Abstract
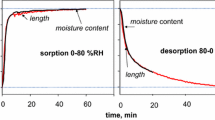
Details on how cellulosic surfaces change under changing moisture are incomplete and even existing results are occasionally neglected. Unlike sometimes reported, water adsorption is unsuitable for surface area measurements. However, water can be utilized for assessing surface dynamics. Hygroscopic changes of pulp and bacterial cellulose were studied by dehydrating the samples in a low polarity solvent and then introducing them into a moist atmosphere in a dynamic vapor sorption (DVS) apparatus at 0–93% relative humidity (RH). The DVS treatment caused hygroscopicity loss near applied RH maxima, however, the hygroscopicity increased at RH values > 10–20% units lower. Additionally, the hygroscopic changes were partially reversible near the RH maximum. Therefore the hygroscopicity of cellulose could be controlled by tailoring the exposure history of the sample. Hornification reduced these changes. The observations support reported molecular simulations where cellulose was shown to restructure its surface depending on the polarity of its environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atalla RH, Brady JW, Matthews JF, Ding S-Y and Himmel ME (2008) Structures of plant cell wall celluloses. In: Biomass recalcitrance. Blackwell Publishing Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444305418.ch6
Banik G, Brückle I (2010) Principles of water absorption and desorption in cellulosic materials. Restaurator 31:164–177. https://doi.org/10.1515/rest.2010.012
Bazooyar F, Bohlén M, Bolton K (2015) Computational studies of water and carbon dioxide interactions with cellobiose. J Mol Model 21:16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-014-2553-5
Belbekhouche S, Bras J, Siqueira G, Chappey C, Lebrun L, Khelifi B, Marais S, Dufresne A (2011) Water sorption behavior and gas barrier properties of cellulose whiskers and microfibrils films. Carbohydr Polym 83:1740–1748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.036
Berthold J, Rinaudo M, Salmén L (1996) Association of water to polar groups; estimations by an adsorption model for ligno-cellulosic materials. Colloids Surf A 112:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-7757(95)03419-6
Bledzki AK, Gassan J (1999) Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibres. Prog Polym Sci 24:221–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6700(98)00018-5
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01269a023
Castro C, Zuluaga R, Álvarez C, Putaux JL, Caro G, Rojas OJ, Mondragon I, Gañán P (2012) Bacterial cellulose produced by a new acid-resistant strain of Gluconacetobacter genus. Carbohydr Polym 89:1033–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.03.045
Caurie M (2012) A method to correct the wide discrepancy between Brunauer, Emmett and Teller water and N2 surface areas of adsorbents. Int J Food Sci Technol 47:2366–2371. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2012.03111.x
Chirkova J, Andersons B, Andersone I (2009) Study of the structure of wood-related biopolymers by sorption methods. BioResources 4:1044–1057
Christensen GN (1959) The rate of sorption of water vapor by wood and pulp. Appita J 13:112–123
Cohan LH (1938) Sorption hysteresis and the vapor pressure of concave surfaces. J Am Chem Soc 60:433–435. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01269a058
Driemeier C, Mendes FM, Oliveira MM (2012) Dynamic vapor sorption and thermoporometry to probe water in celluloses. Cellulose 19:1051–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9727-z
Dufresne A (2012) Cellulose and potential reinforcement. In: Nanocellulose—from nature to high performance tailored materials. Walter de Gruyter GmbH, pp 1–42
Engelund ET, Thygesen LG, Svensson S, Hill CAS (2013) A critical discussion of the physics of wood–water interactions. Wood Sci Technol 47:141–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-012-0514-7
Espino-Pérez E, Bras J, Almeida G, Relkin P, Belgacem N, Plessis C, Domenek S (2016) Cellulose nanocrystal surface functionalization for the controlled sorption of water and organic vapours. Cellulose 23:2955–2970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0994-y
Fernandes Diniz JMB, Gil MH, Castro JAAM (2004) Hornification—its origin and interpretation in wood pulps. Wood Sci Technol 37:489–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-003-0216-2
Fernandes AN, Thomas LH, Altaner CM, Callow P, Forsyth VT, Apperley DC, Kennedy CJ, Jarvis MC (2011) Nanostructure of cellulose microfibrils in spruce wood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:1195–1203. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108942108
Glass SV, Boardman CR, Zelinka SL (2017) Short hold times in dynamic vapor sorption measurements mischaracterize the equilibrium moisture content of wood. Wood Sci Technol 51:243–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-016-0883-4
Grethlein HE (1985) The effect of pore size distribution on the rate of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic substrates. Nat Biotechnol 3:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0285-155
Greyson J, Levi AA (1963) Calorimetric measurements of the heat of sorption of water vapor on dry swollen cellulose. J Polym Sci Part A 1:3333–3342. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1963.100011106
Grunin LY, Grunin YB, Talantsev VI, Nikolskaya EA, Masas DS (2015) Features of the structural organization and sorption properties of cellulose. Polym Sci Ser A 57:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X15010034
Häggkvist M, Li T-Q, Ödberg L (1998) Effects of drying and pressing on the pore structure in the cellulose fibre wall studied by 1H and 2H NMR relaxation. Cellulose 5:33–49. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009212628778
Heiner AP, Kuutti L, Teleman O (1998) Comparison of the interface between water and four surfaces of native crystalline cellulose by molecular dynamics simulations. Carbohydr Res 306:205–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6215(97)10053-2
Hill CAS, Norton A, Newman G (2009) The water vapor sorption behavior of natural fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 112:1524–1537. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.29725
Hill CAS, Keating BA, Jalaludin Z, Mahrdt E (2012) A rheological description of the water vapour sorption kinetics behaviour of wood invoking a model using a canonical assembly of Kelvin-Voigt elements and a possible link with sorption hysteresis. Holzforschung 66:35–47. https://doi.org/10.1515/HF.2011.115
Hubbe MA, Rojas OJ, Lucia LA, Sain M (2008) Cellulosic nanocomposites: a review. Bioresources 3:929–980
Hult E, Larsson PT, Iversen T (2001) Cellulose fibril aggregation—an inherent property of kraft pulps. Polymer (Guildf) 42:3309–3314. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00774-6
Ioelovich M, Leykin A (2011) Study of sorption properties of cellulose and its derivatives. BioResources 6:178–195
Iwamoto S, Abe K, Yano H (2008) The effect of hemicelluloses on wood pulp nanofibrillation and nanofiber network characteristics. Biomacromol 9:1022–1026. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm701157n
Jalaludin Z (2011) The water vapour sorption behaviour of wood. Edinburgh Napier University
Johansson L-S, Tammelin T, Campbell JM, Setälä H, Österberg M (2011) Experimental evidence on medium driven cellulose surface adaptation demonstrated using nanofibrillated cellulose. Soft Matter 7:10917. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1sm06073b
Khanjani P, Väisänen S, Lovikka V, Nieminen K, Maloney T, Vuorinen T (2017) Assessing the reactivity of cellulose by oxidation with 4-acetamido-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxo-piperidinium cation under mild conditions. Carbohydr Polym 176:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.08.092
Klemm D, Philipp B, Heinze T, Heinze U, Wagenknecht W (1998) General considerations on structure and reactivity of cellulose. In: Comprehensive cellulose chemistry. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, pp 9–29
Klemm D, Schumann D, Udhardt U, Marsch S (2001) Bacterial synthesized cellulose—artificial blood vessels for microsurgery. Prog Polym Sci 26:1561–1603. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6700(01)00021-1
Kohler R, Alex R, Brielmann R, Ausperger B (2006) A new kinetic model for water sorption isotherms of cellulosic materials. Macromol Symp 244:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.200651208
Köhnke T, Gatenholm P (2007) The effect of controlled glucuronoxylan adsorption on drying-induced strength loss of bleached softwood pulp. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 22:508–515. https://doi.org/10.3183/NPPRJ-2007-22-04-p508-515
Kulasinski K, Keten S, Churakov SV, Guyer R, Carmeliet J, Derome D (2014) Molecular mechanism of moisture-induced transition in amorphous cellulose. ACS Macro Lett 3:1037–1040. https://doi.org/10.1021/mz500528m
Kulasinski K, Guyer R, Keten S, Derome D, Carmeliet J (2015) Impact of moisture adsorption on structure and physical properties of amorphous biopolymers. Macromolecules 48:2793–2800. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.5b00248
Kulasinski K, Derome D, Carmeliet J (2017) Impact of hydration on the micromechanical properties of the polymer composite structure of wood investigated with atomistic simulations. J Mech Phys Solids 103:221–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2017.03.016
Kymäläinen M, Havimo M, Louhelainen J (2014) Sorption properties of torrefied wood and charcoal. Wood Mater Sci Eng 9:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1080/17480272.2014.916348
Lang ARG, Mason SG (1960) Tritium exchange between cellulose and water: accessibility measurements and effects of cyclic drying. Can J Chem 38:373–387. https://doi.org/10.1139/v60-053
Leppänen K, Andersson S, Torkkeli M, Knaapila M, Kotelnikova N, Serimaa R (2009) Structure of cellulose and microcrystalline cellulose from various wood species, cotton and flax studied by X-ray scattering. Cellulose 16:999–1015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9298-9
Leuk P, Schneeberger M, Hirn U, Bauer W (2015) Heat of sorption: a comparison between isotherm models and calorimeter measurements of wood pulp. Dry Technol 34:563–573. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2015.1062391
Liao R, Zhu M, Xin Zhou, Zhang F, Yan J, Zhu W, Gu C (2012) Molecular dynamics study of the disruption of H-bonds by water molecules and its diffusion behavior in amorphous cellulose. Mod Phys Lett B 26:1250088. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984912500881
Lovikka VA, Khanjani P, Väisänen S, Vuorinen T, Maloney TC (2016) Porosity of wood pulp fibers in the wet and highly open dry state. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 234:326–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.07.032
Matthews JF, Skopec CE, Mason PE, Zuccato P, Torget RW, Sugiyama J, Himmel ME, Brady JW (2006) Computer simulation studies of microcrystalline cellulose Iβ. Carbohydr Res 341:138–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2005.09.028
Maurer RJ, Sax AF, Ribitsch V (2013) Molecular simulation of surface reorganization and wetting in crystalline cellulose I and II. Cellulose 20:25–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9835-9
Mazeau K (2015) The hygroscopic power of amorphous cellulose: a modeling study. Carbohydr Polym 117:585–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.09.095
Medronho B, Duarte H, Alves L, Antunes F, Romano A, Lindman B (2015) Probing cellulose amphiphilicity. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 30:58–66. https://doi.org/10.3183/NPPRJ-2015-30-01-p058-066
Mihranyan A, Llagostera AP, Karmhag R, Strømme M, Ek R (2004) Moisture sorption by cellulose powders of varying crystallinity. Int J Pharm 269:433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2003.09.030
Minor JL (1994) Hornification—its origin and meaning. Prog Pap Recycl 3:93–95
Mohan T, Spirk S, Kargl R, Doliška A, Vesel A, Salzmann I, Resel R, Ribitsch V, Stana-Kleinschek K (2012) Exploring the rearrangement of amorphous cellulose model thin films upon heat treatment. Soft Matter 8:9807–9815. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2sm25911g
Nelson R, Oliver DW (1971) Study of cellulose structure and its relation to reactivity. J Polym Sci Polym Symp 36:305–320. https://doi.org/10.1002/polc.5070360122
Newman RH (2004) Carbon-13 NMR evidence for cocrystallization of cellulose as a mechanism for hornification of bleached kraft pulp. Cellulose 11:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CELL.0000014768.28924.0c
Newns AC (1973) Sorption and Desorption Kinetics of the Cellulose and Water System - Part 2. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 1(69):444–448. https://doi.org/10.1039/F19736900444
Oksanen T, Buchert J, Viikari L (1997) The role of hemiocelluloses in the hornification of bleached kraft pulps. Holzforschung 51:355–360. https://doi.org/10.1515/hfsg.1997.51.4.355
Olsson A-M, Salmén L (2004) The association of water to cellulose and hemicellulose in paper examined by FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydr Res 339:813–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2004.01.005
Pierce C, Wiley JW, Smith RN (1949) Capillarity and surface area of charcoal. J Phys Chem 53:669–683. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150470a007
Robens E, Dąbrowski A, Kutarov VV (2004) Comments on surface structure analysis by water and nitrogen adsorption. J Therm Anal Calorim 76:647–657. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JTAN.0000028044.44316.ce
Rowen JW, Blaine RL (1947) Sorption of nitrogen and water vapor on textile fibers. Ind Eng Chem 39:1659–1663. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50456a029
Salmén L (1982) Temperature and water induced softening behaviour of wood fiber based materials. The Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm
Salmén L, Bergström E (2009) Cellulose structural arrangement in relation to spectral changes in tensile loading FTIR. Cellulose 16:975–82. doi:10.1007/s10570-009-9331-z
Sepall O, Mason SG (1961) Hydrogen exchange between cellulose and water: II. Interconversion of accessible and inaccessible regions. Can J Chem 39:1944–1955. https://doi.org/10.1139/v61-261
Sing KSW (2014) Assessment of surface area by gas adsorption. In: Adsorption by powders and porous solids, 2nd edn. Elsevier Ltd., Amsterdam, pp 237–68
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW, Moscou L, Pierotti RA, Rouquérol J, Siemieniewska T (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198557040603
Sinko R, Qin X, Keten S (2015) Interfacial mechanics of cellulose nanocrystals. MRS Bull 40:340–348. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2015.67
Siró I, Plackett D (2010) Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: a review. Cellulose 17:459–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9405-y
Stone JE, Scallan AM (1966) Influence of drying on the pore structures of the cell wall. In: Consolidation of the paper web: transactions of the symposium held at Cambridge, pp 145–174
Stone JE, Scallan AM (1967) The effect of component removal upon the porous structure of the cell wall of wood. II. Swelling in water and the fiber saturation point. Tappi J 50:496–501
Strømme M, Mihranyan A, Ek R, Niklasson GA (2003) Fractal dimension of cellulose powders analyzed by multilayer BET adsorption of water and nitrogen. J Phys Chem B 107:14378–14382. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp034117w
Suchy M, Kontturi E, Vuorinen T (2010a) Impact of drying on wood ultrastructure: similarities in cell wall alteration between native wood and isolated wood-based fibers. Biomacromolecules 11:2161–2168. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm100547n
Suchy M, Virtanen J, Kontturi E, Vuorinen T (2010b) Impact of drying on wood ultrastructure observed by deuterium exchange and photoacoustic FT-IR spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 11:515–520. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm901268j
Taniguchi T, Harada H, Nakato K (1978) Determination of water adsorption sites in wood by a hydrogen–deuterium exchange. Nature 272:230–231. https://doi.org/10.1038/272230a0
Thybring EE, Thygesen LG, Burgert I (2017) Hydroxyl accessibility in wood cell walls as affected by drying and re-wetting procedures. Cellulose 24:2375–2384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1278-x
Timmermann EO (2003) Multilayer sorption parameters: BET or GAB values? Colloids Surf A 220:235–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(03)00059-1
Topgaard D, Söderman O (2001) Diffusion of water absorbed in cellulose fibers studied with 1 H-NMR. Langmuir 17:2694–2702. https://doi.org/10.1021/la000982l
Weatherwax RC (1977) Collapse of cell-wall pores during drying of cellulose. J Colloid Interface Sci 62:432–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(77)90094-7
Weatherwax RC, Caulfield DF (1971) Cellulose aerogels: an improved method for preparing a highly expanded form of dry cellulose. Tappi J 54:985–986
Weise U, Maloney T, Paulapuro H (1996) Quantification of water in different states of interaction with wood pulp fibres. Cellulose 3:189–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02228801
Willems W (2014a) The water vapor sorption mechanism and its hysteresis in wood: the water/void mixture postulate. Wood Sci Technol 48:499–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-014-0617-4
Willems W (2014b) Hydrostatic pressure and temperature dependence of wood moisture sorption isotherms. Wood Sci Technol 48:483–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-014-0616-5
Xie Y, Hill CAS, Jalaludin Z, Curling SF, Anandjiwala RD, Norton AJ, Newman G (2010) The dynamic water vapour sorption behaviour of natural fibres and kinetic analysis using the parallel exponential kinetics model. J Mater Sci 46:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4935-0
Xie Y, Hill CAS, Jalaludin Z, Sun D (2011) The water vapour sorption behaviour of three celluloses: analysis using parallel exponential kinetics and interpretation using the Kelvin-Voigt viscoelastic model. Cellulose 18:517–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9512-4
Yamane C, Aoyagi T, Ago M, Sato K, Okajima K, Takahashi T (2006) Two different surface properties of regenerated cellulose due to structural anisotropy. Polym J 38:819–826. https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.PJ2005187
Zheng Y, Lin H, Tsao GT (1998) Pretreatment for cellulose hydrolysis by carbon dioxide explosion. Biotechnol Prog 14:890–896. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp980087g
Zografi G, Kontny MJ (1986) The interactions of water with cellulose- and starch-derived pharmaceutical excipients. Pharm Res 3:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016330528260
Zografi G, Kontny MJ, Yang AYS, Brenner GS (1984) Surface area and water vapor sorption of microcrystalline cellulose. Int J Pharm 18:99–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(84)90111-X
Acknowledgments
This work was a part of ACel program of the Finnish Bioeconomy Cluster FIBIC. The funding of the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation (TEKES) and the Academy of Finland (POROFIBRE Project) is acknowledged. Katarina Dimic-Misic is thanked for providing the BC. Benjamin Wilson is thanked for proofreading. Henna Penttinen is thanked for the initial literature review in her interesting undergraduate thesis on cellulose surfaces in environments with different polarities. This work made use of the Aalto University Nanomicroscopy Center (Aalto-NMC) premises.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lovikka, V.A., Rautkari, L. & Maloney, T.C. Changes in the hygroscopic behavior of cellulose due to variations in relative humidity. Cellulose 25, 87–104 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1570-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1570-9