Abstract
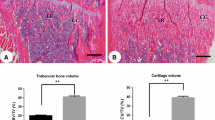
It is known that estrogen deficiency increases osteoclast formation and activity. Autophagy, a cell survival pathway, has been shown to be crucial for osteoclast function. However, little is known about the effects of estrogen depletion on osteoclast autophagy. Here, we evaluated the effects of estrogen deficiency in the immunoexpression of autophagy mediators in alveolar bone osteoclasts of ovariectomized rats. Twelve adult female rats were ovariectomized (OVX-group) or SHAM-operated (SHAM-group). After three weeks, the rats were euthanized and maxillary fragments containing alveolar bone of the first molars were processed for light microscopy or transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Paraffin-sections were subjected to the TRAP method (osteoclast marker) or to the immunohistochemical detections of beclin-1, LC3α, and p62 (autophagy mediators); araldite-sections were processed for TEM. The number of TRAP-positive osteoclasts and the number of immunolabeled-multinucleated cells (MNCs) along the alveolar bone surface of the first molar were computed. The number of TRAP-positive osteoclasts and the number of beclin-1-, LC3α- and p62-immunolabelled osteoclasts were significantly higher in OVX-group than the SHAM-group. MNCs were frequently located juxtaposed to Howship lacunae along the alveolar bone surface, indicating that these cells are osteoclasts. TEM revealed osteoclasts exhibiting autophagosomes. Our data indicate that autophagy plays an important role during estrogen deficiency-induced osteoclastogenesis. Thus, our results contribute to a better understanding on the role of autophagy on osteoclasts under estrogenic deficiency, and reinforce the idea that modulation of autophagy may be a useful tool to inhibit excessive oral bone resorption in post-menopausal women.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai A, Kim S, Goldshteyn V, Kim T, Park NH, Wang CY, Kim RH (2019) Beclin1 modulatesbonehomeostasis by regulatingosteoclast and chondrocyte differentiation. J Bone Miner Res 34:1753–1766. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.3756
Azari A, Schoenmaker T, de Souza Faloni AP, Everts V, de Vries TJ (2011) Jaw and long bone marrow derived osteoclasts differ in shape and their response to bone and dentin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 409:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.04.120
Bento CF, Renna M, Ghislat G, Puri C, Ashkenazi A, Vicinanza M, Menzies FM, Rubinsztein DC (2016) Mammalian autophagy: how does it work? Annu Rev Biochem 85:685–713. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060815-014556
Cann GM, Guignabert C, Ying L, Deshpande N, Bekker JM, Wang L, Zhou B, Rabinovitch M (2008) Developmental expression of LC3alpha and beta: absence of fibronectin or autophagy phenotype in LC3beta knockout mice. Dev Dyn 237:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.21392
Cerri PS (2005) Osteoblasts engulf apoptotic bodies during alveolar bone formation in the rat maxilla. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 286:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.a.20220
Chamoux E, Couture J, Bisson M, Morissette J, Brown JP, Roux S (2009) The p62 P392L mutation linked to Paget’s disease induces activation of human osteoclasts. Mol Endocrinol 23:1668–1680. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2009-0066
Cheng L, Zhu Y, Ke D, Xie D (2020) Oestrogen-activated autophagy has a negative effect on the anti-osteoclastogenic function of oestrogen. Cell Prolif 11:e12789. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12789
Chung YH, Jang Y, Choi B, Song DH, Lee EJ, Kim SM, Song Y, Kang SW, Yoon SY, Chang EJ (2014) Beclin-1 is required for RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Physiol 229:1963–1971. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24646
Chung YH, Yoon SY, Choi B, Sohn DH, Yoon KH, Kim WJ, Kim DH, Chang EJ (2012) Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 regulates Cdc42-dependent actin ring formation in osteoclast. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:989–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2012.03.007
Crockett R, Rogers MJ, Coxon FP, Hocking LJ, Helfrich MH (2011) Bone remodelling at a glance. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 7):991–998. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.063032
Cruzoé-Souza M, Sasso-Cerri E, Cerri OS (2009) Immunohistochemical detection of estrogen receptor beta in alveolar bone cells of estradiol-treated female rats: possible direct action of estrogen on osteoclast life span. J Anat 215:673–681
Daroszewska A, van't Hof RJ, Rojas JA, Layfield R, Landao-Basonga E, Rose L, Rose K, Ralston SH (2011) A point mutation in the ubiquitin-associated domain of SQSMT1 is sufficient to cause a Paget's disease-like disorder in mice. Hum Mol Genet 20:2734–2744. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr172
de Souza Faloni AP, Schoenmaker T, Azari A, Katchburian E, Cerri PS, de Vries TJ, Everts V (2011) Jaw and long bone marrows have a different osteoclastogenic potential. Calcif Tissue Int 88:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-010-9418-4
Deretic V, Saitoh T, Akira S (2013) Autophagy in infection, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 13:722–737. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3532
DeSelm CJ, Miller BC, Zou W, Beatty WL, van Mee E, Takahata Y, Klumperman J, Tooze SA, Teitelbaum SL, Virgin HW (2011) Autophagy proteins regulate the secretory component of osteoclastic bone resorption. Dev Cell 21:966–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2011.08.016
Duran A, Serrano M, Leitges M, Flores JM, Picard S, Brown JP, Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT (2004) The atypical PKC-interacting protein p62 is an important mediator of RANK-activated osteoclastogenesis. Dev Cell 6:303–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00403-9
Emerton KB, Hu B, Woo AA, Sinofsky A, Hernandez C, Majeska RJ, Jepsen KJ, Schaffler MB (2010) Osteocyte apoptosis and control of bone resorption following ovariectomy in mice. Bone 46:577–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2009.11.006
Eskelinen EL (2008) Fine structure of the autophagosome. Methods Mol Biol 445:11–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-157-4_2
Faloni AP, Sasso-Cerri E, Katchburian E, Cerri PS (2007) Decrease in the number and apoptosis of alveolar bone osteoclasts in estrogen-treated rats. J Periodontal Res 42:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0765.2006.00932.x
Faloni AP, Sasso-Cerri E, Rocha FR, Katchburian E, Cerri PS (2012) Structural and functional changes in the alveolar bone osteoclasts of estrogen-treated rats. J Anat 220:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2011.01449.x
Feng Y, He D, Yao Z, Klionsky DJ (2014) The machinery of macroautophagy. Cell Res 24:24–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2013.168
Filomeni G, De Zio D, Cecconi F (2015) Oxidative stress and autophagy: the clash between damage and metabolic needs. Cell Death Differ 22:377–388. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2014.150
Florencio-Silva R, Sasso GR, Simões MJ, Simões RS, Baracat MC, Sasso-Cerri E, Cerri PS (2017) Osteoporosis and autophagy: what is the relationship? Rev Assoc Med Bras 63:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9282.63.02.173
Florencio-Silva R, Sasso GRS, Sasso-Cerri E, Simões MJ, Cerri PS (2018) Effects of estrogen status in osteocyte autophagy and its relation to osteocyte viability in alveolar process of ovariectomized rats. Biomed Pharmacother 98:406–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017
Glick D, Barth S, Macleod KF (2010) Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol 221:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2697
Goyal L, Goyal T, Gupta ND (2017) Osteoporosis and periodontitis in postmenopausal women: a systematic review. J Midlife Health 8:151–158. https://doi.org/10.4103/jmh.JMH_55_17
Hiruma Y, Kurihara N, Subler MA, Zhou H, Boykin CS, Zhang H, Ishizuka S, Dempster DW, Roodman GD, Windle JJ (2008) A SQSTM1/p62 mutation linked to Paget’s disease increases the osteoclastogenic potential of the bone microenvironment. Hum Mol Genet 17:3708–3719. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddn266
Ichimura Y, Komatsu M (2010) Selective degradation of p62 by autophagy. Semin Immunopathol 32:431–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-010-0220-1
Johnston BD, Ward WE (2015) The ovariectomized rat as a model for studying alveolar bone loss in postmenopausal women. Biomed Res Int 2015:635023. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/635023
Kaur J, Debnath J (2015) Autophagy at the crossroads of catabolism and anabolism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16:461–472. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm4024
Khosla S (2010) Pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Transl Endocrinol Metab 1:55–86. https://doi.org/10.1210/TEAM.9781879225718.ch2
Khosla S, Oursler MJ, Monroe DG (2012) Estrogen and the skeleton. Trends Endocrinol Metab 23:576–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2012.03.008
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD, Adeli K et al (2016) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy 12:1–222. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1100356
Kurihara N, Hiruma Y, Zhou H, Subler MA, Dempster DW, Singer FR, Reddy SV, Gruber HE, Windle JJ, Roodman GD (2007) Mutation of the sequestosome 1 (p62) gene increases osteoclastogenesis but does not induce Paget disease. J Clin Investig 117:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI28267
Levine B, Klionsky DJ (2004) Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell 6:463–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1534-5807(04)00099-1
Li JY, Tawfeek H, Bedi B, Yang X, Adams J, Gao KY, Zayzafoon M, Weitzmann MN, Pacifici R (2011) Ovariectomy disregulates osteoblast and osteoclast formation through the T-cell receptor CD40 ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:768–773. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1013492108
Li RF, Chen G, Ren JG, Zhang W, Wu ZX, Liu B, Zhao Y, Zhao YF (2014) The adaptor protein p62 is involved in RANKL-induced autophagy and osteoclastogenesis. J Histochem Cytochem 62:879–888. https://doi.org/10.1369/0022155414551367
Lin NY, Beyer C, Giessl A, Kireva T, Scholtysek C, Uderhardt S, Munoz LE, Dees C, Distler A, Wirtz S, Krönke G, Spencer B, Distler O, Schett G, Distler JH (2013) Autophagy regulates TNFalpha-mediated joint destruction in experimental arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 72:761–768. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201671
Lin NY, Chen CW, Kagwiria R, Liang R, Beyer C, Distler A, Luther J, Engelke K, Schett G, Distler JH (2016) Inactivation of autophagy ameliorates glucocorticoid-induced and ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Ann Rheum Dis 75:1203–1210. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207240
Lippai M, Lőw P (2014) The role of the selective adaptor p62 and ubiquitin-like proteins in autophagy. BioMed Res Int 2014:832704. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/832704
Longhini R, de Oliveira PA, de Souza Faloni AP, Sasso-Cerri E, Cerri PS (2013) Increased apoptosis in osteoclasts and decreased RANKL immunoexpression in periodontium of cimetidine-treated rats. J Anat 222:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.12011
Luo P, Gao F, Han J, Sun W, Li Z (2018) The role of autophagy in steroid necrosis of the femoral head: a comprehensive research review. Int Orthop 42:1747–1753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3994-8
Martinet W, Roth L, De Meyer GRY (2017) Standard immunohistochemical assays to assess autophagy in mammalian tissue. Cells 6(3):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells6030017
McManus S, Roux S (2012) The adaptor protein p62/SQSTM1 in osteoclast signaling pathways. J Mol Signal 7:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-2187-7-1
Morissette J, Laurin N, Brown JP (2006) Sequestosome 1: mutation frequencies, haplotypes, and phenotypes in familial Paget’s disease of bone. J Bone Miner Res 21(Suppl 2):P38-44. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.06s207
Onal M, Piemontese M, Xiong J, Wang Y, Han L, Ye S, Komatsu M, Selig M, Weinstein RS, Zhao H, Jilka RL, Almeida M, Manolagas SC, O’Brien CA (2013) Suppression of autophagy in osteocytes mimics skeletal aging. J Biol Chem 288:17432–17440. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.444190
Park HJ, Son HJ, Sul OJ, Suh JH, Choi HS (2018) 4-Phenylbutyric acid protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced bone loss by modulating autophagy in osteoclasts. Biochem Pharmacol 151:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.02.019
Shapiro IM, Layfield R, Lotz M, Settembre C, Whitehouse C (2014) Boning up on autophagy: the role of autophagy in skeletal biology. Autophagy 10:7–19. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.26679
Schaffler MB, Cheung WY, Majeska R, Kennedy O (2014) Osteocytes: master orchestrators of bone. Calcif Tissue Int 94:5–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-013-9790-y
Shen G, Ren H, Shang Q, Qiu T, Yu X, Zhang Z, Huang J, Zhao W, Zhang Y, Liang D, Jiang X (2018) Autophagy as a target for glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis therapy. Cell Mol Life Sci 75:2683–2693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2776-1
Siddiqui JA, Partridge NC (2016) Physiological bone remodeling: systemic regulation and growth factor involvement. Physiology (Bethesda) 31:233–245. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00061.2014
Song L, Tan J, Wang Z, Ding P, Tang Q, Xia M, Wei Y, Chen L (2019) Interleukin-17A facilitates osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption via activation of autophagy in mouse bone marrow macrophages. Mol Med Rep 19:4743–4752. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10155
Sul OJ, Park HJ, Son HJ, Choi HS (2017) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced autophagy is responsible for enhanced osteoclastogenesis. Mol Cells 40:880–887
Sun Q, Fan W, Zhong Q (2009) Regulation of Beclin 1 in autophagy. Autophagy 5:713–716. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.5.5.8524
Sundaram K, Shanmugarajan S, Rao DS, Reddy SV (2011) Mutant p62P392L stimulation of osteoclast differentiation in Paget’s disease of bone. Endocrinology 152:4180–4189. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2011-1225
Svedha PR, Mahendra J, Theayarajar R, Namachivayam A (2017) Comparison of bone mineral density among pre- and post-menopausal women with and without chronic generalized periodontitis. J Indian Soc Periodontol 21:119–124. https://doi.org/10.4103/jisp.jisp_43_16
Usategui-Martín R, García-Aparicio J, Corral-Gudino L, Calero-Paniagua I, Del Pino-Montes J, González Sarmiento R (2015) Polymorphisms in autophagy genes are associated with paget disease of bone. PLoS ONE 10:e0128984. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128984
Wang T, He H, Liu S, Jia C, Fan Z, Zhong C, He C (2019) Autophagy: a promising target for age-related osteoporosis. Curr Drug Targets 20:354–365. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389450119666180626120852
Wein MN (2017) Bone lining cells: normal physiology and role in response to anabolic osteoporosis treatments. Curr Mol Bio Rep 3:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40610-017-0062-x
Weitzmann MN, Pacifici R (2006) Estrogen deficiency and bone loss: an inflammatory tale. J Clin Invest 116:1186–1194. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI28550
Xu XC, Chen H, Zhang X, Zhai ZJ, Liu XQ, Zheng XY, Zhang J, Qin A, Lu EY (2015) Effects of oestrogen deficiency on the alveolar bone of rats with experimental periodontitis. Mol Med Rep 12:3494–3502. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3875
Xue Y, Liang Z, Fu X, Wang T, Xie Q, Ke D (2019) IL-17A modulates osteoclast precursors’ apoptosis through autophagy-TRAF3 signaling during osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 508:1088–1092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.029
Yan K, Wu C, Ye Y, Li L, Wang X, He W, Ren S, Xu Y (2020) A20 inhibits osteoclastogenesis via TRAF6-dependent autophagy in human periodontal ligament cells under hypoxia. Cell Prolif 53:e12778. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12778
Yang Z, Klionsky DJ (2010) Mammalian autophagy: core molecular machinery and signaling regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2009
Yin Z, Pascual C, Klionsky DJ (2016) Autophagy: machinery and regulation. Microb Cell 3:588–596
Zach F, Polzer F, Mueller A, Gessner A (2018) p62/sequestosome 1 deficiency accelerates osteoclastogenesis in vitro and leads to Paget’s disease-like bone phenotypes in mice. J Biol Chem 293:9530–9541. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.002449
Zhang X, Xu X, Liu X, Mao C, Qin A, Lu E (2018) Bis-enoxacin blocks alveolar bone resorption in rats with ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. Mol Med Rep 17:3232–3238. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8223
Zhang Y, Cui Y, Wang L, Han J (2020) Autophagy promotes osteoclast podosome disassembly and cell motility athrough the interaction of kindlin3 with LC3. Cell Signal. 67:109505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109505
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank Mr Paulo Celso Franco, Mr Luis Antônio Potenza and Mr Pedro Sérgio Simões for technical assistances. This research was supported by public funding from São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP: 2012/19428-8) and National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and CAPES (code 001) – Brazil.
Funding
This research was supported by public funding from São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP—Grant Numbers 2012/19428-8; 2012/22666-8), National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and by Coordination of Improvement of Higher Level Personnel (CAPES, code 001), Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: RF-S, GRSS, MJS, PSC; Resources: MJS, PSC; Execution of experiment: RF-S, GRSS; Data collection and analysis: RF-S, GRSS, ES-C, PSC; Writing—original draft: RF-S; Writing—review and editing: RF-S, GRSS, MJS, ES-C, PSC. Supervision: MJS, PSC. Project Administration: RF-S. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethical Committee for Animal Research of Universidade Federal de São Paulo (UNIFESP).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Florencio-Silva, R., Sasso, G.R.S., Sasso-Cerri, E. et al. Immunoexpression pattern of autophagy mediators in alveolar bone osteoclasts following estrogen withdrawal in female rats. J Mol Histol 52, 321–333 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09953-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09953-x