (1980) Population density of aphid at the time of settling and ovariole maturation in Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Entomophaga 23:213–216
Jalali MA, Tirry L, De Clercq P (2010) Effect of temperature on the functional response of Adalia bipunctata to Myzus persicae. BioControl 55:261–269
Jaleel W, Tao X, Wang D, Lu L, He Y (2018) Using two-sex life table traits to assess the fruit preference and fitness of Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). J Econ Entomol 111:2936–2945
Kalinoski RM, DeLong JP (2016) Beyond body mass: how prey traits improve predictions of functional response parameters. Oecologia 180:543–550
Kessler A, Baldwin IT (2002) Manduca quinquemaculata’s optimization of intra-plant oviposition to predation, food quality, and thermal constraints. Ecology 83:2346–2354
Khaliq A, Attique M, Sayyed A (2007) Evidence for resistance to pyrethroids and organophosphates in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) from Pakistan. Bull Entomol Res 97:191–200
Khuhro RD, Nizamani IA, Talpur MA (2002) Population abundance of predators in alfalfa and cotton fields at Tandojam. Pak J Appl Sci 2:300–303
Lal MN, Ram B (2004) Cabbage butterfly, Pieris brassicae L. An upcoming menance for Brassicae oilseed crop in northern India. Cruciferae Newsl 25:83–86
Liu P, Jia W, Zheng X, Zhang L, Sangbaramou R, Tan S, Liu Y, Shi W (2018) Predation functional response and life table parameters of Orius sauteri (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) feeding on Megalurothrips usitatus (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Fla Entomol 101:254–259
Mahr SER, Cloyd RA, Mahr DL, Sadorf CS (2001) Biological control of insects and other pests of greenhouse crops. North Central Regional Publication 581, University of Wisconsin, p. 100.
Musa PD, Ren SX (2005) Development and reproduction of Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) on three bean species. Insect Sci 12:25–30
Omkar SS (2003) Influence of six aphid prey species on development and reproduction of a ladybird beetle, Coccinella septempunctata. BioControl 48:379–393
Pasandideh A, Talebi AA, Hajiqanbar H, Tazerouni Z (2015) Host stage preference and age-specific functional response of Praon volucre (Hymenoptera: Braconidae, Aphidiinae) a parasitoid of Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Crop Prot 4:563–575
Petchidurai G, Chitra R, Sahayaraj K (2019) Polymorphism of Rhynocoris marginatus (Fab.)(Heteroptera: Ruduviidae) on the biology, biological control potential. J Biopestic 12(1):114–125
Rana JS, Dixon AFG, Jarošík V (2002) Costs and benefits of prey specialization in a generalist insect predator. J Anim Ecol 71(1):15–22
Sahayaraj K (2001) A qualitative study of food consumption, growth and fecundity of a reduviid predator in relation to prey density. Entomol Croat 5:19–30
Sahayaraj K, Delma JCR, Martin P (2003) Biological control potential of aphidophagous reduviid predator Rhynocoris marginatus. Int Arch Newsl 23:29–30
Sahayaraj K, Paulraj MG (2001) Rearing and life table of reduviid predator Rhynocoris marginatus Fab. on Spodoptera litura Fab. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae. J Appl Entomol 125:321–325
Sahayaraj K, Raju G (2006) Assessing the intraguild predation of Rhynocoris marginatus (Fab.) (Heteroptera: Reduviidae: Harpactorinae) and Menochiluss exmaculatus (Fab.) of cotton pest Aphis craccivora. Hexapoda 13:62–65
Sahayaraj K, Ravi C (2007) Evaluation of reduviid predators and plant products against chosen groundnut pests. Arch Phytopathol Plant Prot 40:281–290
Saleem MA, Ahmad M, Ahmad M, Aslam M, Sayyed AH (2008) Resistance to selected organochlorine, organophosphates, carbamates and pyrethroids in Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from Pakistan. J Econ Entomol 101:1667–1675
Sayyed AH, Saeed S, Noor-Ul-Ane M, Crickmore N (2008) Genetic, biochemical, and physiological characterization of spinosad resistance in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J Econ Entomol 101:1658–1666
Shad SA, Sayyed AH, Fazal S, Saleem MA, Zaka SM, Ali M (2012) Field evolved resistance to carbamates, organophosphates, pyrethroids and new chemistry insecticides in Spodoptera litura Fab. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Pest Sci 85:153–162
Sharma P, Verma S, Chandel R, Shah M, Gavkare O (2017) Functional response of Harmonia dimidiata (fab.) to melon aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover under laboratory conditions. Phytoparasitica 45:373–379
Southwood TRE, Henderson PA (2009) Ecological methods. Wiley, Hoboken
Tazerouni Z, Talebi A, Fathipour Y, Soufbaf M (2016) Age-specific functional response of Aphidius matricariae and Praon volucre (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) on Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Neotrop Entomol 45:642–651
Tuan SJ, Lee CC, Chi H (2014) Population and damage projection of Spodoptera litura (F.) on peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.) under different conditions using the age-stage, two-sex life table. Pest Manag Sci 70:805–813
White TCR (1970) Some aspects of the life history, host selection, dispersal and oviposition of adult Cardiaspina densidextra. Aust J Zool 18:105–117
Younas M, Naeem M, Raqib A, Masud S (2004) Population dynamics of cabbage butterfly (Pieris brassicae) and cabbage aphids (Brevicoryne brassicae) on five cultivars of cauliflower at Peshawar [Pakistan]. Asian J Plant Sci 3(3):391–393
Zhou ZS, Chen ZP, Xu ZF (2012) Effects of three Spodoptera litura control strategies on arthropod diversity and abundance in tobacco agroecosystems in South China. Pak J Zool 44(1):151–157
Acknowledgements
The authors are very thankful to Prof. Dr. Hsin Chi, Department of Entomology, National Chung Hsing University, Taiwan who helped in data analysis and preparing the figures. Providing facilities for the experiment by the Department of Plant Pathology, University of Sargodha is greatly acknowledged.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA, MIU and RRK: Conceptualization, MA and RRK: Methodology, MA, MT, and MR: Formal analysis, AS and SA: Data curation, MA, and MR: Writing—original draft preparation, SA and AS: Literature review, MR and MT: Visualization, MIU: Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
As no human or mammalian subjects were involved in this research, no ethics approvals were required for this study.
Consent to participate
All authors consent to participate in publication of these data.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to publish this work.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Eric Riddick
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arshad, M., Ullah, M.I., Khan, R.R. et al. Demographic parameters of the reduviid predator, Rhynocoris marginatus (Reduviidae: Hemiptera) fed on two lepidopterous insect pests. BioControl 66, 227–235 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-020-10060-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-020-10060-9