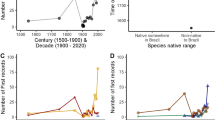
Abstract
Compared to other facets of invasion science, the impacts of biological invasions have been understudied, but many studies have been published in the last decade. This paper reviews the growing body of evidence of impacts of invasions in South Africa. We classified information for individual species into ten ecological and four social categories of impact. We also reviewed studies that upscaled this information to larger spatial scales, as well as progress with assigning invasive species to impact severity categories. We identified 123 studies that documented the impacts of 71 invasive alien species, about 5 of the country’s naturalized alien biota. The most frequently reported impact category was species interactions (changes to habitat suitability, pollination networks or seed dispersal mechanisms), followed by direct competition, changes to ecosystem functioning (hydrology or nutrient dynamics), hybridization and predation. Trees and shrubs accounted for more than half of the species studied, but there were examples from most other groups of plants and animals. The social consequences of invasions have been less well studied at the level of individual species. Most studies (72%) considered the impacts of a single species, based on data collected on < 1 ha, and were completed in less than a year. Space-for-time substitution was widely used, but widespread collection of data from numerous small plots allowed for reporting impact over larger spatial scales. We also identified seven studies that either monitored impacts over longer periods (up to 40 years), or repeated surveys in the same area to assess change over time. Prominent landscape-scale impacts included reductions in water resources, the attrition of native biodiversity, reductions in rangeland productivity, predation of marine birds and freshwater fishes, and disease organisms affecting native mammals and trees. Nineteen studies at broader scales estimated substantial impacts on landscape-scale water yield, habitats and biodiversity, rangeland productivity, and the economic value of ecosystem services. Despite considerable progress, our understanding remains fragmentary. Impacts are expected to grow as invasions enter exponential phases of spread and densification and as the duration of invasions increases. A robust understanding needs to be developed to provide justification for management costs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
This review is based on published information, and all studies that were included are listed in the supplementary tables.
References
Allen DG, Harrison JA, Navarro RA, van Wilgen BW, Thompson MW (1997) The impact of commercial afforestation on bird populations in Mpumalanga province, South Africa - insights from bird atlas data. Biol Conserv 79:173–185
Appleton CC, Forbes AT, Demetriades NT (2009) The occurrence, bionomics and potential impacts of the invasive freshwater snail Tarebia granifera (Lamarck, 1822) (Gastropoda: Thiaridae) in South Africa. Zool Mededel 83:525–536
Aslan CE, Dickson BG (2020) Non-native plants exert strong but under-studied influence on fire dynamics. NeoBiota 61:47–64
Bacher S, Blackburn TM, Essl F, Genovesi P, Heikkilä J, Jeschke JM, Jones G, Keller R, Kenis M, Kueffer C, Martinou AF, Nentwig W, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Rabitsch W, Richardson DM, Roy HE, Saul WC, Scalera R, Vilà M, Wilson JRU, Kumschick S (2018) Socio-economic impact classification of alien taxa (SEICAT). Methods Ecol Evol 9:159–168
Blackburn TM, Essl F, Evans T, Hulme PE, Jeschke JM, Kühn I, Kumschick S, Marková Z, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Rabitsch W, Ricciardi A, Richardson DM, Vilà M, Wilson JRU, Winter M, Genovesi P, Bacher S (2014) A unified classification of alien species based on the magnitude of their environmental impacts. PLoS Biol 12:e1001850
Blignaut J, van Heerden J (2009) The impact of water scarcity on economic development initiatives. Water SA 35:415–420
Bond WJ, Slingsby P (1984) Collapse of an ant-plant mutualism: the Argentine ant (Iridomyrmex humilis) and myrmemochorous Proteaceae. Ecology 4:1031–1037
Branch GM, Steffani CN (2004) Can we predict the effects of alien species? A case-history of the invasion of South Africa by Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 300:189–215
Clusella-Trullas S, Garcia RA (2017) Impacts of invasive plants on animal diversity in South Africa: A synthesis. Bothalia 47(2):a2166. https://doi.org/10.4102/abc.v47i2.2166
D’Amato ME, Esterhuyse MM, van der Waal BCW, Brink D, Volckaert FAM (2007) Hybridization and phylogeography of the Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus in southern Africa evidenced by mitochondrial and microsatellite DNA genotyping. Conserv Genet 8:475–488
Dean WRJ, Anderson MD, Milton SJ, Anderson TA (2002) Avian assemblages in native Acacia and alien Prosopis drainage line woodland in the Kalahari, South Africa. J Arid Environm 51:1–19
De Lange WJ, van Wilgen BW (2010) An economic assessment of the contribution of weed biological control to the management of invasive alien plants and to the protection of ecosystem services in South Africa. Biol Invasions 12:4113–4124
De Vos V, Bengis RG, Kriek NP et al (2001) The epidemiology of tuberculosis in free-ranging African buffalo (Syncerus caffer) in the Kruger National Park, South Africa. Onderstep J Vet Res 68:119–130
De Wit M, Crookes D, van Wilgen BW (2001) Conflicts of interest in environmental management: Estimating the costs and benefits of a tree invasion. Biol Invasions 3:167–178
Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (2020) Annual Performance Plan 2019/2020. Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pretoria
Downey PO, Richardson DM (2016) Alien plant invasions and native plant extinctions: a six-threshold framework AoB Plants 8: plw047; doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plw047
Drake JA, Mooney HA, Di Castri F, Goves RH, Kruger FJ, Rejmánek M, Williamson M (eds)(1989) Biological invasions: a global perspective. Wiley, Chichester
Dzikiti S, Schachtschneider K, Naiken V, Gush M, Moses G, Le Maitre DC (2013) Water relations and the effects of clearing invasive Prosopis trees on groundwater in an arid environment in the Northern Cape, South Africa. J Arid Environm 90:103–113
Dzikiti S, Gush MB, Le Maitre DC, Maherry A, Jovanovic NZ, Ramoelo A, Cho MA (2016) Quantifying potential water savings from clearing invasive alien Eucalyptus camaldulensis using in situ and high resolution remote sensing data in the Berg River catchment, Western Cape, South Africa. For Ecol Manage 361:69–80
Dzikiti S, Ntshidi Z, Le Maitre DC, Bugan RDH, Mazvimavi D, Schachtschneider K, Jovanovic NZ, Pienaar HH (2017) Assessing water use by Prosopis invasions and Vachellia karroo trees: Implications for groundwater recovery following alien plant removal in an arid catchment in South Africa. For Ecol Manage 398:153–163
Essl F, Hulme PE, Jeschke JM, Keller RP, Pyšek P, Richardson DM, Saul WC, Bacher S, Dullinger S, Estevez RA, Kueffer C, Roy H, Seebens H, Rabitsch W (2017) Scientific and normative foundations for the valuation of alien species impacts: thirteen core principles. Bioscience 67:166–178
Ferrar AA, Kruger FJ (1983) South African programme for the SCOPE project on the ecology of biological invasions. South African National Scientific Programmes Report no. 72. Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, Pretoria
Forsyth GG, Le Maitre DC, van Wilgen BW, O’Farrell PJ (2012) The prioritisation of invasive alien plant control projects using a multi-criteria decision model informed by stakeholder input and spatial data. J Environm Manage 103:51–57
Gibson MR, Pauw A, Richardson DM (2013) Decreased insect visitation to a native species caused by an invasive tree in the Cape Floristic Region. Biol Conserv 157:196–203
Gibson MR, Richardson DM, Pauw A (2012) Can floral traits predict an invasive plant’s impact on native plant–pollinator communities? J Ecol 100:1216–1223
Görgens AHM, van Wilgen BW (2004) Invasive alien plants and water resources: an assessment of current understanding, predictive ability and research challenges. S Afr J Sci 100:27–34
Grass I, Berens DG, Farwig N (2014) Natural habitat loss and exotic plants reduce the functional diversity of flower visitors in a heterogeneous subtropical landscape. Funct Ecol 28:1117–1126
Hagen BL, Kumschick S (2018) The relevance of using various scoring schemes revealed by an impact assessment of feral mammals. NeoBiota 38:37–75
Hansen S, Roets F, Seymour CL, Thébault E, van Veen FJF, Pryke JS (2017) Alien plants have greater impact than habitat fragmentation on native insect flower visitation networks. Diversity Distrib 24:58–68
Higgins SI, Turpie JK, Costanza R et al (1997) An ecological economic simulation model of mountain fynbos ecosystems – dynamics, valuation and management. Ecol Econ 22:155–169
Hill MP, Moran VC, Hoffmann JH, Neser S, Zimmermann HG, Simelane DO, Klein H, Zachariades C, Wood AR, Byrne MJ, Paterson ID, Martin GD, Coetzee JA (2020) More than a century of biological control against invasive alien plants in South Africa: a synoptic view of what has been accomplished. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya TA (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 553–572
Hirsch H, Allsopp MH, Canavan S et al (2019) Eucalyptus camaldulensis in South Africa – past, present, future. Trans Royal Soc S Afr 75:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/0035919X.2019.1669732
Holmes PM, Esler KJ, Gaertner M, Geerts S, Hall SA, Nsikani MM, Richardson DM, Ruwanza S (2020) Biological invasions and ecological restoration in South Africa. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya T (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 665–700
Ivanova IM, Symes CT (2019) Invasion of Psittacula krameri in Gauteng, South Africa: are other birds impacted? Biodiv Conserv 28:3633–3656
Jansen C (2020) A global impact assessment of Acacia species introduced to South Africa. Honours thesis, Department of Botany and Zoology, Stellenbosch University
Jeschke JM, Bacher S, Blackburn TM, Dick JTA, Essl F, Evans T, Gaertner M, Hulme PE, Kühn I, Mrugała A, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Rabitsch W, Ricciardi A, Richardson DM, Sendek A, Vilà M, Winter M, Kumschick S (2014) Defining the impact of non-native species: resolving disparity through greater clarity. Conserv Biol 28:1188–1194
Kesner D, Kumschick S (2018) Gastropods alien to South Africa cause severe environmental harm in their global alien ranges across habitats. Ecol Evol 8:8273–8285
Kraaij T, Baard JA, Arndt J, Vhengani L, van Wilgen BW (2018) An assessment of climate, weather and fuel factors influencing a large, destructive wildfire in the Knysna region, South Africa. Fire Ecol 14:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42408-018-0001-0
Kuebbing SE, Patterson CM, Classen AT, Simberloff D (2016) Co-occurring nonnative woody shrubs have additive and non-additive soil legacies. Ecol Appl 26:1896–1906
Kumschick S, Gaertner M, Vilà M, Essl F, Jeschke JM, Pyšek P, Ricciardi A, Bacher S, Blackburn TM, Dick JTA, Evans T, Hulme PE, Kühn I, Mrugala A, Pergl J, Rabitsch W, Richardson DM, Sendek A, Winter M (2015) Ecological impacts of alien species: Quantification, scope, caveats and recommendations. Bioscience 65:55–63
Latimer AM, Silander JA, Gelfand AE, Rebelo AG, Richardson DM (2004) Quantifying threats to biodiversity from invasive alien plants and other factors: a case study from the Cape Floristic Region. S Afr J Sci 100:81–86
Le Maitre DC, Blignaut JN, Clulow A, Dzikiti S, Everson CS, Görgens AHM, Gush MB (2020) Impacts of plant invasions on terrestrial water flows in South Africa. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya TA (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 431–457
Le Maitre DC, Gaertner M, Marchante E, Ens EJ, Holmes PM, Pauchard A, O’Farrell PJ, Rogers AM, Blanchard R, Blignaut J, Richardson DM (2011) Impacts of invasive Australian acacias: implications for management and restoration. Diversity Distrib 17:1015–1029
Le Maitre DC, van Wilgen BW, Chapman RA, McKelly D (1996) Invasive plants and water resources in the Western Cape Province, South Africa: modelling the consequences of a lack of management. J Appl Ecol 33:161–172
Le Maitre DC, Versfeld DB, Chapman RA (2000) The impact of invading alien plants on surface water resources in South Africa: a preliminary assessment. Water SA 26:397–408
Le Maitre DC, van Wilgen BW, Gelderblom CM, Bailey C, Chapman RA, Nel JA (2002) Invasive alien trees and water resources in South Africa: case studies of the costs and benefits of management. For Ecol Manage 160:143–159
Levine JM, Vila M, D’Antonio CM, Dukes JS, Grigulis K, Lavore S (2003) Mechanisms underlying the impacts of exotic plant invasions. Proc Royal Soc Lond B 270:775–781
Loewenthal D, Paijmans DM, Hockey PAR (2016) Factors affecting the breeding success of the African Black Oystercatcher (Haematopus moquini): a perspective on protection and food availability. Afr Zool 51:193–202
Lubke RA (1985) Erosion of the beach at St Francis Bay, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Biol Conserv 32:99–127
Macdonald IAW, Kruger FJ, Ferrar A (eds) (1986) The ecology and management of biological invasions in southern Africa. Oxford University Press, Cape Town
McClelland GTW, Altwegg R, van Aarde RJ, Ferreira S, Burger AE, Chown SL (2017) Climate change leads to increasing population density and impacts of a key island invader. Ecol Appl 28:212–224
McConnachie AJ, De Wit MP, Hill MP, Byrne MJ (2003) Economic evaluation of the successful biological control of Azolla filiculoides in South Africa. Biol Cont 28:25–32
Measey J, Hui C, Somers M (2020) Terrestrial vertebrate invasions in South Africa. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya TA (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 113–150
Mgobozi PM, Somers MJ, Dippenaar-Schoeman AS (2008) Spider responses to alien plant invasion: the effect of short- and long-term Chromolaena odorata invasion and management. J Appl Ecol 45:1189–1197
Mittermeier RA, Robles-Gil P, Hoffmann M et al (2004) Hotspots revisited: Earth’s biologically richest and most endangered terrestrial ecoregions. CEMEX, Mexico City
Ndhlovu T, Milton-Dean SJ, Esler KJ (2011) Impact of Prosopis (mesquite) invasion and clearing on the grazing capacity of semiarid Nama Karoo rangeland, South Africa. Afr J Range For Sci 28:129–137
Nsikani MM, Novoa A, van Wilgen BW, Keet J-H, Gaertner M (2017) Acacia saligna’s soil legacy effects persist up to 10 years after clearing: implications for ecological restoration. Austral Ecol 42:880–889
Ntshidi Z, Gush MB, Dzikiti S, Le Maitre DC (2018) Characterising the water use and hydraulic properties of riparian tree invasions: a case study of Populus canescens in South Africa. Water SA 44:328–337
Nuñez MA, Chiuffo MC, Torres A, Paul T, Dimarco RD, Raal P, Policelli N, Moyano J, Garcia R, van Wilgen BW, Pauchard A, Richardson DM (2017) Ecology and management of invasive Pinaceae around the world: progress and challenges. Biol Invasions 19:3099–3120
O’Connor T, van Wilgen BW (2020) The impact of alien plants on rangelands in South Africa. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya T (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 445–473
Odendaal LJ, Haupt TM, Griffiths CL (2008) The alien invasive land snail Theba pisana in the West Coast National Park: is there cause for concern? Koedoe 90:93–98
Paap T, de Beer ZW, Migliorini D, Nel WJ, Wingfield MJ (2018) The polyphagous shot hole borer (PSHB) and its fungal symbiont Fusarium euwallaceae: a new invasion in South Africa. Austral Plant Pathol 47:231–237
Paap T, Wingfield MJ, De Beer ZW, Roets F (2020) Lessons from a major pest invasion: The polyphagous shot hole borer in South Africa. S Afr J Sci 116(11/12), Art. #8757, 4 pages. https://doi.org/10.17159/ sajs.2020/8757
Parker IM, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM et al (1999) Impact: toward a framework for understanding the ecological effect of invaders. Biol Invasions 1:3–19
Preston IR, Le Maitre DC, Blignaut JN, Louw L, Palmer CG (2018) Impact of invasive alien plants on water provision in selected catchments. Water SA 44:719–729
Pryke JS, Samways MJ, Hockey PAR (2011) Persistence of the threatened Knysna warbler Bradypterus sylvaticus in an urban landscape: do gardens substitute for fire? Afr J Ecol 49:199–208
Pyšek P, Richardson DM (2010) Invasive species, environmental change and management, and ecosystem health. Annu Rev Environ Resour 35:25–55
Pyšek P, Richardson DM, Pergl J, Jarošík V, Sixtová Z, Weber E (2008) Geographical and taxonomical biases in invasion ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 23:237–244
Rahlao SJ, Milton SJ, Esler KJ, van Wilgen BW, Barnard P (2009) Effects of invasion of fire-free arid shrublands by a fire-promoting invasive alien grass (Pennisetum setaceum) in South Africa. Austral Ecol 34:920–928
Raimondo D, Staden VL, Foden W, Victor JE, Helme NA, Turner RC, Kamundi DA, Manyama PA (2009) Red list of South African Plants. South African National Biodiversity Institute, Pretoria
Renwick AR, White PCL, Bengis RG (2007) Bovine tuberculosis in southern African wildlife: a multi-species host–pathogen system. Epidemiol Infect 135:529–540
Richardson DM (ed) (2011) Fifty years of invasion ecology: the legacy of Charles Elton. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford
Richardson DM, Abrahams B, Boshoff N, Davies SJ, Measey J, van Wilgen BW (2020a) South Africa’s Centre for Invasion Biology: An experiment in invasion science for society. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey GJ, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya T (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 859–895
Richardson DM, Foxcroft LC, Latombe G et al (2020b) The biogeography of South African terrestrial plant invasions. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya TA (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 65–94
Richardson DM, Kluge RL (2008) Seed banks of invasive Australian Acacia species in South Africa: role in invasiveness and options for management. Perspect Plant Ecol Evol Syst 10:161–177
Richardson DM, van Wilgen BW (1986) Effects of thirty–five years of afforestation with Pinus radiata on the composition of mesic mountain fynbos near Stellenbosch. S Afr J Bot 52:309–315
Richardson DM, van Wilgen BW (2004) Invasive alien plants in South Africa: how well do we understand the ecological impacts? S Afr J Sci 100:45–52
Rivers-Moore NA, Fowles B, Karssing RJ (2013) Impacts of trout on aquatic macroinvertebrates in three Drakensberg rivers in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Afr J Aquat Sci 38:93–99
Robinson TB, Branch GM, Griffiths CL, Govender A, Hockey PAR (2007) Changes in South African rocky intertidal invertebrate community structure associated with the invasion of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Marine Ecol Prog Ser 340:163–171
Robinson TB, Peters K, Brooker B (2020) Coastal invasions: The South African context. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya TA (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 229–247
Rodwell TC, Whyte IJ, Boyce WM (2001) Evaluation of population effects of bovine tuberculosis in free-ranging African buffalo (Syncerus caffer). J Mammal 82:231–238
Rouget M, Richardson DM, Cowling RM, Lloyd JW, Lombard AT (2003) Current patterns of habitat transformation and future threats to biodiversity in terrestrial ecosystems of the Cape Floristic Region, South Africa. Biol Conserv 112:63–85
Rouget M, Richardson DM, Nel JL, Le Maitre DC, Egoh B, Mgidi T (2004) Mapping the potential spread of major plant invaders in South Africa using climatic suitability. Diversity Distrib 10:475–484
Rouget M, Robertson MP, Wilson JRU, Hui C, Essl F, Renteria JL, Richardson DM (2016) Invasion debt—quantifying future biological invasions. Diversity Distrib 22:445–456
Sadchatheeswaran S, Branch GM, Moloney CL, Robinson TB (2018) Impacts of alien ‘ecosystem engineers’ overwhelm interannual and seasonal shifts in rocky-shore community composition on Marcus Island, South Africa. Afr J Marine Sci 40:137–147
Samways MJ, Caldwell PM, Osborn R (1996) Ground-living invertebrate assemblages in native, planted and invasive vegetation in South Africa. Agric Ecosys Environm 59:19–32
Schachtschneider K, February EC (2013) Impact of Prosopis invasion on a keystone tree species in the Kalahari desert. Plant Ecol 214:597–605
Schoeman CS, Samways MJ (2011) Synergisms between alien trees and the Argentine ant on indigenous ant species in the Cape Floristic Region, South Africa. Afr Entomol 19:96–105
Seymour CL, Simmons RE, Morling F, George ST, Peters K, O’Riain MJ (2020) Caught on camera: The impacts of urban domestic cats on wild prey in an African city and neighbouring protected areas. Global Ecol Conserv 23:e01187
Shackleton RT, Le Maitre DC, Richardson DM, van Wilgen BW (2015) The impact of invasive alien Prosopis species (mesquite) on native plants in different environments in South Africa. S Afr J Bot 97:25–31
Shackleton RT, Le Maitre DC, van Wilgen BW, Richardson DM (2017) Towards a national strategy to optimise the management of a widespread invasive tree (Prosopis: mesquite) in South Africa. Ecosystem Services 27:242–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2016.11.022
Shelton JM, Samways MJ, Day JA (2015a) Predatory impact of non-native rainbow trout on endemic fish populations in headwater streams in the Cape Floristic Region of South Africa. Biol Invasions 17:365–379
Shelton JM, Samways MJ, Day JA (2015b) Non-native rainbow trout change the structure of benthic communities in headwater streams of the Cape Floristic Region, South Africa. Hydrobiologia 745:1–15
Simberloff D (1996) Hybridization between native and introduced wildlife species: importance for conservation. Wildl Biol 2:143–150
Steenkamp HE, Chown SL (1996) Influence of dense stands of an exotic tree, Prosopis glandulosa Benson, on a savanna dung beetle (Coleoptera: Scarabaeinae) assemblage in southern Africa. Biol Conserv 78:305–311
Strobel GA, Lanier GN (1981) Dutch elm disease. Sci Am 245:56–67
Taylor MR, Peacock F, Wanless RW (2015) The Eskom red data book of birds of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland. Birdlife South Africa, Johannesburg
Tererai F, Gaertner M, Jacobs SM, Richardson DM (2013) Eucalyptus invasions in riparian forests: effects on native vegetation community diversity, stand structure and composition. For Ecol Manage 297:84–93
Turpie J, Forsythe K, Seyler H, Howard G, Letley G (2019) Identification of priority areas for clearing invasive alien plants from Greater Cape Town’s water supply catchment areas. Technical Report No: AEC/1762/1, Anchor Environmental, Cape Town
Turpie J, Heydenrych B (2000) Economic consequences of alien infestation of the Cape Floral Kingdom’s Fynbos vegetation. In: Perrings C, Williamson M, Dalmazzone S (eds) The economics of biological invasions. Edward Elgar, Cheltenham, pp 152–182
van der Merwe M, Dippenaar-Schoeman AS, Scholtz CH (1996) Diversity of ground-living spiders at Ngome State Forest, KwazuluNatal: a comparative survey in indigenous forest and pine plantations. Afr J Ecol 34:342–350
van Helden L, van Helden PD, Meiring C (2020) Pathogens of vertebrate animals as invasive species: insights from South Africa. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya TA (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 249–274
van Lill WS, Kruger FJ, van Wyk DB (1980) The effect of afforestation with Eucalyptus grandis Hill ex Maiden and Pinus patula Schlecht. et Cham. on streamflow from experimental catchments at Mokobulaan, Transvaal. J Hydrol 48:107–118
van Sittert L (2002) Our irrepressible fellow-colonist: the biological invasion of prickly pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) in the Eastern Cape c.1890 - c.1910. J Hist Geogr 28:397–419
van Wilgen BW (2020) A brief, selective history of researchers and research initiatives related to biological invasions in South Africa. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya TA (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 31–63
van Wilgen BW, Carruthers J, Cowling RM, Esler KJ, Forsyth AT, Gaertner M, Hoffmann MT, Kruger FJ, Midgley GF, Richardson DM, Palmer G, Pence GQK, Raimondo D, van Wilgen NJ, Wilson JRU (2016) Ecological research and conservation management in the Cape Floristic Region between 1945 and 2015: History, current understanding and future challenges. Trans Roy Soc S Afr 71:207–304
van Wilgen BW, Cowling RM, Burgers CJ (1996) Valuation of ecosystem services: a case study from the fynbos, South Africa. Bioscience 46:184–189
van Wilgen BW, Davies SJ, Richardson DM (2014) Invasion science for society: a decade of contributions from the Centre for Invasion Biology. S Afr J Sci. https://doi.org/10.1590/sajs.2014/a0074
van Wilgen BW, de Wit MP, Anderson HJ, Le Maitre DC, Kotze IM, Ndala S, Brown B, Rapholo MB (2004) Costs and benefits of biological control of invasive alien plants: case studies from South Africa. S Afr J Sci 100:113–122
van Wilgen BW, Le Maitre DC, Cowling RM (1998) Ecosystem services, efficiency, sustainability and equity: South Africa’s Working for Water programme. Trends Ecol Evol 13:378
van Wilgen BW, Measey GJ, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya T (eds) (2020a) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham
van Wilgen BW, Measey GJ, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya T (2020b) Biological invasions in South Africa: An overview. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya TA (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 3–29
van Wilgen BW, Reyers B, Le Maitre DC, Richardson DM, Schonegevel L (2008) A biome-scale assessment of the impact of invasive alien plants on ecosystem services in South Africa. J Environm Manage 89:336–349
van Wilgen BW, Richardson DM (1985) The effects of alien shrub invasions on vegetation structure and fire behavior in South African fynbos shrublands: a simulation study. J Appl Ecol 22:955–966
van Wilgen BW, Richardson DM (2012) Three centuries of managing introduced conifers in South Africa: benefits, impacts, changing perceptions and conflict resolution. J Environm Manage 106:56–68
van Wilgen BW, Scott DF (2001) Managing fires on the Cape Peninsula: dealing with the inevitable. J Medit Ecol 2:197–208
van Wilgen BW, Wannenburgh A (2016) Co-facilitating invasive species control, water conservation and poverty relief: achievements and challenges in South Africa’s Working for Water programme. Curr Opin Environm Sust 19:7–17
van Wilgen BW, Wilson JR (eds) (2018) The status of biological invasions and their management in South Africa 2017. South African National Biodiversity Institute, Kirstenbosch and DST-NRF Centre of Excellence for Invasion Biology, Stellenbosch
van Wilgen BW, Little PR, Chapman RA, Görgens AHM, Willems T, Marais C (1997) The sustainable development of water resources: history, financial costs and benefits of alien plant control programmes. S Afr J Sci 93:404–411
van Wilgen NJ, van Wilgen BW, Midgley GF (2020) Biological invasions as a component of South Africa’s global change research effort. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey GJ, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya T (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Berlin, pp 835–857
van Wyk DB (1987) Some effects of afforestation on streamflow in the western Cape Province, South Africa. Water SA 13:31–36
Vilà M, Hulme PE (eds) (2017) Impact of biological invasions on ecosystem services. Springer, Cham
Visser BG, Hockey PAR, Dean WRJ (2002) Breeding behavior and performance of the Knysna Warbler Bradypterus sylvaticus on the Cape Peninsula, South Africa. Ostrich 73:83–86
Visser V, Wilson JRU, Canavan K et al (2017) Grasses as invasive plants in South Africa revisited: patterns, pathways and management. Bothalia 47(2):a2169. https://doi.org/10.4102/abc.v47i2.2169
Watkins BP, Cooper J (1986) Introduction, present status and control of alien species at the Prince Edward islands. S Afr J Antarct Res 16:86–94
Wilson JRU, Faulkner KT, Rahlao SJ, Richardson DM, Zengeya TA, van Wilgen BW (2018) Indicators for monitoring biological invasions at a national level. J Appl Ecol 55:2612–2620
Wilson JR, Foxcroft LC, Geerts S, Hoffman TM, MacFadyen S, Measey J, Mills A, Richardson DM, Robertson MP, van Wilgen BW (2020) The role of environmental factors in promoting and limiting biological invasions in South Africa. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey J, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya TA (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 355–385
Wise RM, van Wilgen BW, Hill MP, Schulthess F, Tweddle D, Chabi-Olay A, Zimmermann HG (2008) The economic impact and appropriate management of selected invasive alien species on the African continent. CSIR report number: CSIR/NRE/RBSD/ER/2007/0044/C, Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, Pretoria
Wise RM, van Wilgen BW, Le Maitre DC (2012) Costs, benefits and management options for an invasive alien tree species: the case of mesquite in the Northern Cape. J Arid Environm 84:80–90
Woodford DJ, Impson ND, Day JA, Bills IR (2005) The predatory impact of invasive alien smallmouth bass, Micropterus dolomieu (Teleostei: Centrarchidae), on indigenous fishes in a Cape Floristic Region mountain stream. African J Aquat Sci 30:167–173
Woodford DJ, Richardson DM, MacIsaac HJ, Mandrak NE, van Wilgen BW, Wilson JRU, Weyl OLF (2016) Confronting the wicked problem of managing biological invasions. NeoBiota 31:63–86
Yapi TS, O’Farrell PJ, Dziba LE, Esler KJ (2018) Alien tree invasion into a South African montane grassland ecosystem: impact of Acacia species on rangeland condition and livestock carrying capacity. Int J Biodiv Sci Ecosys Serv Manage 14:105–116
Yelenik SG, Stock WD, Richardson DM (2004) Ecosystem level impacts of invasive Acacia saligna in the South African Fynbos. Rest Ecol 12:44–51
Zengeya T, Ivey P, Woodford D, Weyl OLF, Novoa A, Shackleton R, Richardson DM, van Wilgen BW (2017) Managing conflict-generating invasive species in South Africa: challenges and trade-offs. Bothalia 47(2):a2160. https://doi.org/10.4102/abc.v47i2.2160
Zengeya TA, Kumschick S, Weyl OLF, van Wilgen BW (2020) An evaluation of the impacts of alien species on biodiversity in South Africa using different assessment methods. In: van Wilgen BW, Measey GJ, Richardson DM, Wilson JR, Zengeya T (eds) Biological invasions in South Africa. Springer, Cham, pp 475–499
Zengeya TA, Wilson JR (eds) (2020) The status of biological invasions and their management in South Africa in 2019. South African National Biodiversity Institute, Kirstenbosch and DSI-NRF Centre of Excellence for Invasion Biology, Stellenbosch
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support for research on biological invasions in South Africa over 17 years from the DSI-NRF Centre of Excellence for Invasion Biology. Many colleagues kindly supplied information or discussed diverse issues pertaining to impacts with us during the preparation of this review. We are particularly grateful to Charles Griffiths, Dai Herbert, Sabrina Kumschick, Nelson Miranda, Tammy Robinson and Jane Turpie. John Wilson provided valuable comments on an earlier draft of this paper. We dedicate this paper to the memory of our late colleague and friend Olaf Weyl, freshwater ecologist extraordinaire, enthusiastic collaborator, and mentor to many students. His insights into the impacts of biological invasions on South Africa’s freshwater ecosystems will be sorely missed.
Funding
This work was funded by the DSI-NRF Centre for Invasion Biology, the National Research Foundation for South Africa (grants 109467, 103602, and 85417 to BvW, TAZ and DMR respectively), the South African National Biodiversity Institute and the Millennium Trust. DMR acknowledges support from the Oppenheimer Memorial Trust (grant 18576/03). TAZ thanks the South African Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BvW and DMR initiated the review. BvW sourced material, conducted the classifications and wrote the paper. DMR and TZ sourced additional material and worked on various drafts of the paper. All authors read and approved the final version before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts or competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Wilgen, B.W., Zengeya, T.A. & Richardson, D.M. A review of the impacts of biological invasions in South Africa. Biol Invasions 24, 27–50 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-021-02623-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-021-02623-3