Abstract
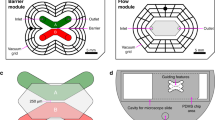
We present a method for depositing cells in the microchambers of a sealed microfluidic device and establishing flow across the chambers independently and serially. The device comprises a transparent poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) microfluidic network (MFN) having 2 cell chambers with a volume of 0.49 µL, 6 microchannels for servicing the chambers, and 1 microchannel linking both chambers. The MFN is sealed with a Si chip having 6 vias and ports that can be left open or connected to high-precision pumps. Liquids are drawn through each chamber in parallel or sequentially at flow rates from 0.1 to 10 µL min−1. Plugs of liquid as small as 0.5 µL can be passed in one chamber within 5 s to 5 min. Plugs of liquid can also be introduced into a chamber for residence times of up to 30 min. By injecting different liquids into 3 ports, 3 adjacent laminar streams of liquid can be drawn inside one chamber with lateral concentration gradients between the streams ranging from 20 to 500 µm. The flexibility of this device for depositing cells and exposing them to liquids in parallel or serially is illustrated by depositing two types of cells, murine N9 microglia and human SH-S5Y5 neuroblastoma. Microfluidic communication between the chambers is illustrated by stimulating N9 microglia using ATP to induce these cells to release plasma membrane vesicles. The vesicles are drawn through the second chamber containing neuroblastoma and collected in a port of the device for off-chip analysis using confocal fluorescence microscopy. Cells in the MFN can also be fixed using a solution of formaldehyde for further analysis after disassembly of the MFN and Si lid. This microfluidic device offers a simple, flexible, and powerful method for depositing two cell populations in separate chambers and may help investigating pathways between the cells populations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Bianco, E. Pravettoni, A. Colombo, U. Schenk, T. Moeller, M. Matteoli, C.J. Verderio, J. Immunol. 174, 7268–7277 (2005)
F. Bianco, C. Perrotta, L. Novellino, M. Francolini, L. Riganti, E. Menna, L. Saglietti, E.H. Schuchman, R. Furlan, E. Clementi, M. Matteoli, C. Verderio, EMBO J. 28, 1043–1054 (2009)
D.N. Breslauer, P.J. Lee, L.P. Lee, Mol. BioSyst. 2, 97–112 (2006)
S. Cesaro-Tadic, G. Dernick, D. Juncker, G. Buurman, H. Kropshofer, B. Michel, C. Fattinger, E. Delamarche, Lab Chip 4, 563–569 (2004)
S. Chung, R. Sudo, P.J. Mack, C.-R. Wan, V. Vickerman, R.D. Kamm, Lab Chip 9, 269–275 (2009)
J.L. DeRisi, V.R. Iyer, P.O. Brown, Science 278, 680–686 (1997)
J. El-Ali, P.K. Sorger, K.F. Jensen, Nature 442, 403–411 (2006)
E. Figallo, C. Cannizzaro, S. Gerecht, J.A. Burdick, R. Langer, N. Elvassore, G. Vunjak-Novakovic, Lab Chip 7, 710–719 (2007)
D. Gerber, S. Maerkl, S.R. Quake, Nat. Methods 6, 71–74 (2008)
G. Hu, D. Li, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 6, 99–107 (2009)
P.J. Hung, P.J. Lee, P. Sabounchi, N. Aghdam, R. Lin, L.P. Lee, Lab Chip 5, 44–48 (2005)
H. Kaji, T. Yokoi, T. Kawashima, M. Nishizawa, Lab Chip 9, 427–432 (2009)
A. Khademhosseini, J. Yeh, G. Eng, J. Karp, H. Kaji, J. Borenstein, O.C. Farokhzad, R. Langer, Lab Chip 5, 1380–1386 (2005)
L. Kim, Y.C. Toh, J. Voldman, H. Yu, Lab Chip 7, 681–694 (2007)
P.J. Lee, P.J. Hung, R. Shaw, L. Jan, L.P. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 223902–3 (2005)
N.M. Lewandowski, S.A. Small, J. Neurosci. 25, 10341–10346 (2005)
N. Li, A. Tourovskaia, A. Folch, Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng 31, 423–488 (2003)
D.J. Lockhart, H. Dong, M.C. Byrne, M.T. Follettie, M.V. Gallo, M.S. Chee, M. Mittmann, C. Wang, M. Kobayashi, H. Horton, E.L. Brown, Nat. Biotechnol. 14, 1675–1680 (1996)
R.D. Lovchik, C. von Arx, A. Viviani, E. Delamarche, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 390, 801–808 (2008)
R.D. Lovchik, F. Bianco, M. Matteoli, E. Delamarche, Lab Chip 9, 1395–1402 (2009)
E.M. Lucchetta, J.H. Lee, L.A. Fu, N.H. Patel, R.F. Ismagilov, Nature 434, 1134–1138 (2005)
S.H. Ma, L.A. Lepak, R.J. Hussain, W. Shain, M.L. Shuler, Lab Chip 5, 74–85 (2005)
I. Meyvantsson, D.J. Beebe, Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1, 423–449 (2008)
P.S. Mischel, T.F. Cloughesy, S.F. Nelson, Lab Chip 5, 782–792 (2004)
A. Piruska, I. Nikcevic, S.H. Lee, C. Ahn, W.R. Heineman, P.A. Limbach, C.J. Seliskar, Lab Chip 5, 1348–1354 (2005)
A. Prokop, Z. Prokop, D. Schaffer, E. Kozlov, J. Wikswo, D. Cliffel, F. Baudenbacher, Biomed. Microdev. 6, 325–339 (2004)
W. Streit, Brain Res. Rev. 48, 234–239 (2005)
J.H. Sung, M.L. Shuler, Lab Chip 9, 1385–1394 (2009)
S. Takayama, E. Ostuni, P. LeDuc, K. Naruse, D.E. Ingber, G.M. Whitesides, Nature 411, 1016 (2001)
A.M. Taylor, S.W. Rhee, C.H. Tu, D.H. Cribbs, C.W. Cotman, N.L. Jeon, Langmuir 19, 1551–1556 (2003)
P.A. Verhoef, M. Estacion, W. Schilling, G.R. Dubyak, J. Immunol. 170, 5728–5738 (2003)
G.M. Whitesides, E. Ostuni, S. Takayama, X.Y. Jiang, D.E. Ingber, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 3, 335–373 (2001)
Y.N. Xia, G.M. Whitesides, Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 37, 550–575 (1998)
J.H. Yeon, J.-K. Park, Biochip J. 1, 17–27 (2007)
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Stutz for his help with the fabrication of the Si chips and molds for the PDMS MFNs, L. Gervais and C. Verderio for discussions, and W. Riess and M. Despont for their continuous support. This work was partially supported by CARIPLO n. 2006-0948 to MM and by MIUR art. 11 D.M. n. 593/2000 to MM and FB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lovchik, R.D., Tonna, N., Bianco, F. et al. A microfluidic device for depositing and addressing two cell populations with intercellular population communication capability. Biomed Microdevices 12, 275–282 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9382-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9382-9