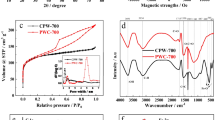
Abstract
In recent decades, the release of emerging pharmaceutical contaminants has been recognized as a challenging environmental issue. This study focuses on the adsorption of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) by pectin (Pec)-based bio-adsorbent. Pec was extracted from orange peel-waste biomass (OPB) by a microwave-assisted extraction method. Further, different concentrations of Pec from OPB (Pec-OPB); 0.5, 1, 2 and 4g were super-magnetized with Fe3O4 nanoparticles (denoted as Fe3O4@Pec-OPB(0.5g), Fe3O4@Pec-OPB(1g), Fe3O4@Pec-OPB(2g) and Fe3O4@Pec-OPB(4g), respectively). Among these synthesized bio-adsorbents, Fe3O4@Pec-OPB(1g) gave significant SMX adsorption and hence studied further in detail. Surface-morphology, structure, functional-groups, magnetic-property, and elemental-composition of facile of Fe3O4@Pec-OPB(1g) was characterized by standard analytical techniques. Different parameters for SMX adsorption on Fe3O4@Pec-OPB(1g) were investigated, such as optimal pH (4.0), kinetics (best-fitted pseudo-second-order kinetic model) and isotherm models (best-fitted Redlich-Peterson model). The maximum adsorption capacity (qm) of Fe3O4@Pec-OPB(1g) was 120 mg g−1 of SMX. Thermodynamic analysis corroborated the endothermic nature of the adsorption process. Therefore, the nano-bio-adsorbent Fe3O4@Pec-OPB(1g) exhibits excellent potential for capturing the SMX from water, suggesting that Fe3O4@Pec-OPB(1g) could be a viable option for adsorptive reclamation of hazardous cationic pollutants from water.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahsan MA, Islam MT, Hernandez C et al (2018) Adsorptive removal of sulfamethoxazole and bisphenol a from contaminated water using functionalized carbonaceous material derived from tea leaves. J Environ Chem Eng 6:4215–4225. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2018.06.022
Asgari M, Anisi H, Mohammadi H, Sadighi S (2014) Designing a commercial scale pressure swing adsorber for hydrogen purification. Pet Coal 56:552–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Babaladimath G, Badalamoole V (2018) Magnetic nanoparticles embedded in pectin-based hydrogel for the sustained release of diclofenac sodium. Polym Int 67:983–992. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.5587
Çalişkan E, Göktürk S (2010) Adsorption characteristics of sulfamethoxazole and metronidazole on activated carbon. Sep Sci Technol 45:244–255. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390903409419
Canzano S, Iovino P, Salvestrini S, Capasso S (2012) Comment on “Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution by raw pine and acid-treated pine cone powder as adsorbent: equilibrium, thermodynamic, kinetics, mechanism and process design”. Water Res 46:4314–4315. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2012.05.040
Chen H, Gao B, Li H (2014) Functionalization, pH, and ionic strength influenced sorption of sulfamethoxazole on graphene. J Environ Chem Eng 2:310–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2013.12.021
Chen J, Pang S, He L, Nugen SR (2016) Highly sensitive and selective detection of nitrite ions using Fe3O4@SiO2/Au magnetic nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Biosens Bioelectron 85:726–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOS.2016.05.068
Chen B, Sun W, Wang C, Guo X (2017) Size-dependent impact of inorganic nanoparticles on sulfamethoxazole adsorption by carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng J 316:160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2017.01.087
Chitra R, Sathya P, Selvasekarapandian S et al (2018) Synthesis and characterization of iota-carrageenan solid biopolymer electrolytes for electrochemical applications. Ionics (Kiel). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2687-z
Dai J, Wu S, Jiang W et al (2013) Facile synthesis of pectin coated Fe3O4 nanospheres by the sonochemical method. J Magn Magn Mater 331:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.11.004
Dawood S, Sen TK (2012) Author’s Responses to the comment by Canzano et al and also corrigendum to “Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution by raw pine and acid-treated pine cone powder as adsorbent: equilibrium, thermodynamic, kinetics, mechanism and process design” published in Water Research, Vol. 46, pp. 1933–1946, 2012. Water Res 46:4316–4317. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2012.05.043
Debnath S, Maity A, Pillay K (2014) Magnetic chitosan–GO nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization and batch adsorber design for Cr(VI) removal. J Environ Chem Eng 2:963–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2014.03.012
Dutta K, Lee M-Y, Lai WW-P et al (2014) Removal of pharmaceuticals and organic matter from municipal wastewater using two-stage anaerobic fluidized membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 165:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2014.03.054
Farías T, de Ménorval LC, Zajac J, Rivera A (2011) Benzalkonium chloride and sulfamethoxazole adsorption onto natural clinoptilolite: effect of time, ionic strength, pH and temperature. J Colloid Interface Sci 363:465–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2011.07.067
Fernandez ME, Ledesma B, Román S et al (2015) Development and characterization of activated hydrochars from orange peels as potential adsorbents for emerging organic contaminants. Bioresour Technol 183:221–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2015.02.035
Forsting T, Gottschalk HC, Hartwig B et al (2017) Correcting the record: the dimers and trimers of: trans-N-methylacetamide. Phys Chem Chem Phys 19:10727–10737. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cp07989j
Fukahori S, Fujiwara T, Ito R, Funamizu N (2011) pH-Dependent adsorption of sulfa drugs on high silica zeolite: modeling and kinetic study. Desalination 275:237–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2011.03.006
García-González CA, Carenza E, Zeng M et al (2012) Design of biocompatible magnetic pectin aerogel monoliths and microspheres. RSC Adv 2:9816–9823. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra21500d
Gnanasambandam R, Proctor A (2000) Determination of pectin degree of esterification by diffuse reflectance. Food Chem 68:327–332
Gong JL, Wang XY, Zeng GM et al (2012) Copper (II) removal by pectin-iron oxide magnetic nanocomposite adsorbent. Chem Eng J 185–186:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.050
Guo S, Gao M, Shen T et al (2019a) Effective adsorption of sulfamethoxazole by novel Organo-Vts and their mechanistic insights. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 286:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2019.05.032
Guo X, Chen C, Wang J (2019b) Sorption of sulfamethoxazole onto six types of microplastics. Chemosphere 228:300–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2019.04.155
Gupta VK, Pathania D, Asif M, Sharma G (2014) Liquid phase synthesis of pectin–cadmium sulfide nanocomposite and its photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. J Mol Liq 196:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2014.03.021
Han X, Liang CF, Li TQ et al (2013) Simultaneous removal of cadmium and sulfamethoxazole from aqueous solution by rice straw biochar. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 14:640–649. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200353
Ji L, Liu F, Xu Z et al (2010) Adsorption of pharmaceutical antibiotics on template-synthesized ordered micro- and mesoporous carbons. Environ Sci Technol 44:3116–3122. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903716s
Jossens L, Prausnitz JM, Fritz W et al (1978) Thermodynamics of multi-solute adsorption from dilute aqueous solutions. Chem Eng Sci 33:1097–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(78)85015-5
Kadam AA, Lee DS (2015) Glutaraldehyde cross-linked magnetic chitosan nanocomposites: reduction precipitation synthesis, characterization, and application for removal of hazardous textile dyes. Bioresour Technol 193:563–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.148
Kadam AA, Jang J, Lee DS (2016) Facile synthesis of pectin-stabilized magnetic graphene oxide Prussian blue nanocomposites for selective cesium removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.103
Kadam AA, Jang J, Lee DS (2017) Supermagnetically tuned halloysite nanotubes functionalized with aminosilane for covalent laccase immobilization. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b02531
Kadam A, Saratale RG, Shinde S et al (2019) Adsorptive remediation of cobalt oxide nanoparticles by magnetized α-cellulose fibers from waste paper biomass. Bioresour Technol 273:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.11.041
Kang AJ, Brown AK, Wong CS, Yuan Q (2018) Removal of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole by anoxic/anaerobic/oxic granular and suspended activated sludge processes. Bioresour Technol 251:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2017.12.021
Lai K, Zhai F, Zhang Y et al (2011) Application of surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for analyses of restricted sulfa drugs. Sens Instrum Food Qual Saf 5:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-011-9115-7
Lan YK, Chen TC, Tsai HJ et al (2016) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole on carboxylic-functionalized carbon nanofibers-encapsulated Ni magnetic nanoparticles. Langmuir 32:9530–9539. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b02904
Li D, Wang J, Guo Z et al (2017) Pectin gels cross-linked by Ca2+: an efficient material for methylene blue removal. J Mol Liq 238:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2017.04.116
Li Z, Li M, Wang Z, Liu X (2020a) Coadsorption of Cu(II) and tylosin/sulfamethoxazole on biochar stabilized by nano-hydroxyapatite in aqueous environment. Chem Eng J 381:122785. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2019.122785
Li Z, Wang Z, Wu X et al (2020b) Competitive adsorption of tylosin, sulfamethoxazole and Cu(II) on nano-hydroxyapatite modified biochar in water. Chemosphere 240:124884. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2019.124884
Lim J, Yoo J, Ko S, Lee S (2012) Extraction and characterization of pectin from Yuza (Citrus junos) pomace: a comparison of conventional-chemical and combined physical-enzymatic extractions. Food Hydrocoll 29:160–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.02.018
Liu L, Cao J, Huang J et al (2010) Extraction of pectins with different degrees of esterification from mulberry branch bark. Bioresour Technol 101:3268–3273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.062
Liu Y, Liu X, Zhang G et al (2019) Adsorptive removal of sulfamethazine and sulfamethoxazole from aqueous solution by hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide modified activated carbon. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 564:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFA.2018.12.041
Lu L, Gao M, Gu Z et al (2014) A comparative study and evaluation of sulfamethoxazole adsorption onto organo-montmorillonites. J Environ Sci (China) 26:2535–2545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.04.007
Miran W, Nawaz M, Jang J, Lee DS (2016) Conversion of orange peel waste biomass to bioelectricity using a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Sci Total Environ 547:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2016.01.004
Mittal A, Jhare D, Mittal J (2013) Adsorption of hazardous dye Eosin Yellow from aqueous solution onto waste material De-oiled Soya: isotherm, kinetics and bulk removal. J Mol Liq 179:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2012.11.032
Munck C, Albertsen M, Telke A et al (2015) Limited dissemination of the wastewater treatment plant core resistome. Nat Commun 6:2–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9452
Namanga J, Foba J, Ndinteh DT et al (2013) Synthesis and magnetic properties of a superparamagnetic nanocomposite “pectin-magnetite nanocomposite”. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/137275
Oyelude EO, Awudza JAM, Twumasi SK (2017) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study of removal of eosin yellow from aqueous solution using teak leaf litter powder. Sci Rep 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12424-1
Özkaya B (2006) Adsorption and desorption of phenol on activated carbon and a comparison of isotherm models. J Hazard Mater 129:158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.025
Pamphile N, Xuejiao L, Guangwei Y, Yin W (2019) Synthesis of a novel core-shell-structure activated carbon material and its application in sulfamethoxazole adsorption. J Hazard Mater 368:602–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2019.01.093
Popa AC, Stan GE, Husanu MA et al (2017) Bioglass implant-coating interactions in synthetic physiological fluids with varying degrees of biomimicry. Int J Nanomed 12:683–707. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S123236
Popoola LT (2019) Tetracycline and sulfamethoxazole adsorption onto nanomagnetic walnut shell-rice husk: isotherm, kinetic, mechanistic and thermodynamic studies. Int J Environ Anal Chem 00:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1646739
Prakash Maran J, Sivakumar V, Thirugnanasambandham K, Sridhar R (2013) Optimization of microwave assisted extraction of pectin from orange peel. Carbohydr Polym 97:703–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.05.052
Qiang Z, Bao X, Ben W (2013) MCM-48 modified magnetic mesoporous nanocomposite as an attractive adsorbent for the removal of sulfamethazine from water. Water Res 47:4107–4114. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2012.10.039
Rakhshaee R, Panahandeh M (2011) Stabilization of a magnetic nano-adsorbent by extracted pectin to remove methylene blue from aqueous solution: a comparative studying between two kinds of cross-likened pectin. J Hazard Mater 189:158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.02.013
Reguyal F, Sarmah AK (2018) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole by magnetic biochar: effects of pH, ionic strength, natural organic matter and 17α-ethinylestradiol. Sci Total Environ 628–629:722–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.323
Rostamian R, Behnejad H (2016) A comparative adsorption study of sulfamethoxazole onto graphene and graphene oxide nanosheets through equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic modeling. Process Saf Environ Prot 102:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSEP.2015.12.011
Sahu S, Dutta RK (2011) Novel hybrid nanostructured materials of magnetite nanoparticles and pectin. J Magn Magn Mater 323:980–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.11.085
Santos CM, Dweck J, Viotto RS et al (2015) Application of orange peel waste in the production of solid biofuels and biosorbents. Bioresour Technol 196:469–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2015.07.114
Shabani-Nooshabadi M, Roostaee M (2016) Modification of carbon paste electrode with NiO/graphene oxide nanocomposite and ionic liquids for fabrication of high sensitive voltammetric sensor on sulfamethoxazole analysis. J Mol Liq 220:329–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2016.05.001
Shamsara O, Jafari SM, Muhidinov ZK (2017) Development of double layered emulsion droplets with pectin/β-lactoglobulin complex for bioactive delivery purposes. J Mol Liq 243:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2017.08.036
Teixeira S, Delerue-Matos C, Santos L (2012) Removal of sulfamethoxazole from solution by raw and chemically treated walnut shells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:3096–3106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0853-9
Wang S, Chen F, Wu J et al (2007) Optimization of pectin extraction assisted by microwave from apple pomace using response surface methodology. J Food Eng 78:693–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JFOODENG.2005.11.008
Wu D, Pan B, Wu M et al (2012) Coadsorption of Cu and sulfamethoxazole on hydroxylized and graphitized carbon nanotubes. Sci Total Environ 427–428:247–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2012.03.039
Xiao K, Liu H, Li Y et al (2018) Correlations between hydrochar properties and chemical constitution of orange peel waste during hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour Technol 265:432–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2018.06.014
Yao Y, Gao B, Chen H et al (2012) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole on biochar and its impact on reclaimed water irrigation. J Hazard Mater 209–210:408–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.046
Zhang X, Pan B, Yang K et al (2010) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole on different types of carbon nanotubes in comparison to other natural adsorbents. J Environ Sci Heal Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst Environ Eng 45:1625–1634. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2010.506127
Zhang D, Pan B, Wu M et al (2011) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole on functionalized carbon nanotubes as affected by cations and anions. Environ Pollut 159:2616–2621. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2011.05.036
Zhou Y, Liu X, Xiang Y et al (2017) Modification of biochar derived from sawdust and its application in removal of tetracycline and copper from aqueous solution: adsorption mechanism and modelling. Bioresour Technol 245:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2017.08.178
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (NRF-2019R1G1A1009363).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadam, A.A., Sharma, B., Saratale, G.D. et al. Super-magnetization of pectin from orange-peel biomass for sulfamethoxazole adsorption. Cellulose 27, 3301–3318 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-02988-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-02988-z