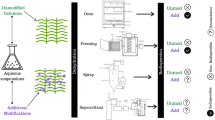
Abstract
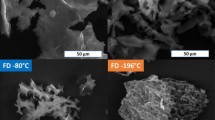
This study investigates the role of drying method and dissolving solvent has on the properties of regenerated cellulose fibres, leading to the preparation of porous cellulose fibres. The fibres are produced by wet spinning using 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (BmimAc) as the solvent, and then dried using freeze drying or supercritical drying resulting in highly porous fibres. The properties of these fibres are compared to the traditional air-dried regenerated cellulose fibre. It was found that freeze drying produced fibres with micron pores on the surface and nanopores within the core, whereas supercritical-dried fibres had a smooth surface and a nanoporous core. The addition of DMSO to the spinning dope for supercritical dried fibres reduced the fibre diameter under identical draw conditions and increased the surface area to 260 m2/g.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchtová N, Budtova T (2016) Cellulose aero-, cryo-and xerogels: towards understanding of morphology control. Cellulose 4:2585–2595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0960-8
Budtova T (2019) Cellulose II aerogels: a review. Cellulose 1:81–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2189-1
Cai J, Kimura S, Wada M, Kuga S, Zhang L (2008) Cellulose aerogels from aqueous alkali hydroxide–urea solution. Chemsuschem 1–2:149–154. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.200700039
Clough MT, Geyer K, Hunt PA et al (2015) Ionic liquids: not always innocent solvents for cellulose. Green Chem 1:231–243. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4gc01955e
Ebner G, Schiehser S, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2008) Side reaction of cellulose with common 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids. Tetrahedron Lett 51:7322–7324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.10.052
García-González C, Alnaief M, Smirnova I (2011) Polysaccharide-based aerogels—Promising biodegradable carriers for drug delivery systems. Carbohyd Polym 4:1425–1438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.066
Gavillon R, Budtova T (2008) Aerocellulose: new highly porous cellulose prepared from cellulose-NaOH aqueous solutions. Biomacromol 1:269–277. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm700972k
Gericke M, Trygg J, Fardim P (2013) Functional cellulose beads: preparation, characterization, and applications. Chem Rev 7:4812–4836. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300242j
Guillen GR, Pan Y, Li M, Hoek EM (2011) Preparation and characterization of membranes formed by nonsolvent induced phase separation: a review. Ind Eng Chem Re 7:3798–3817. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie101928r
Hummel M, Michud A, Tanttu M et al (2015) Ionic Liquids for the Production of Man-Made Cellulosic Fibers: Opportunities and Challenges Cellulose Chemistry and Properties: Fibers. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Nanocelluloses and Advanced Materials, pp 133–168
Illera D, Mesa J, Gomez H, Maury H (2018) Cellulose aerogels for thermal insulation in buildings: trends and challenges. Coatings 10:345. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8100345
Innerlohinger J, Weber HK, Kraft G (2006) Aerocellulose: aerogels and aerogel-like materials made from cellulose. Macromol Sy. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.200651212
Karadagli I, Schulz B, Schestakow M et al (2015) Production of porous cellulose aerogel fibers by an extrusion process. J Supercrit Fluid. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2015.06.011
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink HP, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem Int Ed Edit 22:3358–3393. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200460587
Lavoine N, Bergstrm L (2017) Nanocellulose-based foams and aerogels: processing, properties, and applications. J Mater Chem A. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA02807E
Le KA, Rudaz C, Budtova T (2014) Phase diagram, solubility limit and hydrodynamic properties of cellulose in binary solvents with ionic liquid. Carbohyd Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.085
Legras A, Kondor A, Heitzmann MT, Truss RW (2015) Inverse gas chromatography for natural fibre characterisation: Identification of the critical parameters to determine the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller specific surface area. J Chromatogr A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.11.033
Liebert TF, Heinze TJ, Edgar KJ (2010) Cellulose solvents: for analysis, shaping and chemical modification. J Am Chem Soc 50:17976–17976
Liebner F, Potthast A, Rosenau T, Haimer E, Wendland M (2008) Cellulose aerogels: highly porous, ultra-lightweight materials. Holzforschung 2:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1515/HF/2008.051
Lv Y, Wu J, Zhang J et al (2012) Rheological properties of cellulose/ionic liquid/dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) solutions. Polymer 12:2524–2531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2012.03.037
Ma Y, Zeng B, Wang X, Byrne N (2019) Circular textiles: closed loop fibre to fibre wet spun process for recycling cotton from denim. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:11937–11943. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b06166
Minnick DL, Flores RA, DeStefano MR, Scurto AM (2016) Cellulose solubility in ionic liquid mixtures: temperature, cosolvent, and antisolvent effects. J Phys Chem B 32:7906–7919. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b04309
O’Connell D, Birkinshaw C, O’Dwyer T (2008) Heavy metal adsorbents prepared from the modification of cellulose: A review. Bioresource Technol 15:6709–6724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.01.036
O’Sullivan AC (1997) Cellulose: the structure slowly unravels. Cellulose 3:173–207. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018431705579
Park S, Baker JO, Himmel ME, Parilla PA, Johnson DK (2010) Cellulose crystallinity index: measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol Biofuels 1:1
Pircher N, Carbajal L, Schimper C et al (2016) Impact of selected solvent systems on the pore and solid structure of cellulose aerogels. Cellulose 3:1949–1966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0896-z
Rudaz C, Courson R, Bonnet L et al (2014) Aeropectin: fully biomass-based mechanically strong and thermal superinsulating aerogel. Biomacromol 6:2188–2195. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm500345u
Schulz B, Meinert T, Bierbüsse D, Busen M, Seide G (2016) Cellulose aerogel fibers tested on a REXUS 18 rocket - the ACTOR project. Chem-Ing-Tech 10:1501–1507. https://doi.org/10.1002/cite.201600003
Segal L, Creely J, Martin AJ, Conrado C (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J. 29(10):786–794
Sescousse R, Tatiana B (2009) Influence of processing parameters on regeneration kinetics and morphology of porous cellulose from cellulose–NaOH–water solutions. Cellulose. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9287-z
Sescousse R, Gavillon R, Budtova T (2011) Aerocellulose from cellulose–ionic liquid solutions: preparation, properties and comparison with cellulose–NaOH and cellulose–NMMO routes. Carbohyd Polym 4:1766–1774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.043
Sing K (2001) The use of nitrogen adsorption for the characterisation of porous materials. Colloid Surface A. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(01)00612-4
Sixta H, Michud A, Hauru L et al (2015) Ioncell-F: a high-strength regenerated cellulose fibre. Nord Pulp Pap Res J. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2015-30-01-p043-057
Sun L, Chen JY, Jiang W, Lynch V (2015) Crystalline characteristics of cellulose fiber and film regenerated from ionic liquid solution. Carbohyd Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.11.008
Swatloski RP, Spear SK, Holbrey JD, Rogers RD (2002) Dissolution of cellulose [correction of cellose] with ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 18:4974–4975. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja025790m
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV et al (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 9–10:1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Zeng B, Wang X, Byrne N (2019) Development of cellulose based aerogel utilizing waste denim-A Morphology study. Carbohyd Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.070
Zeng B, Wang X, Byrne N (2020) Cellulose beads derived from waste textiles for drug delivery. Polymers-Basel 7:1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071621
Zhang L, Ruan D, Gao S (2002) Dissolution and regeneration of cellulose in NaOH/thiourea aqueous solution. J Polym Sci Pol Phys 14:1521–1529. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.10215
Zhang S, Chen C, Duan C et al (2018) Regenerated cellulose by the lyocell process, a brief review of the process and properties. BioResources 2:4577–4592
Zhao Y, Liu X, Wang J, Zhang S (2013) Insight into the cosolvent effect of cellulose dissolution in imidazolium-based ionic liquid systems. J Phys Chem B 30:9042–9049. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4038039
Zhou J, Hsieh YL (2019) Nanocellulose aerogel-based porous coaxial fibers for thermal insulation. Nano Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104305
Zhu S, Wu Y, Chen Q et al (2006) Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids and its application: a mini-review. Green Chem 4:325–327. https://doi.org/10.1039/B601395C
Funding
The authors thank Deakin University for funding this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
There is no animal or human participant in the study.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, B., Byrne, N. The effect of drying method on the porosity of regenerated cellulose fibres. Cellulose 28, 8333–8342 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04068-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04068-2