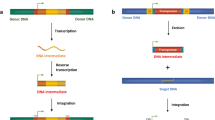
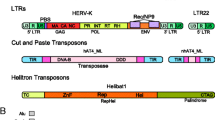
Abstract
Most models of genome size evolution emphasize changes in relative rates of and/or the efficacy of selection on insertions and deletions. However, transposable elements (TEs) are a major contributor to genome size evolution, and since they experience their own selective pressures for expansion, genome size changes may in part be driven by the dynamics of co-evolution between TEs and their hosts. Under this perspective, predictions about the conditions that allow for genome expansion may be altered. In this review, we outline the evidence for TE–host co-evolution, discuss the conditions under which these dynamics can change, and explore the possible contribution to the evolution of genome size. Aided partly by advances in our understanding of the mechanisms of TE silencing via small RNAs, there is growing evidence that the evolution of transposition rates can be important in driving genome expansion and contraction. Shifts in genome size and transposon abundance associated with interspecific hybridization and changes in mating system are consistent with an important role for transposition rate evolution, although other possible explanations persist. More understanding of the potential for the breakdown of host silencing mechanisms and/or the potential for TEs to evade host immune responses will improve our understanding of the importance of changes in TE activity in driving genome size evolution.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LTR:
-
Long terminal repeat
- MITE:
-
Miniature inverted repeat transposable element
- piRNA:
-
piwi-interacting RNA
- siRNA:
-
small interfering RNA
- TE:
-
Transposable element
References
Albach DC, Greilhuber J (2004) Genome size variation and evolution in Veronica. Ann Bot 94:897–911
Almeida R, Allshire RC (2005) RNA silencing and genome regulation. Trends Cell Biol 15:251–258
Aravin AA, Hannon GJ, Brennecke J (2007) The piwi-piRNA pathway provides an adaptive defense in the transposon arms race. Science 318:761–764
Baack EJ, Whitney KD, Rieseberg LH (2005) Hybridization and genome size evolution: timing and magnitude of nuclear DNA content increases in Helianthus homoploid hybrid species. New Phytol 167:623–630
Bennet MD, Leitch IJ (2005) Genome size evolution in plants. In: Gregory TR (ed) The evolution of the genome. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Blumenstiel JP (2011) Evolutionary dynamics of transposable elements in a small RNA world. Trends Genet 27:23–31
Blumenstiel JP, Hartl DL (2005) Evidence for maternally transmitted small interfering RNA in the repression of transposition in Drosophila virilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15965–15970
Brennecke J, Aravin AA, Stark A et al (2007) Discrete small RNA-generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila. Cell 128(6):1089–1103
Charlesworth B, Barton N (2004) Genome size: does bigger mean worse? Curr Biol 14:R233–R235
Charlesworth B, Langley CH (1986) The evolution of self-regulated transposition of transposable elements. Genetics 112:359–383
Charlesworth B, Langley CH (1989) The population genetics of Drosophila transposable elements. Annu Rev Genet 22:251–287
Cui H, Fedoroff NV (2002) Inducible DNA demethylation mediated by the maize Suppressor-mutator transposon-encoded TnpA protein. Plant Cell 14:2883–2899
Desset S, Meignin C, Dastugue B, Vaury C (2003) COM, a heterochromatic locus governing the control of independent endogenous retrovirus from Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 164:501–509
Dolgin ES, Charlesworth B (2006) The fate of transposable elements in asexual populations. Genetics 174:817–827
Gilbert C, Schaack S, Pace JK II, Brindley PJ, Feschotte C (2010) A role for host–parasite interactions in the horizontal transfer of transposons across phyla. Nature 464:1347–1350
González J, Petrov D (2009) Genetics. MITEs—the ultimate parasites. Science 325:1352–1353
Govindaraju DR, Cullis CA (1991) Modulation of genome size in plants—the influence of breeding systems and neighborhood size. Evol Trends Plants 5:43–51
Gregory TR (2004) Insertion–deletion biases and the evolution of genome size. Gene 324:15–34
Gregory TR (2005) The evolution of the genome. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 89–162
Grivna ST, Beyret E, Wang Z, Lin H (2006) A novel class of small RNAs in mouse spermatogenic cells. Genes Dev 20:1709–1714
Hanada K, Vallejo V, Nobuta K et al (2009) The functional role of pack-MULEs in rice inferred from purifying selection and expression profile. Plant Cell 21:25–38
Hawkins JS, Kim H, Nason JD, Wing RA, Wendel JF (2006) Differential lineage-specific amplification of transposable elements is responsible for genome size variation in Gossypium. Genome Res 16:1252–1261
Hollister JD, Gaut BS (2009) Epigenetic silencing of transposable elements: a trade-off between reduced transposition and deleterious effects on neighboring gene expression. Genome Res 19:1419–1428
Hollister JD, Smith LM, Guo Y, Ott F, Weigel D, Gaut BS (2011) Transposable elements and small RNAs contribute to gene expression divergence between Arabidopsis thaliana and Arabidopsis lyrata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:2322–2327
Hu TT, Pattyn P, Bakker EG et al (2011) The Arabidopsis lyrata genome sequence and the basis of rapid genome size change in Arabidopsis. Nat Genet 43:476–481
Hutvágner G, Zamore PD (2002) A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science 297:2056–2060
International Brachypodium Initiative (2010) Genome sequencing and analysis of the model grass Brachypodium distachyon. Nature 463:763–768
International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409:860–921
Jian N, Bao Z, Zhang X, Eddy SR, Wessler SR (2004) Pack-MULE transposable elements mediate gene evolution in plants. Nature 431:569–573
Josefsson C, Dilkes B, Comai L (2006) Parent-dependent loss of gene silencing during interspecies hybridization. Curr Biol 16:322–1328
Juretic N, Hoen DR, Huynh ML, Harrison PM, Bureau TE (2005) The evolutionary fate of MULE-mediated duplications of host gene fragments in rice. Genome Res 15:1292–1297
Kawakami T, Strakosh SC, Zhen Y, Ungerer MC (2010) Different scales of Ty1/copia-like retrotransposon proliferation in the genomes of three diploid hybrid sunflower species. Heredity 104:341–350
King KC, Delph LF, Jokela J, Lively CM (2009) The geographic mosaic of sex and the red queen. Curr Biol 19:1438–1441
Kolaczkowski B, Hupalo DN, Kern AD (2010) Recurrent adaptation in RNA-interference genes across the Drosophila phylogeny. Mol Biol Evol 24:1–12
Lai Z, Nakazato T, Salmaso M et al (2005a) Extensive chromosomal repatterning and the evolution of sterility barriers in hybrid sunflower species. Genetics 171:291–303
Lai J, Li Y, Messing J, Dooner HK (2005b) Gene movement by helitron transposons contributes to the haplotype variability of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:9068–9073
Lisch D (2005) Pack-MULEs: theft on a massive scale. BioEssays 27:353–355
Lisch D (2009) Epigenetic regulation of transposable elements in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60:43–66
Lister R, O'Malley RC, Tonti-Fillippini J et al (2008) Highly integrated single-base resolution maps of the epigenome in Arabidopsis. Cell 133:523–536
Lockton S, Gaut BS (2010) The evolution of transposable elements in natural population of self-fertilizing Arabidopsis thaliana and its outcrossing relative Arabidopsis lyrata. BMC Evol Biol 10:10
Lockton S, Ross-Ibarra J, Gaut BS (2008) Demography and weak selection drives patterns of transposable element diversity in natural populations of Arabidopsis lyrata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13965–13970
Lozovskaya ER, Scheinker VS, Evgen'ev MB (1990) A hybrid dysgenesis syndrome in Drosophila virilis. Genetics 126:619–623
Lu J, Clark AG (2010) Population dynamics of PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) and their targets in Drosophila. Genome Res 20:212–227
Lynch M (2007) The origins of genome architecture. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Lynch M (2011) Statistical inference on the mechanisms of genome evolution. PLoS Genet 7:e1001389. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001389
Lynch M, Conery JS (2003) The origins of genome complexity. Science 302:1401–1404
Lyozin GT, Makarova KS, Veikodvorskaja VV et al (2001) The structure and evolution of Penelope in the virilis species group of Drosophila: an ancient lineage of retroelements. J Mol Evol 52:445–456
Madlung A, Tyagi AP, Watson B et al (2005) Genomic changes in synthetic Arabidopsis polyploids. Plant J 41:221–230
Malone CD, Hannon GJ (2009) Small RNAs as guardians of the genome. Cell 136:656–668
Matzke M, Kanno T, Daxinger L, Huettel B, Matzke AJ (2009) RNA-mediated chromatin-based silencing in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:367–376
Morgan M (2001) Transposable element number in mixed mating populations. Genet Res 77:261–275
Morgante M, Brunner S, Pea G, Fengler K, Zuccolo A, Rafalski A (2005) Gene duplication and exon shuffling by helitron-like transposons generate intraspecies diversity in maize. Nat Genet 37:997–1002
Muotri AR, Marchetto MCN, Coufai NG, Gage FH (2007) The necessary junk: new functions for transposable elements. Hum Mol Genet 16:159–167
Nuzhdin SV, Pasyukova EG, Morozova EA, Flavell AJ (1998) Quantitative genetic analysis of copia retrotransposon activity in inbred Drosophila melanogaster lines. Genetics 150:755–766
Obbard DJ, Gordon KHJ, Buck AH, Jiggins FM (2009) The evolution of RNAi as a defence against viruses and transposable elements. Phil Trans R Soc B 364:99–115
Obbard DJ, Jiggins FM, Bradshaw NJ, Little TJ (2010) Recent and recurrent selective sweeps of the antiviral RNAi gene Argonaute-2 in three species of Drosophila. Mol Biol Evol 28:1043–1056
Orgel LE, Crick FH (1980) Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature 284:604–607
Pagel M, Johnstone RA (1992) Variation across species in the size of the nuclear genome supports the junk-DNA explanation for the C-value paradox. Proc R Soc Lond B 249:119–124
Pannell JR (2009) Mating-system evolution: succeeding by celibacy. Curr Biol 19:983–985
Paterson AH, Bowers JE, Bruggmann R et al (2009) The Sorghum bicolor genome and the diversification of grasses. Nature 457:551–556
Petrov DA (2001) Evolution of genome size: new approaches to an old problem. Trends Genet 17:23–28
Petrov DA, Schutzman JL, Hartl DL, Lozovksaya ER (1995) Diverse transposable elements are mobilized in hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila virilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8050–8054
Petrov DA, Sangster TA, Johnston JS, Hartl DL, Shaw KL (2000) Evidence for DNA loss as a determinant of genome size. Science 287:1060–1062
Pettersson ME, Kurland CG, Berg OG (2009) Deletion rate evolution and its effect on genome size and coding density. Mol Biol Evol 26:1421–1430
Piegu B, Guoyot R, Picault N et al (2006) Doubling genome size without polyploidization: dynamics of retrotransposon-mediated genome expansion in Oryza australiensis, a wild relative of rice. Genome Res 16:1262–1269
Prud'homme NM, Masson GM, Terzian C, Bucheteon A (1995) Flamenco a gene controlling the gypsy retrovirus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 139:697–711
Rieseberg LH (1997) Hybrid origins of plant species. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 28:359–389
Rieseberg LH, Beckstrom-Sternberg SM, Liston, Arias DM (1991) Phylogenetic and systematic inferences from chloroplast DNA and isozyme variation in Helianthus sect. Helianthus (Asteraceae). Syst Bot 16:50–76
Roth BM, Pruss GJ, Vance VB (2004) Plant viral suppressors of RNA silencing. Virus Res 102:97–108
Schnable PS, Ware D, Fulton RS et al (2009) The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 326:1112–1115
Shan XH, Liu ZL, Dong ZY et al (2005) Mobilization of the active MITE transposons mPing and Pong in rice by introgression from wild rice (Zizania latifolia Griseb.). Mol Biol Evol 22:976–990
Shpiz S, Kwon D, Uneva A et al (2007) Characterization of Drosophila telomeric retroelement TAHRE: transcription, transpositions, and RNAi-based regulation of expression. Mol Biol Evol 24:2535–2545
Simmons MJ, Ryzek DF, Lamour C et al (2007) Cytotype regulation by telomeric P elements in Drosophila melanogaster: evidence for involvement of an RNA interference gene. Genetics 176:1945–1955
Slotkin KR, Martienssen R (2007) Transposable elements and the epigenetic regulation of the genome. Nat Rev Genet 8:272–285
Slotkin RK, Freeling M, Lisch D (2003) Mu killer causes the heritable inactivation of the Mutator family of transposable elements in Zea mays. Genetics 165:781–797
Slotkin RK, Freeling M, Lisch D (2005) Heritable transposon silencing initiated by a naturally occurring transposon inverted duplication. Nat Genet 37:641–644
Slotkin KR, Vaughn M, Borges F (2009) Epigenetic reprogramming and small RNA silencing of transposable elements in pollen. Cell 136:461–472
Staton SE, Ungerer MC, Moore RC (2009) The genomic organization of Ty3/Gypsy-like retrotransposons in Helianthus (Asteraceae) homoploid hybrid species. Am J Bot 96:1646–1655
Tenaillon MI, Hollister JD, Gaut BS (2010) A triptych of the evolution of plant transposable elements. Trends Plant Sci 15:471–478
The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815
Ungerer MC, Strakosh SC, Zhen Y (2006) Genome expansion in three hybrid sunflower species is associated with retrotransposon proliferation. Curr Biol 16:872–873
Vitte C, Panaud O (2005) LTR retrotransposons and flowering plant genome size: emergence of the increase/decrease model. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:91–107
Vu W, Nuzhdin S (2011) Genetic variation of copia suppression in Drosophila melanogaster. Heredity 106:207–217
Wang NN, Wang HY, Wang H et al (2010) Transpositoinal reactivation of the Dart transposon family in rice lines derived from introgressive hybridization with Zizania latifolia. BMC Plant Biol 10:190
Waugh O'Neill RJ, O'Neill MJ, Marshall Graves JA (1998) Undermethylation associated with retroelement activation and chromosome remodelling in an interspecific mammalian hybrid. Nature 393:68–72
Whitney KD, Garland T Jr (2010) Did genetic drift drive increases in genome complexity? PLoS Genet 6:e1001080. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001080
Whitney KD, Baack EJ, Hamrick JL et al (2010) A role for nonadtive processes in plant genome evolution? Evolution 64:2097–2109
Whitney KD, Boussau B, Baack EJ, Garland T Jr (2011) Drift and genome complexity revisited. PLoS Genet 7:e1002092. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002092
Wicker T, Guyot R, Yahiaoui N (2003) CACTA transposons in Triticeae—a diverse family of high-copy repetitive elements. Plant Physiol 132:52–63
Wicker T, Zimmerman W, Perovic D et al (2005) A detailed look at 7 million years of genome evolution in 439 kb contiguous barley Hv-elF4E locus: recombination, rearrangements and repeats. Plant J 41:184–194
Wright S, Finnegan D (2001) Genome evolution: sex and transposable element. Curr Biol 11:R296–R299
Wright SI, Schoen DJ (1999) Transposon dynamic and the breeding system. Genetica 107:139–148
Wright SI, Le QH, Schoen DJ et al (2001) Population dynamics of an Ac-like transposable element in self- and cross-pollinating Arabidopsis. Genetics 158:1279–1288
Wright SI, Ness RW, Foxe JP, Barrett SCH (2008) Genomic consequences of outcrossing and selfing in plants. Int J Plant Sci 169:105–118
Yang GJ, Nagel DN, Feschotte C, Hancock NC, Wessler SR (2009) Tuned for transposition: molecular determinants underlying the hyperactivity of a stowaway MITE. Science 325:1391–1394
Zhang X (2008) The epigenetic landscape of plants. Science 320:489–492
Zilberman D, Henikoff S (2007) Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation patterns. Development 134:3959–3965
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: T. Ryan Gregory and Jillian D. Bainard.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ågren, J.A., Wright, S.I. Co-evolution between transposable elements and their hosts: a major factor in genome size evolution?. Chromosome Res 19, 777–786 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-011-9229-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-011-9229-0