Abstract
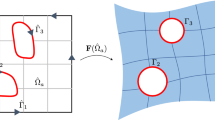
The discretization of the computational domain plays a central role in the finite element method. In the standard discretization the domain is triangulated with a mesh and its boundary is approximated by a polygon. The boundary approximation induces a geometry-related error which influences the accuracy of the solution. To control this geometry-related error, iso-parametric finite elements and iso-geometric analysis allow for high order approximation of smooth boundary features. We present an alternative approach which combines parametric finite elements with smooth bijective mappings leaving the choice of approximation spaces free. Our approach allows to represent arbitrarily complex geometries on coarse meshes with curved edges, regardless of the domain boundary complexity. The main idea is to use a bijective mapping for automatically warping the volume of a simple parameterization domain to the complex computational domain, thus creating a curved mesh of the latter. Numerical examples provide evidence that our method has lower approximation error for domains with complex shapes than the standard finite element method, because we are able to solve the problem directly on the exact domain without having to approximate it.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aigner, M., Heinrich, C., Jüttler, B., Pilgerstorfer, E., Simeon, B., Vuong, A.V.: Swept Volume Parameterization for Isogeometric Analysis. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Bathe, K.J., Wilson, E.L.: Numerical methods in finite element analysis. AMC 10, 12 (1976)
Bazilevs, Y., Michler, C., Calo, V., Hughes, T.: Isogeometric variational multiscale modeling of wall-bounded turbulent flows with weakly enforced boundary conditions on unstretched meshes. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199(13–16), 780–790 (2010)
Bertrand, F., Mun̈zenmaier, S., Starke, G.: First-order system least squares on curved boundaries: higher-order Raviart–Thomas elements. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 52(6), 3165–3180 (2014)
Bertrand, F., Mun̈zenmaier, S., Starke, G.: First-order system least squares on curved boundaries: lowest-order Raviart–Thomas elements. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 52(2), 880–894 (2014)
Bey, J.: Tetrahedral grid refinement. Computing 55, 355–378 (1995)
Braess, D.: Finite Elements, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2007)
Bramble, J.H., Pasciak, J.E., Steinbach, O.: On the stability of the L\(^2\)-projections in H\(^1\). Math. Comput. 71(237), 147–156 (2002)
Brenner, S., Scott, R.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods, Texts in Applied Mathematics, vol. 15. Springer, New York (2008)
Briggs, W.L., Henson, V.E., McCormick, S.F.: A Multigrid Tutorial, 2nd edn. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia (2000)
Ciarlet, P.G., Raviart, P.A.: Interpolation theory over curved elements, with applications to finite element methods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1(2), 217–249 (1972)
Dickopf, T., Krause, R.: Monotone Multigrid Methods Based on Parametric Finite Elements. Submitted to Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering. Technical Report, ICS, USI (2011)
Dörfler, W., Rumpf, M.: An adaptive strategy for elliptic problems including a posteriori controlled boundary approximation. Math. Comput. Am. Math. Soc. 67(224), 1361–1382 (1998)
Eck, M., DeRose, T., Duchamp, T., Hoppe, H., Lounsbery, M., Stuetzle, W.: Multiresolution analysis of arbitrary meshes. In: Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH ’95, pp. 173–182. ACM (1995)
Erikson, A.P., Åström, K.: On the bijectivity of thin-plate splines. In: Åström, K, Persson, L.E., Silvestrov, S.D. (eds.) Analysis for Science, Engineering and Beyond: The Tribute Workshop in Honour of Gunnar Sparr held in Lund, May 8–9, 2008, pp. 93–141. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2012)
Floater, M.S.: Mean value coordinates. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 20(1), 19–27 (2003)
Greco, F., Sukumar, N.: Derivatives of maximum-entropy basis functions on the boundary: theory and computations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 94(12), 1123–1149 (2013)
Hackbusch, W.: Multi-Grid Methods and Applications, Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 4. Springer, Berlin (1985)
Hormann, K., Sukumar, N.: Maximum entropy coordinates for arbitrary polytopes. Comput. Graph. Forum 27(5), 1513–1520 (2008)
Hughes, T.J., Cottrell, J.A., Bazilevs, Y.: Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 194(39), 4135–4195 (2005)
Jacobson, A.: Bijective Mappings with Generalized Barycentric Coordinates: A Counterexample. Technical Report, Department of Computer Science, ETH Zurich (2012)
Ju, T., Schaefer, S., Warren, J.: Mean value coordinates for closed triangular meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 24(3), 561–566 (2005)
Khronos OpenCL Working Group: The OpenCL Specification, version 1.0.29. http://khronos.org/registry/cl/specs/opencl-1.0.29.pdf (2008)
Kikuchi, N., Oden, J.T.: Contact Problems in Elasticity: A Study of Variational Inequalities and Finite Element Methods, vol. 8. SIAM, Philadelphia (1988)
Krause, R., Sander, O.: Automatic construction of boundary parametrizations for geometric multigrid solvers. Comput. Vis. Sci. 9(1), 11–22 (2006)
Krause, R., Zulian, P.: A parallel approach to the variational transfer of discrete fields between arbitrarily distributed finite element meshes. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 38(3), C307–C333 (2016)
Lee, A.W., Sweldens, W., Schröder, P., Cowsar, L., Dobkin, D.: Maps: multiresolution adaptive parameterization of surfaces. In: Proceedings of the 25th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, pp. 95–104. ACM (1998)
Li, B., Li, X., Wang, K., Qin, H.: Surface mesh to volumetric spline conversion with generalized polycubes. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 19(9), 1539–1551 (2013)
Lian, H., Bordas, S.P.A., Sevilla, R., Simpson, R.N.: Recent Developments in CAD/Analysis Integration. ArXiv e-prints (2012)
Luo, X., Shephard, M.S., Remacle, J.F.: The influence of geometric approximation on the accuracy of high order methods. Rensselaer SCOREC Report, vol. 1 (2001)
Martin, T., Cohen, E.: Volumetric parameterization of complex objects by respecting multiple materials. Comput. Graph. 34(3), 187–197 (2010)
McKeeman, W.M.: Algorithm 145: adaptive numerical integration by Simpson’s rule. Commun. ACM 5(12), 604–608 (1962)
Melenk, J., Wohlmuth, B.: On residual-based a posteriori error estimation in hp-fem. Adv. Comput. Math. 15(1), 311–331 (2001)
Randrianarivony, M.: Tetrahedral Transfinite Interpolation with B-patch Faces: Construction and Regularity, vol. 803. INS Preprint (2008)
Randrianarivony, M.: On transfinite interpolations with respect to convex domains. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 28(2), 135–149 (2011)
Schneider, T., Hormann, K.: Smooth bijective maps between arbitrary planar polygons. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 35–36(c), 243–354 (2015)
Schneider, T., Hormann, K., Floater, M.S.: Bijective composite mean value mappings. Comput. Graph. Forum 32(5), 137–146 (2013)
Scott, L.R.: Finite element techniques for curved boundaries. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1973)
Scott, R.: Interpolated boundary conditions in the finite element method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 12(3), 404–427 (1975)
Sevilla, R., Fernández-Méndez, S., Huerta, A.: Nurbs-enhanced finite element method (nefem). Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 18(4), 441–484 (2011)
Thiery, J.M., Tierny, J., Boubekeur, T.: Jacobians and Hessians of mean value coordinates for closed triangular meshes. Vis. Comput. 30(9), 981–995 (2014)
Wohlmuth, B.I.: A mortar finite element method using dual spaces for the Lagrange multiplier. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 38, 989–1012 (1998)
Xue, D., Demkowicz, L., et al.: Control of geometry induced error in hp finite element (fe) simulations. I. Evaluation of fe error for curvilinear geometries. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model 2(3), 283–300 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the SNF under Project Number 200020_156178, SCCER-SoE, and SCCER-FURIES. The method presented in this paper is implemented within the MOONoLith software library. We thank the anonymous reviewers for their useful comments which helped improving both content and presentation of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zulian, P., Schneider, T., Hormann, K. et al. Parametric finite elements with bijective mappings. Bit Numer Math 57, 1185–1203 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-017-0669-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-017-0669-6
Keywords
- Finite element method
- Discretization
- Barycentric coordinates
- Bijective mapping
- Super parametric
- Parametrization