Abstract
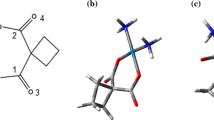
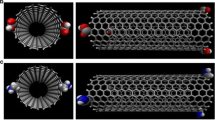
One of the applications of nanotechnology is use of carbon nanotubes for the targeted delivery of drug molecules. To demonstrate the physical and chemical properties of biomolecules and identify new material of drug properties, the interaction of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with biomolecules is a subject of many investigations. CNTs is a synthetic compound with extraordinary mechanical, thermal, electrical, optical, and chemical properties widely applied for technological purposes. In this article we have tried to investigate thermodynamic parameters and dielectric effects in different solvents for one of the most famous anticancer drug “cisplatin” combined to SWCNT, by Monte Carlo and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Cause of platinum element in cisplatin we have done calculations as Gibbs free energy, thermal enthalpy, thermal energy and entropy at 6-31G** basis set with SCRF model of solvent. In this work, the major point has been embedded that results of both two methods of Monte Carlo and DFT can overlap with each other and cisplatin- SWCNT is a suitable compound for drug delivery in different media.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Peyrone (1844). Ann. Chemie. Pharm. 51(1), 1.
T. Stephen (2005). C&EN News 83, 25.
B. Rosenberg, L. Van Camp, and T. Krigas (1965). Nature 205(4972), 698.
B. Rosenberg, L. Van Camp, E. B. Grimley, and A. J. Thomson (1967). J. Biol. Chem. 242(6), 1347.
A. J. Thomson, D. A. Christie, and E. M. Tansey (2007). Wellcome Trust Witnesses to Twentieth Century Medicine 30, 6.
B. Rosenberg, L. Vancamp, J. E. Trosko, and V. H. Mansour (1969). Nature 222(5191), 385.
F. G. Pruefer, F. Lizarraga, V. Maldonado, and J. Melendez-Zajgla (2008). J. Chemother. 20, 348.
A. Bianco, K. Kostarelos, and M. Prato (2005). Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 9, 674.
M. Khalehian, M. Zahmatkesh, F. Mollaamin, and M. Monajjemi (2011). Fullerenes, Nanotubes, and Carbon Nanostructures 19(4), 251.
B. Ghalandari, M. Monajjemi, and F. Mollaamin (2011). J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 8(7), 1212.
M. Monajjemi, L. Mahdavian, and F. Mollaamin (2008). Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 22(2), 1.
M. Monajjemi, L. Mahdavian, F. Mollaamin, and M. Khaleghian (2009). Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 54(9), 14651473.
T. Ramanathan, F. T. Fisher, R. S. Ruoff, and L. C. Brinson (2005). Chem. Mater. 17(6), 1290.
A. Star, E. Tu, J. Niemann, J. Christophe, P. Gabriel, C. S. Joiner, and C. Valcke (2006). Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 103(4), 921.
C. Hu, Y. Zhang, G. Bao, Y. Zhang, M. Liu, and Z. L. Wang (2005). J. Phys. Chem. B 109(43), 20072.
M. E. Hughes, E. Brandin, and J. A. Golovchenko (2007). Nano. Lett. 7(5), 1191.
M. Kastner (2010). Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15, 1589.
M. Monajjemi, S. Ketabi, H. Zadeh, and A. Amiri (2006). Biochemistry (Mosc) 71(S1), S1.
M. Monajjemi, S. Ketabi, and A. Amiri (2006). Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 80(S1), S55.
Hypercube, Inc., Gainesville, FL, USA.
M. J. Frisch et al, in GAUSSIAN 03, Revision C.02 (Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, 2004).
M. Monajjemi, M. H. Razavian, F. Mollaamin, F. Naderi, and B. Honarparvar (2008). Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 82(13), 113.
F. Mollaamin, M. T. Baei, M. Monajjemi, R. Zhiani, and B. Honarparvar (2008). Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 82(13), 2354.
A. Maiti (2008). Microelectronics 39(20), 208.
D. Srivastava and S. N. Atluri (2002). Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 3(5), 531.
A. D. Beck (1993). J. Chem. Phys. 98(7), 5648.
M. Monajjemi, B. H. Honarparvar, H. Haeri, and M. Heshmat (2006). Russ. J. Phys. Chem. C 80(1), S40.
A. Tsolakidis and E. Kaxiras (2005). J. Phys. Chem. A 109(10), 2373.
A. Szarecka, J. Rychlewski, and U. Rychlewska (1998). Comput. Method Sci. Technol. 4, 25.
M. Karelson and A. Lomaka (2001). Arkivoc. III, 51.
G. Lu, P. Maragakis, and E. Kaxiras (2005). Nano. Lett. 5(5), 897.
X. Li, Y. Peng, and X. Qu (2006). Nucl. Acids Res. 34(13), 3670.
X. Zhao and J. K. Johnson (2007). J. Am. Chem Soc. 129(34), 10438.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monajjemi, M., Mollaamin, F. Molecular Modeling Study of Drug-DNA Combined to Single Walled Carbon Nanotube. J Clust Sci 23, 259–272 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-011-0426-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-011-0426-y