Abstract
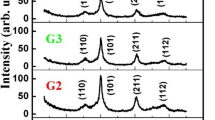
A comparative study of spray-deposited NixZn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0 to 0.5) thin films has been performed specifically on their structural and gas sensing properties. The films were characterized by X-ray diffraction and field emission scanning electron microscopy. The structural and morphological study reveal the formation of nanocrystalline cubic spinel structure with porous surface morphology. The Rietveld refinement study shows the crystalline structure and it gives proper atomic distribution among spinel sites. The gas sensing study indicates the selectivity of material toward SO2 gas. The study of dependence between the optimal operating temperature and nickel substitution shows a reduction in the operating temperature of the sensor. The optimized film with composition Ni0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4 shows the maximum response to SO2 gas at a lower operating temperature of 130 °C. These results can be applied in designing low energy consumption SO2 gas sensors.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
N. Aggarwal, S.B. Narang, Magnetic characterization of Nickel-Zinc spinel ferrites along with their microwave characterization in Ku band. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 513, 167052 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167052
A.I. Tovstolytkin, M.M. Kulyk, V.M. Kalita, S.M. Ryabchenko, V.O. Zamorskyi, O.P. Fedorchuk, S.O. Solopan, A.G. Belous, Nickel-zinc spinel nanoferrites: magnetic characterization and prospects of the use in self-controlled magnetic hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 473, 422–427 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.10.075
T. Tsoncheva, I. Spassova, G. Issa, R. Ivanova, D. Kovacheva, D. Paneva, D. Karashanova, N. Velinov, B. Tsyntsarski, B. Georgieva, M. Dimitrov, N. Petrov, Ni0.5M0.5Fe2O4 (M = Cu, Zn) ferrites hosted in nanoporous carbon from waste materials as catalysts for hydrogen production. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 12, 1371–1384 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01094-2
S.A. Jadhav, S.B. Somvanshi, M.V. Khedkar, S.R. Patade, K.M. Jadhav, Magneto-structural and photocatalytic behavior of mixed Ni–Zn nano-spinel ferrites: visible light-enabled active photodegradation of rhodamine B. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 11352–11365 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03684-1
B. Gayathri Manju, P. Raji, Green synthesis of nickel–copper mixed ferrite nanoparticles: structural, optical, magnetic, electrochemical and antibacterial studies. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 7710–7720 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07603-x
A. Rahman, H. Abdullah, M.S. Zulfakar, M.J. Singh, M.T. Islam, Microwave dielectric properties of MnxZn(1–x)Fe2O4 ceramics and their compatibility with patch antenna. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 77, 470–479 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3937-4
P.T. Phong, P.H. Nam, D.H. Manh, D.K. Tung, I.-J. Lee, N.X. Phuc, Studies of the magnetic properties and specific absorption of Mn0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 287–294 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-014-3463-0
M.V. Nikolic, Z.Z. Vasiljevic, M.D. Lukovic, V.P. Pavlovic, J.B. Krstic, J. Vujancevic, N. Tadic, B. Vlahovic, V.B. Pavlovic, Investigation of ZnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanocrystalline screen-printed thick films for application in humidity sensing. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 16, 981–993 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.13190
V.D. Kapse, S.A. Ghosh, F.C. Raghuwanshi, S.D. Kapse, U.S. Khandekar, Nanocrystalline Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4: a novel semiconducting material for ethanol detection. Talanta 78, 19–25 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.10.031
A.P. Kazin, M.N. Rumyantseva, V.E. Prusakov, I.P. Suzdalev, A.M. Gaskov, Nanocrystalline ferrites NixZn1−xFe2O4: influence of cation distribution on acidic and gas sensing properties. J. Solid State Chem. 184, 2799–2805 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2011.08.029
H.R. Ebrahimi, M. Parish, G.R. Amiri, B. Bahraminejad, S. Fatahian, Synthesis, characterization and gas sensitivity investigation of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 414, 55–58 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.04.043
S.P. Dalawai, T.J. Shinde, A.B. Gadkari, P.N. Vasambekar, Ni–Zn ferrite thick film gas sensors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 9016–9025 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3585-z
S.B. Madake, M.R. Hattali, K.Y. Rajpure, Porogen induced formation of mesoporous zinc ferrite thin films and their chemiresistive properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 263, 114867 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114867
S.S. Kumbhar, M.A. Mahadik, V.S. Mohite, Y.M. Hunge, K.Y. Rajpure, C.H. Bhosale, Effect of Ni content on the structural, morphological and magnetic properties of spray deposited Ni–Zn ferrite thin films. Mater. Res. Bull. 67, 47–54 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.02.056
S.S. Kumbhar, M.A. Mahadik, V.S. Mohite, K.Y. Rajpure, C.H. Bhosale, Synthesis and characterization of spray deposited nickel–zinc ferrite thin films. Energy Procedia 54, 599–605 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.07.301
P. Surendran, A. Lakshmanan, S.S. Priya, K. Balakrishnan, P. Rameshkumar, T.A. Hegde, G. Vinitha, G. Ramalingam, A.A. Raj, Investigations on solid-state parameters of third-order nonlinear optical Ni1−xZnxFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by microwave-assisted combustion method. Appl. Phys. A 126, 257 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3435-6
J. Gao, Y. Cui, Z. Yang, The magnetic properties of NixZn1−xFe2O4 films fabricated by alternative sputtering technology. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 110, 111–114 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2003.10.111
D. Guo, Z. Zhang, M. Lin, X. Fan, G. Chai, Y. Xu, D. Xue, Ni–Zn ferrite films with high resonance frequency in the gigahertz range deposited by magnetron sputtering at room temperature. J. Phys. D 42, 125006 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/42/12/125006
K. Momma, F. Izumi, VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 44, 1272–1276 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889811038970
P. Sahoo, Surface topography, in: Tribology for Engineers (Elsevier, 2011), pp. 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857091444.1
A. Singh, A. Singh, S. Singh, P. Tandon, Fabrication of copper ferrite porous hierarchical nanostructures for an efficient liquefied petroleum gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B 244, 806–814 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.01.069
X.-Z. Song, Y.-L. Meng, Z. Tan, L. Qiao, T. Huang, X.-F. Wang, Concave ZnFe2O4 hollow octahedral nanocages derived from Fe-doped MOF-5 for high-performance acetone sensing at low-energy consumption. Inorg. Chem. 56, 13646–13650 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b02425
Y. Lü, W. Zhan, Y. He, Y. Wang, X. Kong, Q. Kuang, Z. Xie, L. Zheng, MOF-templated synthesis of porous Co3O4 concave nanocubes with high specific surface area and their gas sensing properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 4186–4195 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am405858v
L. Li, J. Tan, M. Dun, X. Huang, Porous ZnFe2O4 nanorods with net-worked nanostructure for highly sensor response and fast response acetone gas sensor. Sens. Actuators 248, 85–91 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.03.119
Y. Zou, H. Wang, R. Yang, X. Lai, J. Wan, G. Lin, D. Liu, Controlled synthesis and enhanced toluene-sensing properties of mesoporous NixCo1−xFe2O4 nanostructured microspheres with tunable composite. Sens. Actuators B 280, 227–234 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.10.030
P. Karthick Kannan, R. Saraswathi, Impedimetric detection of alcohol vapours using nanostructured zinc ferrite. Talanta 129, 545–551 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.06.028
Q. Zhou, W. Zeng, W. Chen, L. Xu, R. Kumar, A. Umar, High sensitive and low-concentration sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas sensor application of heterostructure NiO–ZnO nanodisks. Sens. Actuators B 298, 126870 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126870
L.P. Belo, L.K. Elliott, R.J. Stanger, R. Spörl, K.V. Shah, J. Maier, T.F. Wall, High-temperature conversion of SO2 to SO3: homogeneous experiments and catalytic effect of fly ash from air and oxy-fuel firing. Energy Fuels 28, 7243–7251 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ef5020346
M.J. King, W.G. Davenport, M.S. Moats, Catalytic oxidation of SO2 to SO3, in: Sulfuric Acid Manufacture (Elsevier, 2013), pp. 73–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-098220-5.00007-1
B. Yang, C. Wang, R. Xiao, H. Yu, C. Huang, J. Wang, J. Xu, H. Liu, F. Xia, J. Xiao, High NH3 selectivity of NiFe2O4 sensing electrode for potentiometric sensor at elevated temperature. Anal. Chim. Acta 1089, 165–173 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.09.006
N. Van Hoang, C.M. Hung, N.D. Hoa, N. Van Duy, I. Park, N. Van Hieu, Excellent detection of H2S gas at ppb concentrations using ZnFe2O4 nanofibers loaded with reduced graphene oxide. Sens. Actuators B 282, 876–884 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.11.157
Y.-J. Hsiao, Y. Nagarjuna, C.-A. Tsai, S.-C. Wang, High selectivity Fe3O4 nanoparticle to volatile organic compound (VOC) for MEMS gas sensors. Mater. Res. Express 7, 065013 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab9bc7
S. Palimar, S.D. Kaushik, V. Siruguri, D. Swain, A.E. Viegas, C. Narayana, N.G. Sundaram, Investigation of Ca substitution on the gas sensing potential of LaFeO3 nanoparticles towards low concentration SO2 gas. Dalton Trans. 45, 13547–13555 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6DT01819J
A. Queraltó, D. Graf, R. Frohnhoven, T. Fischer, H. Vanrompay, S. Bals, A. Bartasyte, S. Mathur, LaFeO3 nanofibers for high detection of sulfur-containing gases. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 6023–6032 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b06132
C. Aranthady, T. Jangid, K. Gupta, A.K. Mishra, S.D. Kaushik, V. Siruguri, G.M. Rao, G.V. Shanbhag, N.G. Sundaram, Selective SO2 detection at low concentration by Ca substituted LaFeO3 chemiresistive gas sensor: a comparative study of LaFeO3 pellet vs thin film. Sens. Actuators B 329, 129211 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.129211
Acknowledgements
All authors are thankful to the University Grant Commission (UGC) for the DSA-SAP Phase-II Program and the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India for the PURSE Phase-II Program through which research facilities were made available in the Department of Physics, Shivaji University, Kolhapur.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SBM contributed to investigation, methodology, software, and writing and preparation of the original draft. ARP contributed to methodology and software. RSP contributed to software and formal analysis. NAN contributed to visualization and formal analysis. JBT contributed to conceptualization, formal analysis, and writing and preparation of the original draft. KYR contributed to supervision, conceptualization, resource, and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madake, S.B., Patil, A.R., Pedanekar, R.S. et al. The influence of nickel substitution on the structural and gas sensing properties of sprayed ZnFe2O4 thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 6273–6282 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07802-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07802-z