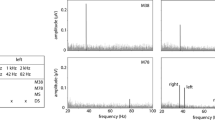
Abstract
The acoustic envelope of human speech correlates with the syllabic rate (4–8 Hz) and carries important information for intelligibility, which is typically compromised in multi-talker, noisy environments. In order to better understand the dynamics of selective auditory attention to low frequency modulated sound sources, we conducted a two-stream auditory steady-state response (ASSR) selective attention electroencephalogram (EEG) study. The two streams consisted of 4 and 7 Hz amplitude and frequency modulated sounds presented from the left and right side. One of two streams had to be attended while the other had to be ignored. The attended stream always contained a target, allowing for the behavioral confirmation of the attention manipulation. EEG ASSR power analysis revealed a significant increase in 7 Hz power for the attend compared to the ignore conditions. There was no significant difference in 4 Hz power when the 4 Hz stream had to be attended compared to when it had to be ignored. This lack of 4 Hz attention modulation could be explained by a distracting effect of a third frequency at 3 Hz (beat frequency) perceivable when the 4 and 7 Hz streams are presented simultaneously. Taken together our results show that low frequency modulations at syllabic rate are modulated by selective spatial attention. Whether attention effects act as enhancement of the attended stream or suppression of to be ignored stream may depend on how well auditory streams can be segregated.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The modulation index defines the ratio between the frequency deviation (Hz) and the modulation rate (Hz).
Abbreviations
- ASSR:
-
Auditory steady-state response
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalogram
References
Aiken SJ, Picton TW (2008) Human cortical responses to the speech envelope. Ear Hear 29:139–157
Akram S, Englitz B, Elhilali M, Simon JZ, Shamma SA (2014) Investigating the neural correlates of a streaming percept in an informational-masking paradigm. PLoS ONE 9:e114427. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114427
Bharadwaj HM, Lee AK, Shinn-Cunningham BG (2014a) Measuring auditory selective attention using frequency tagging. Front Integr Neurosci 8:6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2014.00006
Bharadwaj HM, Verhulst S, Shaheen L, Liberman MC, Shinn-Cunningham BG (2014b) Cochlear neuropathy and the coding of supra-threshold sound. Front Syst Neurosci 8:26. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2014.00026
Bidet-Caulet A, Fischer C, Besle J, Aguera PE, Giard MH, Bertrand O (2007) Effects of selective attention on the electrophysiological representation of concurrent sounds in the human auditory cortex. J Neuros 27:9252–9261. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1402-07.2007
Choi I, Rajaram S, Varghese LA, Shinn-Cunningham BG (2013) Quantifying attentional modulation of auditory-evoked cortical responses from single-trial electroencephalography. Front Hum Neurosci 7:115. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00115
Choi I, Wang L, Bharadwaj H, Shinn-Cunningham B (2014) Individual differences in attentional modulation of cortical responses correlate with selective attention performance. Hear Res 314:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2014.04.008
Cusack R, Deeks J, Aikman G, Carlyon RP (2004) Effects of location, frequency region, and time course of selective attention on auditory scene analysis. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 30:643–656. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.30.4.643
Dau T (1996) Modeling auditory processing of amplitude modulation. Ph.D. thesis, Universität Oldenburg, Germany
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134:9–12
Ding N, Simon JZ (2012) Emergence of neural encoding of auditory objects while listening to competing speakers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:11854–11859. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1205381109
Ding N, Simon JZ (2013) Adaptive temporal encoding leads to a background-insensitive cortical representation of speech. J Neurosci 33:5728–5735. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5297-12.2013
Ding N, Simon JZ (2014) Cortical entrainment to continuous speech: functional roles and interpretations. Front Hum Neurosci 8:311. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00311
Doelling KB, Arnal LH, Ghitza O, Poeppel D (2014) Acoustic landmarks drive delta-theta oscillations to enable speech comprehension by facilitating perceptual parsing. NeuroImage 85 Pt 2:761–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.06.035
Doherty KA, Lutfi RA (1999) Level discrimination of single tones in multitone complex by normal-hearing and hearing-imaired listeners. J Acoust Soc Am 105:1831–1840
Draganova R, Ross B, Borgmann C, Pantev C (2002) Auditory cortical response patterns to multiple rhythms of AM sounds. Ear Hear 23:254–265
Draganova R, Ross B, Wollbrink A, Pantev C (2008) Cortical steady-state responses to central and peripheral auditory beats. Cereb Cortex 18:1193–1200. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhm153
Drullman R, Festen JM, Plomp R (1994a) Effect of reducing slow temporal modulations on speech reception. J Acoust Soc Am 95:2670–2680
Drullman R, Festen JM, Plomp R (1994b) Effect of temporal envelope smearing on speech reception. J Acoust Soc Am 95:1053–1064
Dubno JR (1984) Effects of age and mild hearing loss on speech recognition in noise. J Acoust Soc Am 76:87. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.391011
Elhilali M, Xiang J, Shamma SA, Simon JZ (2009) Interaction between attention and bottom-up saliency mediates the representation of foreground and background in an auditory scene. PLoS Biol 7:e1000129. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000129
Fritz JB, Elhilali M, David SV, Shamma SA (2007) Auditory attention–focusing the searchlight on sound. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17:437–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2007.07.011
Galambos R, Makeig S, Talmachoff PJ (1981) A 40-Hz auditory potential recorded from the human scalp. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:2643–2647
Gallun FJ, Diedesch AC, Kampel SD, Jakien KM (2013) Independent impacts of age and hearing loss on spatial release in a complex auditory environment. Front Neurosci 7:252. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2013.00252
Gasser T, Bächer P, Möcks J (1982) Transformations towards the normal distribution of broad band spectral parameters of the EEG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 53:119–124
Giani AS, Ortiz E, Belardinelli P, Kleiner M, Preissl H, Noppeney U (2012) Steady-state responses in MEG demonstrate information integration within but not across the auditory and visual senses. NeuroImage 60:1478–1489 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.01.114
Giraud AL, Lorenzi C, Ashburner J, Wable J, Johnsrude I, Frackowiak RS, Kleinschmidt A (2000) Representation of the temporal envelope of sounds in the human brain. J Neurophysiol 84:1588–1598
Glyde H, Cameron S, Dillon H, Hickson L, Seeto M (2013) The effect of hearing impairment and aging on spatial processing. Ear Hear 34:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1097/AUD.0b013e3182617f94
Herdman AT (2011) Neuroimaging evidence for top-down maturation of selective auditory attention. Brain Topogr 24:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-011-0182-1
Herdman AT, Stapells DR (2001) Thresholds determined using the monotic and dichotic multiple auditory steady-state response technique in normal-hearing subjects. Scand Audiol 30:41–49
Herdman AT, Picton TW, Stapells DR (2002) Place specificity of multiple auditory steady-state responses. J Acoust Soc Am 112:1569–1582. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1506367
Hillyard SA, Hink RF, Schwent VL, Picton TW (1973) Electrical signs of selective attention in the human brain. Science 182:177–180
Hillyard SA, Vogel EK, Luck SJ (1998) Sensory gain control (amplification) as a mechanism of selective attention: electrophysiological and neuroimaging evidence. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 353:1257–1270
John MS, Lins OG, Boucher BL, Picton TW (1998) Multiple auditory steady-state responses (MASTER): stimulus and recording parameters. Int J Audiol 37:59–82. https://doi.org/10.3109/00206099809072962
John MS, Purcell D, Dimitrijevic A, Picton TW (2002) Advantages and caveats when recording steady-state responses to multiple simultaneous stimuli. J Am Acad Audiol 13:246–259
Jung TP, Makeig SH, Lee C, McKeown TW, Iragui MJ V (2000a) Removing electroencephalographic artifacts by blind source separation. Psychophysiologie 37:163–178
Jung TP, Makeig SW, Townsend M, Courchesne J, Sejnowski E TJ (2000b) Removal of eye activity artifacts from visual eventrelated potentials in normal and clinical subjects. Clin Neurophysiol 111:1745–1758
Kayser J, Tenke CE (2006) Principal components analysis of Laplacian waveforms as a generic method for identifying ERP generator patterns: I. Evaluation with auditory oddball tasks. Clin Neurophysiol 117:348–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2005.08.034
Kayser J, Tenke CE (2015) Issues and considerations for using the scalp surface Laplacian in EEG/ERP research: a tutorial review. Int J Psychophysiol https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2015.04.012
Kerlin JR, Shahin AJ, Miller LM (2010) Attentional gain control of ongoing cortical speech representations in a “cocktail party”. J Neurosci 30:620–628. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3631-09.2010
Kidd G Jr, Mason CR, Best V, Marrone N (2010) Stimulus factors influencing spatial release from speech-on-speech masking. J Acoust Soc Am 128:1965–1978. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.3478781
Kidd GR, Watson CS, Gygi B (2007) Individual differences in auditory abilities. J Acoust Soc Am 122:418–435. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.2743154
Kocsis Z, Winkler I, Szalardy O, Bendixen A (2014) Effects of multiple congruent cues on concurrent sound segregation during passive and active listening: an event-related potential (ERP) study. Biol Psychol 100:20–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2014.04.005
Kohlrausch A, Fassel R, Dau T (2000) The influence of carrier level and frequency on modulation and beat-detection thresholds for sinusoidal carriers. J Acoust Soc Am 108:723–734
Kubanek J, Brunner P, Gunduz A, Poeppel D, Schalk G (2013) The tracking of speech envelope in the human cortex. PLoS ONE 8:e53398. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053398
Liegeois-Chauvel C, Lorenzi C, Trebuchon A, Regis J, Chauvel P (2004) Temporal envelope processing in the human left and right auditory cortices. Cereb Cortex 14:731–740. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhh033
Linden RD, Picton TW, Hamel G, Campbell KB (1987) Human auditory steady-state evoked potentials during selective attention. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 66:145–159
Lins OG, Picton TW (1995) Auditory steady-state responses to multiple simultaneous stimuli. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 96:420–432
Luo H, Poeppel D (2007) Phase patterns of neuronal responses reliably discriminate speech in human auditory cortex. Neuron 54:1001–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2007.06.004
Mahajan Y, Davis C, Kim J (2014) Attentional modulation of auditory steady-state response. PLoS ONE 9:e110902. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110902
Middlebrooks JC, Onsan ZA (2012) Stream segregation with high spatial acuity. J Acoust Soc Am 132:3896–3911. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4764879
Mirkovic B, Debener S, Jaeger M, De Vos M (2015) Decoding the attended speech stream with multi-channel EEG: implications for online, daily-life applications. J Neural Eng 12:046007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/12/4/046007
Müller N, Schlee W, Hartmann T, Lorenz I, Weisz N (2009) Top-down modulation of the auditory steady-state response in a task-switch paradigm. Front Hum Neurosci 3:1. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.09.001.2009
Norcia AM, Appelbaum LG, Ales JM, Cottereau BR, Rossion B (2015) The steady-state visual evoked potential in vision research: a review. J Vis 15
Nourski KV et al (2009) Temporal envelope of time-compressed speech represented in the human auditory cortex. J Neurosci 29:15564–15574. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3065-09.2009
Oster G (1973) Auditory beats in the brain. Sci Am 229:94–102
Peissig J, Kollmeier B (1997) Directivity of binaural noise reduction in spatial multiple noise-source arrangements for normal and impaired listeners. J Acoust Soc Am 101:1660–1670
Perrin F, Pernier J, Bertrand O, Echallier JF (1989) Spherical splines for scalp potential and current density mapping. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 72:184–187
Picton TW, Skinner CR, Champagne SC, Kellett AJC, Maiste AC (1987) Potentials evoked by the sinusoidal modulation of the amplitude or frequency of a tone. J Acoust Soc Am 82:165–178
Picton TW, John MS, Dimitrijevic A, Purcell D (2003) Human auditory steady-state responses. Int J Audiol 42:177–219
Poeppel D (2003) The analysis of speech in different temporal integration windows: cerebral lateralization as ‘asymmetric sampling in time’. Speech Commun 41:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-6393(02)00107-3
Rees A, Green GG, Kay RH (1986) Steady-state evoked responses to sinusoidally amplitude-modulated sounds recorded in man. Hear Res 23:123–133
Riecke L, Scharke W, Valente G, Gutschalk A (2014) Sustained selective attention to competing amplitude-modulations in human auditory cortex. PLoS ONE 9:e108045. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108045
Rimmele JM, Zion Golumbic E, Schroger E, Poeppel D (2015) The effects of selective attention and speech acoustics on neural speech-tracking in a multi-talker scene. Cortex 68:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2014.12.014
Roß B, Borgmann C, Draganova R, Roberts LE, Pantev C (2000) A high-precision magnetoencephalographic study of human auditory steady-state responses to amplitude-modulated tones. J Acoust Soc Am 108:679–691. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.429600
Ross B, Picton TW, Herdman AT, Pantev C (2004) The effect of attention on the auditory steady-state response. Neurol Clin Neurophysiol 22
Ruggles D, Shinn-Cunningham B (2011) Spatial selective auditory attention in the presence of reverberant energy: individual differences in normal-hearing listeners. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 12:395–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-010-0254-z
Ruggles D, Bharadwaj H, Shinn-Cunningham BG (2011) Normal hearing is not enough to guarantee robust encoding of suprathreshold features important in everyday communication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:15516–15521. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108912108
Sek A (1994) Modulation thresholds and critical modulation frequency based on random amplitude and frequency changes. J Acoust Soc Jpn 15:67–75
Shinn-Cunningham BG, Best V (2008) Selective attention in normal and impaired hearing. Trends Amplif 12:283–299. https://doi.org/10.1177/1084713808325306
Skosnik PD, Krishnan GP, O’Donnell BF (2007) The effect of selective attention on the gamma-band auditory steady-state response. Neurosci Lett 420:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2007.04.072
Sussman ES, Horvath J, Winkler I, Orr M (2007) The role of attention in the formation of auditory streams. Percept Psychophys 69:136–152
Tiitinen HT, Sinkkonen J, Reinikainen K, Alho K, Lavitainen J, Näätänen R (1993) Selective attention enhances the auditory 40-Hz transient response in humans. Nature 264:59–60
Weisz N, Lecaignard F, Muller N, Bertrand O (2012) The modulatory influence of a predictive cue on the auditory steady-state response. Hum Brain Mapp 33:1417–1430. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21294
Woldorff MG, Gallen CC, Hampson SA, Hillyard SA, Pantev C, Sobel D, Bloom FE (1993) Modulation of early sensory processing in human auditory cortex during auditory selective attention. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8722–8726
Wostmann M, Herrmann B, Maess B, Obleser J (2016) Spatiotemporal dynamics of auditory attention synchronize with speech. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1523357113
Xiang J, Simon J, Elhilali M (2010) Competing streams at the cocktail party: exploring the mechanisms of attention and temporal integration. J Neurosci 30:12084–12093. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0827-10.2010
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG Cluster of Excellence 1077 “Hearing4all”) and the University of Oldenburg PhD program “Signals and Cognition” (Niedersächsisches Ministerium für Wissenschaft und Kultur, Hannover, Germany). We would like to thank Mareike Engelberts for her help in recruiting the participants and data collection. Additionally, we thank two anonymous reviewers for useful comments on a previous version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaeger, M., Bleichner, M.G., Bauer, AK.R. et al. Did You Listen to the Beat? Auditory Steady-State Responses in the Human Electroencephalogram at 4 and 7 Hz Modulation Rates Reflect Selective Attention. Brain Topogr 31, 811–826 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-018-0637-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-018-0637-8