Abstract
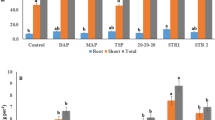
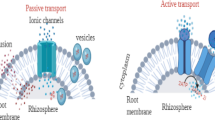
Many studies have conducted to determine the best management practice to reduce the mobility and phytoavailability of the trace metals in contaminated soils. In this study, geochemical speciation and phytoavailability of Zn for sunflower were studied after application of nanoparticles (SiO2 and zeolite, with an application rate of 200 mg kg−1) and bacteria [Bacillus safensis FO-036b(T) and Pseudomonas fluorescens p.f.169] to a calcareous heavily contaminated soil. Results showed that the biotic and abiotic treatments significantly reduced the Zn concentration in the aboveground to non-toxicity levels compared to the control treatment, and the nanoparticle treatments were more effective than the bacteria and control treatments. The concentration of CaCl2-extractable Zn in the treated soils was significantly lower than those of the control treatment. The results of sequential extraction showed that the maximum portion of total Zn belonged to the fraction associated with iron and manganese oxides. On the contrary, the minimum percent belonged to the exchangeable and water-soluble Zn (F1). From the environmental point of view, the fraction associated with iron and manganese oxides is less bioavailable than the F1 and carbonated fractions. On the basis of plant growth promotion, simultaneous application of the biotic and abiotic treatments significantly increased the aboveground dry biomass yield and also significantly reduced the CaCl2-extractable form, uptake by aboveground and translocation factor of Zn compared to the control treatment. Therefore, it might be suggested as an efficient strategy to promote the plant growth and reduce the mobile and available forms of toxic metals in calcareous heavily contaminated soils.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour, A., & Golchin, A. (2011). Immobilization of heavy metals in a contaminated soil in Iran using di-ammonium phosphate, vermicompost and zeolite. Environmental Earth Science, 63, 935–943.
Abdi, G. H., Khui, M. K., & Eshghi, S. (2006). Effects on natural zeolite on growth and flowering on strawberry. International Journal of Agricultural Research, 1, 384–389.
Abreu, C. A., Angela, A. M., Furlani, C., et al. (2006). Quest of water extract analysis of micronutrients in soilless organic substrates. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 37, 2327–2338.
Adrees, M., Ali, Sh, Rizwan, M., et al. (2015). Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 119, 186–197.
Akbari, P., Ghalavand, A., ModarresSanavy, A. M., et al. (2011). The effect of biofertilizers, nitrogen fertilizer and farmyard manure on grain yield and seed quality of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 7, 173–184.
Amoakwah, E., Van Slycken, S., Tack, F. M. G., et al. (2013). Assessing the extraction efficiency of CaCl2 and Rhizon extraction methods after the application of organic matter and CaCl2 as soil amendments to enhance the mobility of Cd and Zn. Environmental & Analytical Toxicology, 3, 167. doi:10.4172/2161-0525.1000167.
Anjum, M., Miandad, R., Waqas, M., et al. (2016). Remediation of wastewater using various nano-materials. Arabian Journal of Chemistry. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.10.004.
Anwaar, S. A., Ali, S., Ali, S., et al. (2014). Silicon (Si) alleviates cotton (Gossypiumhirsutum L.) from zinc (Zn) toxicity stress by limiting Zn uptake and oxidative damage. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(5), 3441–3450. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3938-9.
Bansiwal, A. K., Rayalu, S. S., Labhasetwar, N. K., et al. (2006). Surfactant-modified zeolite as a slow release fertilizer for phosphorus. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54, 4773–4779.
Bokor, B., Bokorová, S., Ondoš, S., et al. (2014a). Ionome and expression level of Si transporter genes (Lsi1, Lsi2, and Lsi6) affected by Zn and Si interaction in maize. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(9), 6800–6811. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3876-6.
Bokor, B., Vaculik, M., Slováková, L., et al. (2014b). Silicon does not always mitigate zinc toxicity in maize. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 36, 733–743.
Bolan, N., Kunhikrishnan, A., Thangarajan, R., et al. (2014). Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils—To mobilize or to immobilize? Journal of Hazardous Materials, 266, 141–166.
Braud, A., Jezequel, K., Bazot, S., et al. (2009). Enhanced phytoextraction of an agricultural Cr and Pb contaminated soil by bioaugmentation with siderophore-producing bacteria. Chemosphere, 74, 280–286.
Braud, A., Jézéquel, K., Vieille, E., et al. (2006). Changes in extractability of Cr and Pb in a polycontaminated soil after bioaugmentation with microbial producers of biosurfactants, organic acids and siderophores. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 6, 261–279.
Calvarro, L. M., de Santiago-Martín, A., Quirós Gómez, J., et al. (2014). Biological activity in metal-contaminated calcareous agricultural soils: The role of the organic matter composition and the particle size distribution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(9), 6176–6187.
Cao, X. D., Wahbi, A., Ma, L., et al. (2009). Immobilization of Zn, Cu, and Pb in contaminated soil using phosphate and phosphoric acid. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 555–564.
Chander, K., & Joergensen, R. G. (2002). Decomposition of 14C labelled glucose in a Pb-contaminated soil remediated with synthetic zeolite and other amendments. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 34, 643–649.
Chang, A. C., Warneke, J. E., Page, A. L., et al. (1984). Accumulation of heavy metals in sewage sludge-treated soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 13, 87–91.
Cornu, J. Y., Elhabiri, M., Ferret, C., et al. (2014). Contrasting effects of pyoverdine on the phytoextraction of Cu and Cd in a calcareous soil. Chemosphere, 103, 212–219.
da Cunha, K. P. V., & do Nascimento, C. W. A. (2009). Silicon effects on metal tolerance and structural changes in maize (Zea mays L.) grown on a cadmium and zinc enriched soil. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 197, 323–330.
da Cunha, K. P. V., do Nascimento, C. W. A., & SilvaJ., A. (2008). Silicon alleviates the toxicity of cadmium and zinc for maize (Zea mays L.) grown on contaminated soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 171, 849–853.
Elliott, H. A., Dempsey, B. A., & Maille, P. J. (1990). Content and fractionation of heavy metals in water treatment sludges. Journal of Environmental Quality, 19, 330–334.
Gee, G. W., & Bauder, J. W. (1986). Particle Size Analysis. In A. Klute (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis: Part 1-physical and mineralogy methods (2nd ed., pp. 383–412). Madison, WI: SSSA.
Hamidpour, M., Khadivi, E., & Afyuni, M. (2016). Residual effects of biosolids and farm manure on speciation and plant uptake of heavy metals in a calcareous soil. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(12), 1–9.
Herman, M. A. B., Nault, B. A., & Smart, C. D. (2008). Effects of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on bell pepper production and green peach aphid infestations in New York. Crop Protection, 27, 996–1002.
Houba, V. J. G., Temminghoff, E. J. M., Gaikhorst, G. A., et al. (2000). Soil analysis procedures using 0.01 M calcium chloride as extraction reagent. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 31(9–10), 1299–1396.
Huang, Q. Y., Chen, W. L., & Guo X. J. (2002). Sequential fractionation of Cu, Zn and Cd in soils in the absence and presence of rhizobia. In Proceedings of 17th WCSS, August 14e21, Thailand, 1453 pp.
Huang, Y., Hu, Y., & Liu, Y. (2009). Combined toxicity of copper and cadmium to six rice genotypes (oryza sativa L.). Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21, 647–653.
Inal, A., Pilbeam, D. J., & Gunes, A. (2009). Silicon increases tolerance to boron toxicity and reduces oxidative damage in Barley. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 32(1), 112–128.
Inglezakis, V. J., Loizidou, M. D., & Grigoropoulou, H. P. (2002). Equilibrium and kinetic ion exchange studies of Pb2+, Cr3+, Fe3+ and Cu2+ on natural clinoptilolite. Water Research, 36(11), 2784–2792.
Issazadeh, K., Savaheli, H., & Momeni, N. (2014). Isolation and identification of heavy metal resistant bacteria from industrial wastewaters in Guilan Province. International Journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research, 2(6), 2066–2071.
Janos, P., Vavrova, J., Herzogova, L., et al. (2010). Effects of inorganic and organic amendments on the mobility (leachability) of heavy metals in contaminated soil: A sequential extraction study. Geoderma, 159, 335–341.
Jones, J., Wolf, B., & Mills, H. A. (1991). Plant analysis handbook: A practical sampling, preparation, analysis, and interpretation guide. Athens, GA: Micro-Macro Publishing.
Kamran, M. A., Eqani, S. A. M. A. S., Bibi, S., et al. (2016). Bioaccumulation of nickel by E. sativa and role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) under nickel stress. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 126, 256–263.
Khare, S., Ahmed, N., Pant, S., et al. (2010). Characterization and evaluation of heavy metal tolerance of bacterial species from soil of waste area near Riyan steel rolling mills, Muzaffarnagar, India. Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 2(1), 88–92.
Khurana, N., & Chatterjee, Ch. (2011). Influence of variable zinc on yield, oil content, and physiology of sunflower. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 32(19–20), 3023–3030.
Kloepper, J. W., & Schroth, M. N. (1978). Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on radishes. In Station de pathologievegetale et phyto-bacteriologie, INRA, Angers, editors. Proceedings of the 4th international conference on plant pathogenic bacteria (Vol. 2, pp. 879–882). Tours: Gilbert-Clarey.
Kloke, A. (1980). Orientierungslaten fur tolerierbare Gesamtgehalteeiniger Elemente in Kulturboden. Mitteilungen der VDLUFA Heft, 1–3, 9–11.
Kumpiene, J., Lagerkvist, A., & Maurice, C. (2008). Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments—A review. Waste Management, 28, 215–225.
Ledin, M., Krantz-Rulcker, C., & Allard, B. (1996). Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 28(6), 791–799.
Li, R. Y., Stroud, J. L., Ma, J. F., et al. (2009). Mitigation of arsenic accumulation in rice with water management and silicon fertilization. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(10), 3778–3783. doi:10.1021/es803643v.
Li, W. C., & Wong, M. H. (2010). Effects of bacteria on metal bioavailability, speciation, and mobility in different metal mine soils: A column study. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 10(2), 313–325.
Liang, Y., Zhang, W., Qin, C., et al. (2006). Effect of exogenous silicon (Si) on H + -ATPase activity, phospholipids and fluidity of plasma membrane in leaves of salt-stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environmental and Experimental Botany, 57, 212–219.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of a DTPA test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 421–428.
Ma, Y., Prasad, M., Rajkumar, M., et al. (2011). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and endophytes acceleratephytoremediation of metalliferous soils. Biotechnology Advances, 29, 248–258.
Mani, D., Kumar, C., & Patel, N. K. (2015). Integrated micro-biochemical approach for phytoremediation of cadmium and zinc contaminated soils. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 111, 86–95.
Marchiol, L., Fellet, G., Perosa, D., et al. (2007). Removal of trace metals by Sorghum bicolor and Helianthus annuus in a site polluted by industrial wastes: A field experience. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 45, 379–387.
Mench, M., Vangronsveld, J., Didier, V., & Clijsters, H. (1994). Evaluation of metal mobility, plant availability and immobilization by chemical agents in a limed-silty soil. Environmental Pollution, 86, 279–286.
Motesharezadeh, B., & Savaghebi-Firoozabadi, G. R. (2010). Bioaccumulation and phyto-translocation of nickel by medicago sativa in a calcareous soil of Iran. Desert, 15, 61–69.
Mousavi, S. M., Bahmanyar, M. A., Pirdashti, H., et al. (2010a). Trace metals distribution and uptake in soil and rice grown on a 3-year vermicompost amended soil. African Journal of Biotechnology. http://www.academicjournals.org/AJB.
Mousavi, S. M., Bahmanyar, M. A., & Pirdashti, H. (2010b). Lead and cadmium availability and uptake by rice plant in response to different biosolids and inorganic fertilizers. American Journal of Agricultural and Biological Sciences, 5(1), 25–31.
Mousavi, S. M., Bahmanyar, M. A., & Pirdashti, H. (2013). Phytoavailability of some micronutrients (Zn and Cu), heavy metals (Pb, Cd), and yield of rice affected by sewage sludge perennial application. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 44, 3246–3258.
Mousavi, S. M., Bahmanyar, M. A., & Pirdashti, H. (2017). Nutritional (Fe, Mn, Ni, and Cr) and growth responses of rice plant affected by perennial application of two bio-solids. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(7), 340. doi:10.1007/s10661-017-6050-z.
Navel, A., & Martins, J. M. F. (2014). Effect of long term organic amendments and vegetation of vineyard soils on the microscale distribution and biogeochemistry of copper. Science of the Total Environment, 466–467, 681–689.
Ok, Y. S., Kim, S. C., Kim, D. K., et al. (2011). Ameliorants to immobilize Cd in rice paddy soils contaminated by abandoned metal mines in Korea. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33, 23–30.
Park, J. H., Bolan, N., Megharaj, M., et al. (2011). Isolation of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their potential for lead immobilization in soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 185, 829–836.
Patten, C. L., & Glick, B. R. (2002). Role of Pseudomonas putida indole acetic acid in development of the host plant root system. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(8), 3795–3801.
Penrose, D. M., & Glick, B. R. (2001). Levels of ACC and related compounds in exudates and extracts of canola seeds treated with ACC-deaminase-containing plant growth promoting bacteria. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 47, 368–372.
Perkins, L. B., Blank, R. R., Ferguson, S. C., et al. (2013). Quick start guide to soil methods for ecologists. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 15, 237–244.
Putwattana, N., Kruatrachue, M., Pokethitiyook, P., et al. (2010). Immobilization of cadmium in soil by cow manure and silicate fertilizer, and reduced accumulation of cadmium in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum). Science Asia, 36, 349–354.
Raval, A. A., & Desai, P. B. (2012). Rhizobacteria from rhizosphere of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) and their effect on plant growth. Research Journal of Recent Sciences, 1, 58–61.
Rogalla, H., & Romheld, V. (2002). Role of leaf apoplast in silicon-mediated manganese tolerance of Cucumissativus L. Plant, Cell and Environment, 25, 549–555.
Saffari, M., Karimian, N., Ronaghi, A., et al. (2016). Stabilization of lead as affected by various amendments and incubation time in a calcareous soil. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 62(3), 317–337.
Sanderson, P., Naidu, R., & Bolan, N. (2014). Ecotoxicity of chemically stabilized metal(loid)s in shooting range soils. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 100, 201–208.
Schalk, I. J., Hannauer, M., & Braud, A. (2011). New roles for bacterial siderophores in metal transport and tolerance. Environmental Microbiology, 13, 2844–2854.
Schwyn, B., & Neilands, J. B. (1987). Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Analytical Biochemistry, 160, 47–56.
Shaheen, S. M., & Rinklebe, J. (2014). Geochemical fractions of chromium, copper, and zinc and their vertical distribution in soil profiles along the Central Elbe River, Germany. Geoderma, 228–229, 142–159.
Shi, X., Zhang, C., Wang, H., et al. (2005). Effect of Si on the distribution of Cd in rice seedlings. Plant and Soil, 272, 53–60.
Shim, J., Shea, P. J., & Oh, B. T. (2014). Stabilization of heavy metals in mining site soil with silica extracted from corn cob. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 225, 2152.
Sparks, D. L. (1996). Methods of soil analysis part 3—Chemical methods. Madison, WI: Soil Science Society of America Inc., American Society of Agronomy Inc.
Syu, C. H., Huang, C. C., Jiang, P. Y., et al. (2016). Effects of foliar and soil application of sodium silicate on arsenic toxicity and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedling grown in As-contaminated paddy soils. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 62(4), 357–366.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Blsson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 52, 45–53.
Weaver, R. W., Angle, S., Bottomley, P., et al. (1994). Methods of soil analysis: Part 2, microbiological and biochemical properties. Wisc: Soil Science Society of America Madison.
Wen, W. J., Yu, S., Yong-Xing, Z., et al. (2013). Mechanisms of enhanced heavy metal tolerance in plants by silicon: A review. Pedosphere, 23(6), 815–825.
Wu, S. C., Luo, Y. M., Cheung, K. C., et al. (2006). Influence of bacteria on Pb and Zn speciation, mobility and bioavailability in soil: A laboratory study. Environmental Pollution, 144, 765–773.
Wu, C., Yan, Sh, Zhang, H., et al. (2015). Chemical forms of cadmium in a calcareous soil treated with different levels of phosphorus-containing acidifying agents. Soil Research, 53, 105–111.
Xiu-Zhen, H., Dong-Mei, Z., Dan-Dan, L., et al. (2012). Growth, cadmium and zinc accumulation of ornamental sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) in contaminated soil with different amendments. Pedosphere, 22(5), 631–639.
Xu, X., Huang, Q., Huang, Q., et al. (2012). Soil microbial augmentation by an EGFP-tagged Pseudomonas putida X4 to reduce phytoavailable cadmium. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 71, 55–60.
Yao, A., Wang, Y., Ling, X., et al. (2017). Effects of an iron-silicon material, a synthetic zeolite and an alkaline clay on vegetable uptake of As and Cd from a polluted agricultural soil and proposed remediation mechanisms. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39(2), 353–367. doi:10.1007/s10653-016-9863-8.
Yasuda, H., Takama, K., Fukuda, T., et al. (1998). Effects of zeolite on water and salt control in soil. Bulletin of the Faculty of Agriculture, Tottori University, 51, 35–42.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Iran National Science Foundation (Grant Number 96000777); and the study held under the auspices of the respected council; in this regard, the authors are truly grateful.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mousavi, S.M., Motesharezadeh, B., Hosseini, H.M. et al. Geochemical fractions and phytoavailability of Zinc in a contaminated calcareous soil affected by biotic and abiotic amendments. Environ Geochem Health 40, 1221–1235 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0038-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0038-z