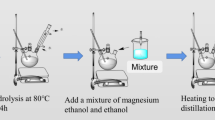
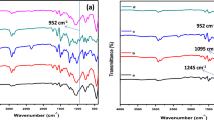
Abstract
Corona discharge always threatens the safe and long-term operation of electrical equipment. Therefore, it is imperative to improve the corona resistance of electrical insulation materials. In this research work, fumed silica (SiO2) with different particle sizes and self-made organic silicon–boron composite oxide (Si–B) are used to modify epoxy resin (EP) for enhancing the corona resistance. Si–B/SiO2/EP nanocomposites with different SiO2 content series and 4 kinds of SiO2 particle size series are prepared by grinding machine dispersing and thermal curing. A strong dependence of the corona resistance on SiO2 filler size in nano-scale and content is revealed experimentally. The filler combination of Si–B and nano-SiO2 can reduce the relative permittivity of the Si–B/SiO2/EP nanocomposites and inhibit the increase of dielectric loss. With the particle size of SiO2 filler increases, the space charge suppression effect and the thermal stability are reduced, but corona resistance life is improved.When the 15-nm SiO2 content is 15 wt%, the corona resistance life of the Si–B/SiO2/EP nanocomposites can reach 8.99 h under 90 °C and 80 kV/mm electric field strength, while pure epoxy is only 0.86 h. The degradation path through the material is the more important factor affecting corona resistance performance–large particle size and well dispersion state can effectively extend the degradation path through the material.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.M.A. Desai, P. Mishra, N.J. Vasa, R. Sarathi, T. Imai, Understanding the performance of corona aged epoxy nano micro composites. Micro Nano Lett. 13(9), 1280–1285 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2018.0164
M.S. Babu, R. Sarathi, N.J. Vasa, T. Imai, Understanding the influence of nano micro filler on electrical and mechanical behaviour of epoxy nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 26(4), 1098–1106 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/tdei.2019.007875
C. Martín, G. Lligadas, J.C. Ronda, M. Galià, V. Cadiz, Synthesis of novel boron-containing epoxy-novolac resins and properties of cured products. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 44(21), 6332–6344 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.21726
S. Li, S. Yu, Y. Feng, Progress in and prospects for electrical insulating materials. High Volt. 1(3), 122–129 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1049/hve.2016.0034
Z. An, H. Xiao, F. Liu, F. Zheng, Q. Lei, Y. Zhang, Improved resistance of epoxy resin to corona discharge by direct fluorination. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23(4), 2278–2287 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2016.7556504
A.J. Reid, M.D. Judd, B.G. Stewart, R.A. Fouracre, Partial discharge current pulses in SF6 and the effect of superposition of their radiometric measurement. J. Phys. D 39, 4167–4177 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/39/19/008
M.T. Nazir, B.T. Phung, S. Yu, S. Li, Resistance against AC corona discharge of micro-ATH/nano-Al2O3 co-filled silicone rubber composites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 25(2), 657–667 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2018.006914
H. Lu, J. Lin, W. Yang et al., Effect of nano-TiO2 surface modification on polarization characteristics and corona aging performance of polyimide nano-composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 134(29), 1–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.45101
C. Zhou, A. Gu, G. Liang, Y. Xia, Tough silica-hybridized epoxy resin/anhydride system with good corona resistance and thermal stability for permanent magnet synchronous wind-driven generators through vacuum pressure impregnation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54(28), 7102–7112 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie504737g
Y. Xia, C. Zhou, G. Liang, A. Gu, W. Wang, Polyester-imide solventless impregnating resin and its nano-silica modified varnishes with excellent corona resistance and thermal stability. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul.22(1), 372–379 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2014.004251
H. Shi, L. Liu, L. Weng, W. Cui, X. Zhu, Preparation and characterization of polyimide/Al2O3 nanocomposite film with good Corona resistance. Polym. Compos. 37(1), 915–924 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.23233
M.-Z. Gao, P.-H. Zhang, Relationship between dielectric properties and nanoparticle dispersion of nano-SiO2/epoxy composite. Acta Phys. Sin. 65(24), 247802 (2016). https://doi.org/10.7498/aps.65.247802
G. Iyer, R.S. Gorur, A. Krivda, Corona resistance of epoxy nanocomposites: experimental results and modeling. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 19(1), 118–125 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2012.6148509
F. Wang, Y. He, T. Zhang, J. Li and L. He. Corona resistance of direct flourinated epoxy/Al2O3 nanocomposites. 2018 International Conference on Diagnostics in Electrical Engineering (Diagnostika), Pilsen, 2018, pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/DIAGNOSTIKA.2018.8526102.
W. Zhao, Y. Fan, H. Chen, Dielectric properties and corona resistance of Si-B/epoxy nano-composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30(17), 16298–16307 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02000-w
W. Sun, N. Bowler, Dielectric properties of silanized-silicon/epoxy nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23(4), 2095–2101 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2016.7556483
Z. Wu, S. Gao, L. Chen et al., Electrically insulated epoxy nanocomposites reinforced with synergistic core-shell SiO2 @MWCNTs and montmorillonite bifillers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 218(23), 1–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.201700357
X. Huang, C. Zhi, P. Jiang, D. Golberg, Y. Bando, T. Tanaka, Polyhedral oligosilsesquioxane-modified boron nitride nanotube based epoxy nanocomposites: an ideal dielectric material with high thermal conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23(14), 1824–1831 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201201824
S. Li, G. Yin, S. Bai, J. Li, A new potential barrier model in epoxy resin nanodielectrics. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 18(5), 1535–1543 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2011.6032822
Z. Lv, X. Wang, K. Wu, X. Chen, Y. Cheng, L. Dissado, Dependence of charge accumulation on sample thickness in nano-SiO2 doped IDPE. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul.20(1), 337–345 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2013.6451375
Y. Han, S. Li, D. Min, Space charge distribution and nonlinear conduction of epoxy nanocomposites. Sens. Mater. 29(8), 1159–1168 (2017). https://doi.org/10.18494/sam.2017.1540
P. Preetha, M.J. Thomas, AC breakdown characteristics of epoxy nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 18(5), 1526–1534 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2011.6032821
G.Y. Li, J.H. Yin, L. Yao, X. Zhao, Particle size effect on the Corona resistant properties of PI/TiO2 composite films. Adv. Mater. Res. 981, 914–917 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.981.914
X. Wang, Y. Fan, H. Chen, R. Yang, W. Zhao, Electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties of Mg(OH)2/PI nanocomposite films. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 27(6), 1778–1786 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-017-0641-6
W. Zhao, H. Chen, Y. Fan, Corona resistance performance of epoxy resin modified by hydrophobic fumed SiO2. Acta Mater. Composit. Sin. 36(08), 1822–1829 (2019). https://doi.org/10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20180925.001
C. Chen, Y. Gu, S. Wang, Z. Zhang, M. Li, Z. Zhang, Fabrication and characterization of structural/dielectric three-phase composite: continuous basalt fiber reinforced epoxy resin modified with graphene nanoplates. Compos. Part A 94, 199–208 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.12.023
P. Maity, S. Basu, V. Parmeswaran, N. Gupta, Degradation of polymer dielectrics with nanometric metal-oxide fillers due to surface discharges. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 15, 52–62 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/t-dei.2008.4446736
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Foundation for Universities of Heilongjiang Province (LGYC2018JC033), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51277044) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51603057)
Funding
Fundamental Research Fundation for Universities of Heilongjiang Province (LGYC2018JC033) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51603057).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Chen, H., Fan, Y. et al. Effect of Size and Content of SiO2 Nanoparticle on Corona Resistance of Silicon–Boron Composite Oxide/SiO2/Epoxy Composite. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 4753–4763 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01733-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01733-0