Abstract
Background
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) has high incidence in Southern China and is derived from the mucosal epithelium of the nasopharynx. Accumulating evidence has revealed that peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (PAD4) exerts carcinogenic effect on certain cancers. We designed this study to probe the specific role that PAD4 plays in NPC and its molecular mechanism.
Methods
PAD4 expression in NPC cells was detected by RT-qPCR analysis. MTT, colony formation, flow cytometry, TUNEL staining, and LC3-II punctuation experiments were done to probe into the biological functions of PAD4 on NPC cellular behaviors in vitro. Subsequently, the upstream regulatory mechanism of PAD4 was investigated by luciferase reporter, RNA pull-down, and RIP assays. The impact of PAD4 on NPC tumor growth in mice was assessed by in vivo xenograft tumor assay.
Results
PAD4 was upregulated in NPC cells. PAD4 knockdown suppressed proliferative ability and promoted apoptosis and autophagy in NPC cells. Additionally, PAD4 expression was negatively regulated by microRNA 3164 (miR-3164). LINC00324 positively upregulated PAD4 expression by interacting with miR-3164 and recruiting HuR protein. The LINC00324/miR-3164/PAD4 axis modulated the PI3K/AKT pathway in NPC cells. Moreover, PAD4 upregulation countervailed the influences of LINC00324 deficiency on NPC cell proliferation, apoptosis, and autophagy and on NPC tumor growth in mice.
Conclusion
LINC00324 promoted NPC malignancy by upregulation of PAD4 to activate the PI3K/AKT pathway.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Afonso-Grunz F, Müller S. Principles of miRNA-mRNA interactions: beyond sequence complementarity. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS. 2015;72:3127–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-1922-2.
Aggarwal S, John S, Sapra L, Sharma SC, Das SN. Targeted disruption of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, via PI3K inhibitors, promotes growth inhibitory effects in oral cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019;83:451–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-018-3746-x.
Barroso MV, Gropillo I, Detoni MAA, Thompson-Souza GA, Muniz VS, Vasconcelos CRI, et al. Structural and signaling events driving aspergillus fumigatus-induced human eosinophil extracellular trap release. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:633696. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.633696.
Chan JJ, Tay Y. Noncoding RNA:RNA regulatory networks in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051310.
Chen G, Gu Y, Han P, Li Z, Zhao JL, Gao MZ. Long noncoding RNA SBF2-AS1 promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and invasion by inhibiting miR-619-5p activity and facilitating HDAC3 expression. J Cell Physiol. 2019a;234:18688–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28509.
Chen H, Tang X, Liu T, Jing L, Wu J. Zingiberene inhibits in vitro and in vivo human colon cancer cell growth via autophagy induction, suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and caspase 2 deactivation Journal of BUON : official journal of the Balkan Union of. Oncology. 2019b;24:1470–5.
Degenhardt K, Mathew R, Beaudoin B, Bray K, Anderson D, Chen G, et al. Autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and restricts necrosis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:51–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2006.06.001.
Dikic I, Elazar Z. Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19:349–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0003-4.
Du Toit A. Cell death: balance through a bivalent regulator. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:546. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3637.
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:351–79. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060308-103103.
Fan T, Zhang C, Zong M, Zhao Q, Yang X, Hao C, et al. Peptidylarginine deiminase IV promotes the development of chemoresistance through inducing autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell & bioscience. 2014;4:49. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-3701-4-49.
Ferrè F, Colantoni A, Helmer-Citterich M. Revealing protein-lncRNA interaction. Brief Bioinform. 2016;17:106–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbv031.
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, González-Barón M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004;30:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2003.07.007.
Gao J, Dai C, Yu X, Yin XB, Zhou F. Long noncoding RNA LINC00324 exerts protumorigenic effects on liver cancer stem cells by upregulating fas ligand via PU box binding protein. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 2020;34:5800–17. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201902705RR.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81683-9.
Hong M, Tang K, Qian J, Deng H, Zeng M, Zheng S, et al. Immunotherapy for EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Crit Rev Oncog. 2018;23:219–34. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevOncog.2018027528.
Hu X, Li Y, Kong D, Hu L, Liu D, Wu J. Long noncoding RNA CASC9 promotes LIN7A expression via miR-758-3p to facilitate the malignancy of ovarian cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:10800–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27903.
Huang F, Wang BR, Wang YG. Role of autophagy in tumorigenesis, metastasis, targeted therapy and drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24:4643–51. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4643.
Ji D, Wang Y, Li H, Sun B, Luo X. Long non-coding RNA LINC00461/miR-149-5p/LRIG2 axis regulates hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;512:176–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.049.
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH. starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D92–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1248.
Li Y, Wang YW, Chen X, Ma RR, Guo XY, Liu HT, et al. MicroRNA-4472 promotes tumor proliferation and aggressiveness in breast cancer by targeting RGMA and inducing. EMT Clin Breast Cancer. 2019;20:e113–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clbc.2019.08.010.
Liu J, Li H, Zheng B, Sun L, Yuan Y, Xing C. Competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) regulation network of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA in colorectal carcinogenesis. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:1868–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05506-9.
Liu R, Chen Y, Liu G, Li C, Song Y, Cao Z, et al. PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:797. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02998-6.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods (San Diego, Calif. 2001;25:402–8. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Lowe SW, Lin AW. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:485–95. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/21.3.485.
Martin SJ. Oncogene-induced autophagy and the Goldilocks principle. Autophagy. 2011;7:922–3. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.7.8.15821.
Mizushima N, Noda T, Yoshimori T, Tanaka Y, Ishii T, George MD, et al. A protein conjugation system essential for autophagy. Nature. 1998;395:395–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/26506.
Ni WJ, Leng XM. miRNA-dependent activation of mRNA translation. MicroRNA (Shariqah, United Arab Emirates. 2016;5:83–6. https://doi.org/10.2174/2211536605666160825151201.
Ogunwobi OO, Kumar A. Chemoresistance mediated by ceRNA networks associated with the PVT1. locus Frontiers in oncology. 2019;9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00834.
Pan ZH, Guo XQ, Shan J, Luo SX. LINC00324 exerts tumor-promoting functions in lung adenocarcinoma via targeting miR-615-5p/AKT1 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:8333–42. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201812_16531.
Panda AC, Martindale JL, Gorospe M. Affinity pulldown of biotinylated RNA for detection of protein-RNA complexes. Bio-protocol. 2016;6. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.2062.
Qin ZQ, Li QG, Yi H, Lu SS, Huang W, Rong ZX, et al. Heterozygous p53-R280T Mutation enhances the oncogenicity of NPC cells through activating PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Front Oncol. 2020;10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00104.
Shah AB, Zulfiqar H, Nagalli S. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2020.
Shi L, Yao H, Liu Z, Xu M, Tsung A, Wang Y. Endogenous PAD4 in breast cancer cells mediates cancer extracellular chromatin network formation and promotes lung metastasis. Molecular cancer research : MCR. 2020;18:735–47. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-19-0018.
Silva JC, Rodrigues NC, Thompson-Souza GA, Muniz VS, Neves JS, Figueiredo RT. Mac-1 triggers neutrophil DNA extracellular trap formation to Aspergillus fumigatus independently of PAD4 histone citrullination. J Leukoc Biol. 2020;107:69–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlb.4a0119-009rr.
Smillie CL, Sirey T, Ponting CP. Complexities of post-transcriptional regulation and the modeling of ceRNA crosstalk. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018;53:231–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409238.2018.1447542.
Song S, Gui L, Feng Q, Taledaohan A, Li Y, Wang W, et al. TAT-Modified Gold nanoparticles enhance the antitumor activity of PAD4 Inhibitors. Int J nanomedicine. 2020;15:6659–71. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.S255546.
Tan WSD, Shen HM, WSF W. Dysregulated autophagy in COPD: a pathogenic process to be deciphered. Pharmacol Res. 2019;144:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019.04.005.
Tatsiy O, McDonald PP. Physiological stimuli induce PAD4-dependent, ROS-independent NETosis, with early and late events controlled by discrete signaling pathways. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2036. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02036.
Tatsiy O, Mayer TZ, de Carvalho OV, Sylvain-Prévost S, Isabel M, Dubois CM, et al. Cytokine production and NET Formation by monosodium urate-activated human neutrophils involves early and late events, and requires upstream TAK1 and Syk. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2996. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02996.
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature. 2014;505:344–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12986.
Tilvawala R, Thompson PR. Peptidyl arginine deiminases: detection and functional analysis of protein citrullination. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2019;59:205–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.01.024.
Vossenaar ER, Zendman AJ, van Venrooij WJ, Pruijn GJ. PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: genes, features and involvement in disease. BioEssays : news and reviews in molecular, cellular and developmental biology. 2003;25:1106–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.10357.
Wei WI, Sham JS. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet (London, England). 2005;365:2041–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(05)66698-6.
Wei L, Wang X, Luo M, Wang H, Chen H, Huang C. The PAD4 inhibitor GSK484 enhances the radiosensitivity of triple-negative breast cancer. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021;40:1074–83. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327120979028.
White E. The role for autophagy in cancer. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:42–6. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci73941.
Wong RS. Apoptosis in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res: CR. 2011;30:87. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-30-87.
Wu S, Gu Z, Wu Y, Wu W, Mao B, Zhao S. LINC00324 accelerates the proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma through regulating WDR66. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235:339–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28973.
Xu Z, Han X, Ou D, Liu T, Li Z, Jiang G, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy for tumor therapy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;104:575–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10257-8.
Yazdani HO, Roy E, Comerci AJ, van der Windt DJ, Zhang H, Huang H, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps drive mitochondrial homeostasis in tumors to augment growth. Cancer Res. 2019;79:5626–39. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-0800.
Yuzhalin AE. Citrullination in cancer. Cancer Res. 2019;79:1274–84. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-2797.
Yuzhalin AE, Gordon-Weeks AN, Tognoli ML, Jones K, Markelc B, Konietzny R, et al. Colorectal cancer liver metastatic growth depends on PAD4-driven citrullination of the extracellular matrix. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4783. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07306-7.
Zhang Y, et al. Comprehensive characterization of lncRNA-mRNA related ceRNA network across 12 major cancers. Oncotarget. 2016;7:64148–67. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11637.
Zhao Y, Li H, Wu R, Li S, Wang P, Wang H, et al. Antitumor effects of oncolytic adenovirus-carrying siRNA targeting potential oncogene EphA3. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0126726. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126726.
Zheng ZQ, Li ZX, Zhou GQ, Lin L, Zhang LL, Lv JW, et al. Long Noncoding RNA FAM225A promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis and metastasis by acting as ceRNA to sponge miR-590-3p/miR-1275 and upregulate ITGB3. Cancer Res. 2019;79:4612–26. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-0799.
Zhou Q, Song C, Liu X, Qin H, Miao L, Zhang X. Peptidylarginine deiminase 4 overexpression resensitizes MCF-7/ADR breast cancer cells to adriamycin via GSK3β/p53 activation. Cancer Manag Res. 2019a;11:625–36. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.S191353.
Zhou RS, Zhang EX, Sun QF, Ye ZJ, Liu JW, Zhou DH, et al. Integrated analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. BMC Cancer. 2019b;19:779. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5983-8.
Zhu JF, Huang W, Yi HM, Xiao T, Li JY, Feng J, et al. Annexin A1-suppressed autophagy promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis by PI3K/AKT signaling activation. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:1154. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1204-7.
Zou Z, Ma T, He X, Zhou J, Ma H, Xie M, et al. Long intergenic non-coding RNA 00324 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation via binding with HuR and stabilizing FAM83B expression. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:717. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0758-8.
Zou Y, Zheng S, Xiao W, Xie X, Yang A, Gao G, et al. circRAD18 sponges miR-208a/3164 to promote triple-negative breast cancer progression through regulating IGF1 and FGF2 expression. Carcinogenesis. 2019;40:1469–79. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgz071.
Acknowledgements
Thank you for all lab members involved in this study.
Funding
The work was supported by Guangxi Key Research Project (grant number: AB17195005) and Nanning Excellent Young Scientist Program and Guangxi Beibu Gulf Economic Zone Major Talent Program (grant number: RC20190104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hao Chen, Lining Wei, Heming Lu, and Yahua Zhong conceived and designed research; Hao Chen, Lining Wei, Min Luo, Xiaochen Wang, Chaohua Zhu, Huixian Huang, and Xu Liu performed the research; Hao Chen, Lining Wei, Heming Lu, and Yahua Zhong analyzed the data; Hao Chen and Lining Wei wrote the paper; Heming Lu, and Yahua Zhong edited the manuscript. All authors approved final version of manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants. The study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ethics Committee of People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figure 1.
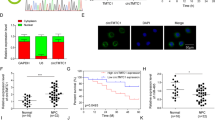
(A) Expression of LINC00324 in NPC tumors and adjacent non-tumor tissues was testified with RT-qPCR. (B) MTT assay evaluated viability of 5-8F and 6-10B cells under indicated transfection. (C) Effects of silenced HuR on expression of LINC00324 or miR-3164 was detected by RT-qPCR. (D) Effects of miR-3164 mimics on expression of LINC00324 or HuR was detected by RT-qPCR. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (PNG 87971 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Wei, L., Luo, M. et al. LINC00324 suppresses apoptosis and autophagy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through upregulation of PAD4 and activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Biol Toxicol 38, 995–1011 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09632-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09632-x