Abstract
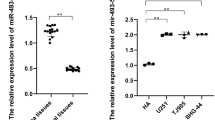
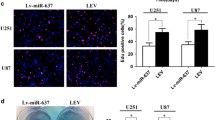
Recently, increasing studies have suggested that miRNAs play a significant role in the occurrence and development of glioma. More researches are needed to explore the role of miRNAs in glioma, which will help to find new therapeutic targets. miR-212-5p has been reported to be involved in the progression in many cancers. However, whether miR-212-5p has a regulative effect on glioma remains un clear. In this study, we aimed to explore the effect of miR-212-5p on glioma development and its mechanism. Here, we demonstrated that miR-212-5p was lowly expressed in glioma cell. miR-212-5p suppressed the glioma cell proliferation, inhibited the migratory and invasive capabilities and promoted apoptosis in glioma cells. Besides, miR-212-5p also inhibited tumor growth in vivo. We found small ubiquitin-like modifier 2 (SUMO2) was the target of miR-212-5p, and miR-212-5p suppressed SUMO2 expression to regulate the proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of glioma cells. These findings indicated that miR-212-5p may be a possible therapeutic target for the treatment for glioma.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Barciszewska AM (2016) MicroRNAs as efficient biomarkers in high-grade gliomas. Folia Neuropathol 54(4):369–374
Bhardwaj VK, Purohit R (2021) Targeting the protein-protein interface pocket of Aurora-A-TPX2 complex: rational drug design and validation. J Biomol Struct Dyn 39(11):3882–3891
Bhaskaran M, Mohan M (2014) MicroRNAs: history, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development and disease. Vet Pathol 51(4):759–774
Chen R, Smith-Cohn M, Cohen AL, Colman H (2017) Glioma subclassifications and their clinical significance. Neurotherapeutics 14(2):284–297
Cheng T-M, Chin Y-T, Hoa Y et al (2018) Resveratrol induces sumoylated COX-2-dependent anti-proliferation in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 112:67–75
Delgado-López PD, Corrales-García EM, Martino J, Lastra-Aras E, Dueñas-Polo MT (2017) Diffuse low-grade glioma: a review on the new molecular classification, natural history and current management strategies. Clin Transl Oncol 19(8):931–944
Grimm SA, Chamberlain MC (2013) Brainstem glioma: a review. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 13(5):346
Hao YL, Jin XJ, Zhao H, et al. Effect of long chain non-coding RNA BANCR on proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Biomedical Engineering and Clinical Medicine. 2019.
Hausser J, Zavolan M (2014) Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions–beyond repression of gene expression. Nat Rev Genet 15(10):599
Hollis AR, Starkey MP (2018) MicroRNAs in equine veterinary science. Equine Vet J 50(6):721–726
Komori T (2015) Pathology and genetics of diffuse gliomas in adults. Neurol Med Chir 55(1):28–37
Kumar A, Purohit R (2014) Use of long term molecular dynamics simulation in predicting cancer associated SNPs. PLoS Comput Biol 10(4):e1003318
Li Y, Wang D, Wang L, Yu J, Fu S (2013) Distinct genomic aberrations between low-grade and high-grade gliomas of Chinese patients. PLoS ONE 8(2):e57168
Lim W, Bae H, Bazer FW, Song G (2019) Ephrin A1 promotes proliferation of bovine endometrial cells with abundant expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclin D1 changing the cell population at each stage of the cell cycle. J Cell Physiol 234(4):4864–4873
Lin JF, Zeng H, Zhao JQ (2018) MiR-212-5p regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of AML cells through targeting FZD5. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(23):8415–8422
Lu TX, Rothenberg ME (2018) MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol 141(4):1202–1207
Lv ZD, Yang DX, Liu XP et al (2017) MiR-212-5p suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer by targeting Prrx2. Cell Physiol Biochem 44(5):1785–1795
Mao F, Wang B, Xiao Q, Cheng F, Lei T, Guo D (2017) LRIG proteins in glioma: Functional roles, molecular mechanisms, and potential clinical implications. J Neurol Sci 383:56–60
Mohr AM, Mott JL (2015) Overview of microRNA biology. Semin Liver Dis 35(1):3–11
Ostrom QT, Bauchet L, Davis FG et al (2014) The epidemiology of glioma in adults: a “state of the science” review. NeuroOncology 16(7):896–913
Rolhion C, Penault-Llorca F, Kémény J-L et al (2001) Interleukin6 overexpression as a marker of malignancy in human gliomas. J Neurosurg 94(1):97–101
Singh R, Bhardwaj VK, Sharma J, Das P, Purohit R (2021) Identification of selective cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitor from the library of pyrrolone-fused benzosuberene compounds: an in silico exploration. J Biomol Struct Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2021.1900918
Tan MY, Mu XY, Liu B et al (2013) SUMO-Specific Protease 2 Suppresses Cell Migration and Invasion through Inhibiting the Expression of MMP13 in Bladder Cancer Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 32(3):542–548
Tang C, Liu P, Zhou Y, Jiang B, Song Y, Sheng L (2019) Sirt6 deletion in hepatocytes increases insulin sensitivity of female mice by enhancing ERα expression. J Cell Physiol 234(10):18615–18625
Tang C, Zhang J, Liu P et al (2020) Chronic exposure to low dose of bisphenol A causes follicular atresia by inhibiting kisspeptin neurons in anteroventral periventricular nucleus in female mice. Neurotoxicology 79:164–176
Thon N, Damianoff K, Hegermann J, Grau S, Goldbrunner R (2010) Presence of pluripotent CD133+ cells correlates with malignancy of gliomas. Mol Cell Neurosci 43(1):51–59
Tsurimoto T (1999) PCNA binding proteins. Front Biosci 4:D849–D858
Xiao X, Jiang Y, Liang W et al (2019) miR-212-5p attenuates ferroptotic neuronal death after traumatic brain injury by targeting Ptgs2. Mol Brain 12(1):78
Funding
This study was supported by Suqian Industrial Development Guide Fund Project (NO: K201902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chong, Y., Zhu, C., Hu, W. et al. miR-212-5p Suppresses Glioma Development via Targeting SUMO2. Biochem Genet 61, 35–47 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10236-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10236-1