Abstract
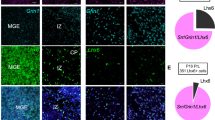
d-serine is synthesized by serine racemase (SR) and is a co-agonist at forebrain N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs). d-serine and SR are expressed primarily in neurons, but not in quiescent astrocytes. In this study, we examined the localization of d-serine and SR in the mouse striatum and the effects of genetically silencing SR expression in GABAergic interneurons (iSR−/−). iSR−/− mice had substantially reduced SR expression almost exclusively in striatum, but only exhibited marginal d-serine reduction. SR positive cells in the striatum showed strong co-localization with dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein (DARPP32) in wild type mice. Transgenic fluorescent reporter mice for either the D1 or D2 dopamine receptors exhibited a 65:35 ratio for co-localization with D1and D2 receptor positive cells, respectively. These results indicate that GABAergic medium spiny neurons receiving dopaminergic inputs in striatum robustly and uniformly express SR. In behavioral tests, iSR−/− mice showed a blunted response to the hedonic and stimulant effects of cocaine, without affecting anxiety-related behaviors. Because the cocaine effects have been shown in the constitutive SR−/− mice, the restriction of the blunted response to cocaine to iSR−/− mice reinforces the conclusion that d-serine in striatal GABAergic neurons plays an important role in mediating dopaminergic stimulant effects. Results in this study suggest that SR in striatal GABAergic neurons is synthesizing d-serine, not as a glutamatergic co-transmitter, but rather as an autocrine whereby the GABAergic neurons control the excitability of their NMDARs by determining the availability of the co-agonist, d-serine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Areal LB, Hamilton A, Martins-Silva C, Pires RGW, Ferguson SSG (2019) Neuronal scaffolding protein spinophilin is integral for cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization and ERK1/2 activation. Mol Brain 12(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-019-0434-7
Balu DT, Coyle JT (2011) Neuroplasticity signaling pathways linked to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35(3):848–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.10.005
Balu DT, Coyle JT (2015) The NMDA receptor ‘glycine modulatory site’ in schizophrenia: d-serine, glycine, and beyond. Curr Opin Pharmacol 20C:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2014.12.004
Balu DT, Pantazopoulos H, Huang CCY, Muszynski K, Harvey TL, Uno Y, Rorabaugh JM, Galloway CR, Botz-Zapp C, Berretta S, Weinshenker D, Coyle JT (2019) Neurotoxic astrocytes express the d-serine synthesizing enzyme, serine racemase, in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 130:104511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104511
Balu DT, Presti KT, Huang CCY, Muszynski K, Radzishevsky I, Wolosker H, Guffanti G, Ressler KJ, Coyle JT (2018) Serine racemase and d-serine in the amygdala are dynamically involved in fear learning. Biol Psychiatry 83(3):273–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.08.012
Balu DT, Takagi S, Puhl MD, Benneyworth MA, Coyle JT (2014) d-serine and serine racemase are localized to neurons in the adult mouse and human forebrain. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34(3):419–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0027-z
Basu AC, Tsai GE, Ma CL, Ehmsen JT, Mustafa AK, Han L, Jiang ZI, Benneyworth MA, Froimowitz MP, Lange N, Snyder SH, Bergeron R, Coyle JT (2009) Targeted disruption of serine racemase affects glutamatergic neurotransmission and behavior. Mol Psychiatry 14(7):719–727. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2008.130
Bechtholt AJ, Smith R, Raber J, Cunningham CL (2004) Enhanced ethanol-, but not cocaine-induced, conditioned place preference in Apoe(−/−) mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 77(4):783–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2004.02.002
Benneyworth MA, Coyle JT (2012) Altered acquisition and extinction of amphetamine-paired context conditioning in genetic mouse models of altered NMDA receptor function. Neuropsychopharmacology 37(11):2496–2504. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.108
Benneyworth MA, Li Y, Basu AC, Bolshakov VY, Coyle JT (2012) Cell selective conditional null mutations of serine racemase demonstrate a predominate localization in cortical glutamatergic neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32(4):613–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9808-4
Bolam JP, Smith Y (1990) The GABA and substance P input to dopaminergic neurones in the substantia nigra of the rat. Brain Res 529(1–2):57–78
Britt JP, Benaliouad F, McDevitt RA, Stuber GD, Wise RA, Bonci A (2012) Synaptic and behavioral profile of multiple glutamatergic inputs to the nucleus accumbens. Neuron 76(4):790–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.040
Carlezon WA Jr, Chartoff EH (2007) Intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) in rodents to study the neurobiology of motivation. Nat Protoc 2(11):2987–2995. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.441
Coyle JT, Balu D, Benneyworth M, Basu A, Roseman A (2010) Beyond the dopamine receptor: novel therapeutic targets for treating schizophrenia. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 12(3):359–382
Cunningham CL (1995) Localization of genes influencing ethanol-induced conditioned place preference and locomotor activity in BXD recombinant inbred mice. Psychopharmacology 120(1):28–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02246142
Cunningham CL, Dickinson SD, Grahame NJ, Okorn DM, McMullin CS (1999) Genetic differences in cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in mice depend on conditioning trial duration. Psychopharmacology 146(1):73–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130051090
Dautan D, Huerta-Ocampo I, Witten IB, Deisseroth K, Bolam JP, Gerdjikov T, Mena-Segovia J (2014) A major external source of cholinergic innervation of the striatum and nucleus accumbens originates in the brainstem. J Neurosci 34(13):4509–4518. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5071-13.2014
Ding X, Ma N, Nagahama M, Yamada K, Semba R (2011) Localization of d-serine and serine racemase in neurons and neuroglias in mouse brain. Neurol Sci 32(2):263–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0422-2
Ehmsen JT, Ma TM, Sason H, Rosenberg D, Ogo T, Furuya S, Snyder SH, Wolosker H (2013) d-serine in glia and neurons derives from 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. J Neurosci 33(30):12464–12469. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4914-12.2013
Finch DM (1996) Neurophysiology of converging synaptic inputs from the rat prefrontal cortex, amygdala, midline thalamus, and hippocampal formation onto single neurons of the caudate/putamen and nucleus accumbens. Hippocampus 6(5):495–512. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1996)6:5%3c495:AID-HIPO3%3e3.0.CO;2-I
Freund TF, Powell JF, Smith AD (1984) Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive boutons in synaptic contact with identified striatonigral neurons, with particular reference to dendritic spines. Neuroscience 13(4):1189–1215
Goto M, Yamauchi T, Kamiya N, Miyahara I, Yoshimura T, Mihara H, Kurihara T, Hirotsu K, Esaki N (2009) Crystal structure of a homolog of mammalian serine racemase from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem 284(38):25944–25952. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.010470
Groenewegen HJ, Wright CI, Beijer AV, Voorn P (1999) Convergence and segregation of ventral striatal inputs and outputs. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:49–63
Hashimoto A, Nishikawa T, Hayashi T, Fujii N, Harada K, Oka T, Takahashi K (1992) The presence of free d-serine in rat brain. FEBS Lett 296(1):33–36
Kemp JM, Powell TP (1971) The connexions of the striatum and globus pallidus: synthesis and speculation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 262(845):441–457
Kita H (1993) GABAergic circuits of the striatum. Prog Brain Res 99:51–72
Lee K, Holley SM, Shobe JL, Chong NC, Cepeda C, Levine MS, Masmanidis SC (2017) Parvalbumin interneurons modulate striatal output and enhance performance during associative learning. Neuron 93(6):1451–1463.e1454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.02.033
Li S, Uno Y, Rudolph U, Cobb J, Liu J, Anderson T, Levy D, Balu DT, Coyle JT (2018) Astrocytes in primary cultures express serine racemase, synthesize d-serine and acquire A1 reactive astrocyte features. Biochem Pharmacol 151:245–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.023
Lin H, Jacobi AA, Anderson SA, Lynch DR (2016) d-serine and serine racemase are associated with PSD-95 and glutamatergic synapse stability. Front Cell Neurosci 10:34. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2016.00034
Matsui T, Sekiguchi M, Hashimoto A, Tomita U, Nishikawa T, Wada K (1995) Functional comparison of d-serine and glycine in rodents: the effect on cloned NMDA receptors and the extracellular concentration. J Neurochem 65(1):454–458
Miya K, Inoue R, Takata Y, Abe M, Natsume R, Sakimura K, Hongou K, Miyawaki T, Mori H (2008) Serine racemase is predominantly localized in neurons in mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 510(6):641–654. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21822
Mothet JP, Pollegioni L, Ouanounou G, Martineau M, Fossier P, Baux G (2005) Glutamate receptor activation triggers a calcium-dependent and SNARE protein-dependent release of the gliotransmitter d-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(15):5606–5611. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408483102
Muschamp JW, Nemeth CL, Robison AJ, Nestler EJ, Carlezon WA Jr (2012) DeltaFosB enhances the rewarding effects of cocaine while reducing the pro-depressive effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist U50488. Biol Psychiatry 71(1):44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.08.011
Nishikawa T (2011) Analysis of free d-serine in mammals and its biological relevance. J Chromatogr B 879(29):3169–3183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.08.030
Ouimet CC, Langley-Gullion KC, Greengard P (1998) Quantitative immunocytochemistry of DARPP-32-expressing neurons in the rat caudatoputamen. Brain Res 808(1):8–12
Ouimet CC, Miller PE, Hemmings HC Jr, Walaas SI, Greengard P (1984) DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. III. Immunocytochemical localization. J Neurosci 4(1):111–124
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic, San Diego
Perez EJ, Tapanes SA, Loris ZB, Balu DT, Sick TJ, Coyle JT, Liebl DJ (2017) Enhanced astrocytic d-serine underlies synaptic damage after traumatic brain injury. J Clin Investig 127(8):3114–3125. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI92300
Peron SP, Freeman J, Iyer V, Guo C, Svoboda K (2015) A cellular resolution map of barrel cortex activity during tactile behavior. Neuron 86(3):783–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.027
Phelps PE, Vaughn JE (1986) Immunocytochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase in rat ventral striatum: a light and electron microscopic study. J Neurocytol 15(5):595–617
Phillipson OT, Griffiths AC (1985) The topographic order of inputs to nucleus accumbens in the rat. Neuroscience 16(2):275–296
Puhl MD, Berg AR, Bechtholt AJ, Coyle JT (2015) Availability of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor coagonists affects cocaine-induced conditioned place preference and locomotor sensitization: implications for comorbid schizophrenia and substance abuse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 353(3):465–470. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.115.223099
Puhl MD, Desai RI, Takagi S, Presti KT, Doyle MR, Donahue RJ, Landino SM, Bergman J, Carlezon WA Jr, Coyle JT (2019) N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor co-agonist availability affects behavioral and neurochemical responses to cocaine: insights into comorbid schizophrenia and substance abuse. Addict Biol 24(1):40–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12577
Sason H, Billard JM, Smith GP, Safory H, Neame S, Kaplan E, Rosenberg D, Zubedat S, Foltyn VN, Christoffersen CT, Bundgaard C, Thomsen C, Avital A, Christensen KV, Wolosker H (2017) Asc-1 transporter regulation of synaptic activity via the tonic release of d-serine in the forebrain. Cereb Cortex 27(2):1573–1587. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhv350
Schell MJ, Molliver ME, Snyder SH (1995) d-serine, an endogenous synaptic modulator: localization to astrocytes and glutamate-stimulated release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(9):3948–3952
Smith KL, John CS, Sypek EI, Ongur D, Cohen BM, Barry SM, Bechtholt AJ (2014) Exploring the role of central astrocytic glutamate uptake in ethanol reward in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38(5):1307–1314. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12361
Soares-Cunha C, Coimbra B, Sousa N, Rodrigues AJ (2016) Reappraising striatal D1- and D2-neurons in reward and aversion. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 68:370–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.05.021
Surmeier DJ, Ding J, Day M, Wang Z, Shen W (2007) D1 and D2 dopamine-receptor modulation of striatal glutamatergic signaling in striatal medium spiny neurons. Trends Neurosci 30(5):228–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2007.03.008
Swanson LW (1982) The projections of the ventral tegmental area and adjacent regions: a combined fluorescent retrograde tracer and immunofluorescence study in the rat. Brain Res Bull 9(1–6):321–353
Takagi S, Balu DT, Coyle JT (2015) Subchronic pharmacological and chronic genetic NMDA receptor hypofunction differentially regulate the Akt signaling pathway and Arc expression in juvenile and adult mice. Schizophr Res 162(1–3):216–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2014.12.034
Thibault D, Loustalot F, Fortin GM, Bourque MJ, Trudeau LE (2013) Evaluation of D1 and D2 dopamine receptor segregation in the developing striatum using BAC transgenic mice. PLoS ONE 8(7):e67219. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067219
Wolosker H, Balu DT, Coyle JT (2016) The rise and fall of the d-serine-mediated gliotransmission hypothesis. Trends Neurosci 39(11):712–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2016.09.007
Wolosker H, Blackshaw S, Snyder SH (1999) Serine racemase: a glial enzyme synthesizing d-serine to regulate glutamate-N-methyl-d-aspartate neurotransmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(23):13409–13414. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.23.13409
Xu ZC, Wilson CJ, Emson PC (1989) Restoration of the corticostriatal projection in rat neostriatal grafts: electron microscopic analysis. Neuroscience 29(3):539–550
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Toru Nishikawa and Dr. Makoto Taniguchi for advice and support, as well as Alexandra Berg and Kendall Presti for animal colony maintenance and genotyping. This research was supported by A Phyllis and Jerome Lyle Rappaport Mental Health Research Scholars Award, 1K99MH099252-01A1, and 5R00MH099252-04 (DTB); R01MH05190 and P50MH0G0450 (JTC). Shunsuke Takagi was supported in part by Strategic Young Researcher Overseas Visits Program for Accelerating Brain Circulation from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (S2301). Since participating in this study, MDP has taken a position at Alkermes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ST and JTC designed the study. DTB and JTC contributed to analysis and interpretation of data and assisted in the preparation of the manuscript. MDP and TA contributed to the histochemical studies and animal behavior testing. All authors had contributed to data collection and interpretation, and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
JTC reports consulting with Concert Pharm and holding a Patent on d-serine for the Treatment of Serious Mental Illness, which is owned by Massachusetts General Hospital. MDP is currently employed by Alkermes Pharm. DTB served as a Consultant for LifeSci Capital and received research support from Takeda Pharmaceuticals. ST and TA report no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All animal procedures were conducted in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Academy of Sciences, 2011) and were approved by the McLean Hospital Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takagi, S., Puhl, M.D., Anderson, T. et al. Serine Racemase Expression by Striatal Neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42, 279–289 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00880-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00880-9