Abstract
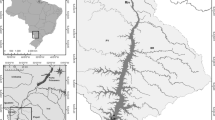
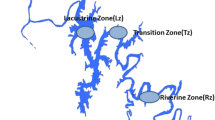
We evaluated a 4-year data set (July 2003 to June 2007) to assess the trophic state and its limiting factors of Three-Gorges Reservoir (TGR), China, a large subtropical reservoir. Based on Carlson-type trophic state index (TSI)CHL, the trophic state of the system was oligotrophic (TSIS < 40) in most months after the reservoir became operational, although both TSITP and TSITN were higher than the critical value of eutrophic state (TSIS > 50). Using Carlson’s (1991) two-dimensional approach, deviations of the TSIS indicated that factors other than phosphorus and nitrogen limited algal growth and that nonalgal particles affected light attenuation. These findings were further supported by the significant correlation among the values of TSICHL − TSISD and nonvolatile suspended solids and water residence time. The logarithmic model showed that an equivalent TSICHL and TSISD could be found at τ = 54 days in the TGR (Fig. 7). Accordingly, nonalgal particulates dominated light attenuation and limited algal biomass of the reservoir when τ < 54 days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1989). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (17th ed.). Washington, DC: American Water Works Association, and Water Pollution Control Federation.
An, K. G., & Park, S. S. (2003). Influence of seasonal monsoon on the trophic state deviation in an Asian reservoir. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 145, 267–287.
Brett, M. T., & Benjamin, M. M. (2008). A review and reassessment of lake phosphorus retention and the nutrient loading concept. Freshwater Biology, 53, 194–211.
Burford, M. A., Johnson, S. A., Cook, A. J., Packer, T. V., Taylor, B. M., & Townsley, E. R. (2007). Correlations between watershed and reservoir characteristics, and algal blooms in subtropical reservoirs. Water Research, 41, 4105–4114.
Cai, Q. H., & Hu, Z. Y. (2006). Studies on eutrophication problem and control strategy in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 30, 7–11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 22, 361–369.
Carlson, R. E. (1991). Expanding the trophic state concept to identify non-nutrient limited lakes and reservoirs. In L. Carpenter (Ed.), Proceedings of a national conference on enhancing the states’ lake management programs (pp. 59–71). Chicago: USEPA.
Carpenter, S. R., Caraco, N. F., Correll, D. L., Howarth, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., & Smith, V. H. (1998). Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications, 8, 559–568.
Carpenter, S. R., Ludwig, D., & Brock, W. A. (1999). Management of eutrophication for lakes subject to potentially irreversible change. Ecological Applications, 9, 751–771.
Chen, X., Yan, Y., Fu, R., Dou, X., & Zhang, E. (2007). Sediment transport from the Yangtze River, China, into the sea over the Post-Three Gorge Dam Period: A discussion. Quaternary International, 186, 55–64.
Dodds, W., & Cole, J. (2007). Expanding the concept of trophic state in aquatic ecosystems: It’s not just the autotrophs. Aquatic Sciences, 69, 427–439.
Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1997). Lake Michigan mass balance, methods compendium: LMMB 065 (ESS method 340.2) (Vol. 3). Chicago: USEPA.
Ferris, J. A., & Lehman, J. T. (2007). Interannual variation in diatom bloom dynamics: Roles of hydrology, nutrient limitation, sinking, and whole lake manipulation. Water Research, 41, 2551–2562.
Friedl, G., & Wüest, A. (2002). Disrupting biogeochemical cycles—consequences of damming. Aquatic Sciences, 64, 55–65.
Gemmer, M., Jiang, T., Su, B., & Kundzewicz, Z. W. (2008). Seasonal precipitation changes in the wet season and their influence on flood/drought hazards in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Quaternary International, 186, 12–21.
Genkai-Kato, M., & Carpenter, S. R. (2005). Eutrophication due to phosphorus recycling in relation to lake morphometry, temperature, and macrophytes. Ecology, 86, 210–219.
George, D. G., & Hurley, M. A. (2003). Using a continuous function for residence time to quantify the impact of climate change on the dynamics of thermally stratified lakes. Journal of Limnology, 62, 21–26.
Ha, K., Jang, M. H., & Joo, G. J. (2003). Winter Stephanodiscus bloom development in the Nakdong River regulated by an estuary dam and tributaries. Hydrobiologia, 506–509, 221–227.
Havens, K. E. (2000). Using trophic state index (TSI) values to draw inferences regarding phytoplankton limiting factors and seston composition from routine water quality monitoring data. Korean Journal of Limnology, 33, 187–196.
Howarth, R. W., & Roxanne, M. (2006). Nitrogen as the limiting nutrient for eutrophication in coastal marine ecosystems: Evolving views over three decades. Limnology and Oceanography, 51, 364–376.
Huang, X. F., Chen, W. M., & Cai, Q. M. (2000). Survery, observation and analysis of lake ecology. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese).
Huang, Z. L., Li, Y. L., Chen, Y. C., & Li, J. X. (2006). Water quality prediction and water environmental carrying capacity calculation for Three Gorges Reservoir. Beijing: China Water Power (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jones, I. D., & Elliott, J. A. (2007). Modelling the effects of changing retention time on abundance and composition of phytoplankton species in a small lake. Freshwater Biology, 52, 988–997.
Kagalou, I., Papastergiadoub, E., & Leonardosa, I. (2008). Long term changes in the eutrophication process in a shallow Mediterranean lake ecosystem of W. Greece: Response after the reduction of external load. Journal of Environmental Management, 87, 497–506.
Kasai, H., Saito, H., Yoshimori, A., & Taguchi, S. (1997). Variability in timing and magnitude of spring bloom in the Oyashio region, the western subarctic Pacific off Hokkaido, Japan. Fisheries Oceanography, 6, 118–129.
Kratzer, C. R., & Brezonik, P. L. (1981). A Carlson-type trophic state index for nitrogen in Florida lakes. Water Resources Bulletin, 17, 713–715.
Lehman, J. T., Platte, R. A., & Ferris, J. A. (2007). Role of hydrology in development of a vernal clear water phase in an urban impoundment. Freshwater Biology, 52, 1773–1781.
Matthews, R., Hilles, M., & Pelletier, G. (2002). Determining trophic state in Lake Whatcom, Washington (USA), a soft water lake exhibiting seasonal nitrogen limitation. Hydrobiologia, 468, 107–121.
Osgood, R. A. (1982). Using differences among Carlson’s trophic state index values in regional water quality assessment. Water Resources Bulletin, 18, 67–74.
Portielje, R., & Molen, D. T. V. D. (1999). Relationships between eutrophication variables: From nutrient loading to transparency. Hydrobiologia, 408/409, 375–387.
Schindler, D. W. (2006). Recent advances in the understanding and management of eutrophication. Limnology and Oceanography, 51, 356–363.
Shao, M., Xie, Z., Han, X., Cao, M., & Cai, Q. (2008). Macroinvertebrate community structure in Three-Gorges Reservoir, China. International Review of Hydrobiology, 93, 175–187.
Smith, V. H., Tilman, G. D., & Nekola, J. C. (1999). Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environmental Pollution, 100, 179–196.
Straškraba, M., & Tundisi, J. G. (1999). Guidelines of lake management: Reservoir water quality management (Vol. 9). Shiga: International Lake Environment Committee.
Verspagen, J. M. H., Passarge, J., Johnk, K. D., Visser, P. M., Peperzak, L., Boers, P., et al. (2006). Water management strategies against toxic microcystis blooms in the Dutch delta. Ecological Applications, 16, 313–327.
Wang, J., Wang, B. S., & Luo, Z. Q. (1997). Dictionary of the Yangtze River. Wuhan: Wuhan (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Cai, Q., Han, X. et al. Factors regulating trophic status in a large subtropical reservoir, China. Environ Monit Assess 169, 237–248 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1165-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1165-5