Abstract
Objectives
To establish a high-throughput method for determination of antibodies intra- and extracellular light chain (LC) to heavy chain (HC) polypeptide ratio as screening parameter during cell line development.
Results
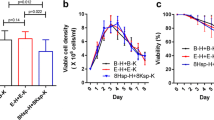
Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) TurboCell pools containing different designed vectors supposed to result in different LC:HC polypeptide ratios were generated by targeted integration. Cell culture supernatants and cell lysates of a fed batch experiment were purified by combined Protein A and anti-kappa affinity batch purification in 96-well format. Capture of all antibodies and their fragments allowed the determination of the intra- and extracellular LC:HC peptide ratios by reduced SDS capillary electrophoresis. Results demonstrate that the method is suitable to show the significant impact of the vector design on the intra- and extracellular LC:HC polypeptide ratios.
Conclusion
Determination of LC:HC polypeptide ratios can give important information in vector design optimization leading to CHO cell lines with optimized antibody assembly and preferred product quality.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding H, Ron D (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol 2:326–332
Bhoskar P, Belongia B, Smith R, Yoon S, Carter T, Xu J (2013) Free light chain content in culture media reflects recombinant monoclonal antibody productivity and quality. Biotechnol Prog 29:122–1139
Gonzales R, Andrews BA, Asenjo JA (2002) Kinetic model of PiP- and PDI-mediated protein folding and assembly. J Theor Biol 214:529–537
Ho S, Koh E, van Beers M, Mueller M, Wan C, Teo G et al (2013) Control of IgG LC:HC ratio in stable transfected CHO cells and study of the impact on expression, aggregation, glycosylation and conformational stability. J Biotechnol 165:157–166
Jefferis R (2005) Glycosylation of recombinant antibody therapeutics. Biotechnol Prog 21:11–16
Jiang Z, Huang Y, Sharfstein S (2006) Regulation of recombinant monoclonal antibody production in Chinese Hamster Ovary cells: a comparative study of gene copy number, mRNA level and protein expression. Biotechnol Prog 22:313–318
Lee CJ, Seth G, Tsukuda J, Hamilton RW (2009) A clone screening method using mRNA levels to determine specific productivity and product quality for monoclonal antibodies. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:1107–1117
Li J, Zhang C, Jostock T, Dübel S (2007) Analysis of IgG heavy chain to light chain ratio with mutant Encephalomyocarditis virus internal ribosome entry site. Protein Eng 20:491–496
Li F, Shen A, Amanullah A (2013) Cell culture processes in monoclonal antibody production. Pharm Sci Encycl 7:1–38
O’Callaghan PM, McLeod J, Pybus LP, Lovelady CS, Wilkinson SJ, Racher AJ, Porter A, James DC (2010) Cell line-specific control of recombinant monoclonal antibody production by CHO cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 106:938–951
Perchiacca JM, Tessier PM (2012) Engineering aggregation-resistant antibodies. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng 3:263–286
Schlatter S, Stansfield S, Dinnis D, Racher A, Birch J, James D (2005) On the optimal ratio of heavy to light chain genes for efficient recombinant antibody production by CHO cells. Biotechnol Prog 21:122–133
Vanhove M, Usherwood YK, Hendershot L (2001) Unassembled Ig heavy chains do not cycle from BiP in vivo but require light chains to trigger their release. Immunity 15:105–114
Vazquez-Rey M, Lang DA (2011) Aggregates in monoclonal antibody manufacturing processes. Biotechnol Bioeng 108:1494–1508
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerster, A., Wodarczyk, C., Reichenbächer, B. et al. A simple method to determine IgG light chain to heavy chain polypeptide ratios expressed by CHO cells. Biotechnol Lett 38, 2043–2049 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2197-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2197-x