Abstract
For the first time, we have been reported the phytosynthesis of ultrathin 2D layered sharp-edged MgO nanosheets using Achyranthes aspera (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2%) via green route without any surfactants and the rarely characterized and emerging pathogens of Eggerthella lenta and Enterobacter aerogenes were used to evaluate the antibacterial activity of biosynthesized MgO nanomaterials. A. aspera has a superior role as a non-toxic bio-reducing agent in an entire synthesized process of MgO nanomaterial. Furthermore, the structure, morphology and physicochemical properties of the synthesized materials were elucidated by the analytical techniques like powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), high resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM), Energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and UV–Visible Spectroscopy (UV–Vis). The scanning electron microscopic analysis (SEM) explored the morphology as a 2D nanostructure of A. aspera mediated ultrathin MgO nanosheets. Further, the microscopic analysis HRTEM revealed that the morphological refinement was greatly achieved by varying the concentration of the leaf extract utilized as a capping as well as the reducing agent. An In vitro antibacterial and antifungal analysis were quantitatively investigated for the 2D nanostructure of A. aspera mediated ultrathin MgO nanosheets. Besides, mechanism involving in the formation of MgO nanosheets and antimicrobial activity are well demonstrated to deepen the knowledge towards enhancement possibilities for the metal oxide nanoparticle synthesis and applications.
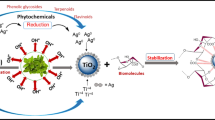
Graphic Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Jeevanandam, Y. San Chan, M.K. Danquah, Biosynthesis and characterization of MgO nanoparticles from plant extracts via induced molecular nucleation. New J. Chem. 41(7), 2800–2814 (2017)
R.K. Sharma, S. Gulati, S. Mehta, Preparation of gold nanoparticles using tea: a green chemistry experiment. J. Chem. Educ. 89(10), 1316–1318 (2012)
S. Taheriniya, Z. Behboodi, Comparing green chemical methods and chemical methods for the synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. IJPSR 7(12), 4927 (2016)
I. Khan, K. Saeed, I. Khan, Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 12, 908–931 (2019)
V. Gnanavel, V. Palanichamy, S. MohanaRoopan, Biosynthesis and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles and its anticancer activity on human colon cancer cell lines (hct-116). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 171, 133–138 (2017)
S. Sabir, M. Arshad, S.K. Chaudhari, Zinc oxide nanoparticles for revolutionizing agriculture: synthesis and applications. TSWJ. 925494 (2014)
M. Arakha, S. Pal, D. Samantarrai, T.K. Panigrahi, B.C. Mallick, K. Pramanik, B. Mallick, S. Jha, Antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticle upon modulation of nanoparticle-bacteria interface. Sci. Rep. 5, 14813 (2015)
R. Thirupathi, G. Solleti, T. Sreekanth, K. Sadasivuni, K. Venkateswara Rao, A comparative study of chemically and biologically synthesized MgO nanomaterial for liquefied petroleum gas detection. J. Electron. Mater. 47(7), 3468–3473 (2018)
M. Shahriarya, H. Veisib, M. Hekmatia, S. Hemmati, In situ green synthesis of ag nanoparticles on herbal tea extract (Stachys lavandulifolia)-modified magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as antibacterial agent and their 4-nitrophenol catalytic reduction activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 90, 57–66 (2018)
Y. Abdallah, S.O. Ogunyemi, A. Abdelazez, M. Zhang, X. Hong, E. Ibrahim, A. Hossain, H. Fouad, B. Li, J. Chen, The green synthesis of MgO nano-flowers using Rosmarinus officinalis l. (rosemary) and the antibacterial activities against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae. Biomed. Res. Int. 8, 5620989 (2019)
C.C. Coelho, R. Araújo, P.A. Quadros, S.R. Sousa, F.J. Monteiro, Antibacterial bone substitute of hydroxyapatite and magnesium oxide to prevent dental and orthopaedic infections. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 97, 529–538 (2019)
A. Marcu, S. Pop, F. Dumitrache, M. Mocanu, C.M. Niculite, M. Gherghiceanu, C.P. Lungu, C. Fleaca, R. Ianchis, A. Barbut, C. Grigoriu, Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as drug delivery system in breast cancer. Appl. Surf. Sci. 15(281), 60–5 (2013)
E. Creamer, B. Gao, A. Zimmerman, W. Harris, Biomass-facilitated production of activated magnesium oxide nanoparticles with extraordinary co2 capture capacity. Chem. Eng. 334, 81–88 (2018)
K.M. Saoud, S. Saeed, R.M. Al-Soubaihi, M.F. Bertino, Microwave assisted preparation of magnesium hydroxide nano-sheets. J. Nanomater. 2, 21–25 (2014)
P. Tamilselvi, A. Yelilarasi, M. Hema, R. Anbarasan, Synthesize of hierarchical structured MgO by sol-gel method. Nano Bull. 2, 130106 (2013)
K. Ganapathi Rao, C.H. Ashok, K. Venkateswara Rao, C.H. Shilpa Chakra, Structural properties of MgO nanoparticles: synthesized by co-precipitation technique. Int. J. Sci. Res. 3(12), 43–46 (2013)
N. Pantidos, L.E. Horsfall, Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by bacteria, fungi and plants. J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 5(5), 1 (2014)
G.S. El-Sayyad, F.M. Mosallam, A.I. El-Batal, One-pot green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using penicillium Chrysogenum melanin pigment and gamma rays with antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant microbes. Adv. Powder Technol. 29, 2616–262519 (2018)
T.B. Nijalingappa, M.K. Veeraiah, R.B. Basavaraj, G.P. Darshan, S.C. Sharma, H. Nagabhushana, Antimicrobial properties of green synthesis of MgO micro architectures via Limonia acidissimafruit extract. Biocatal Agric. Biotechnol. 18, 100991 (2019)
K. Ramanujam, M. Sundrarajan, Antibacterial effects of biosynthesized MgO nanoparticles using ethanolic fruit extract of Emblica officinalis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 141, 296–300 (2014)
N.J. Sushma, D. Prathyusha, G. Swathi, T. Madhavi, B.D. Raju, K. Mallikarjuna, H.S. Kim, Facile approach to synthesize magnesium oxide nanoparticles by using Clitoria ternatea—characterization and in vitro antioxidant studies. Appli. Nanosci. 6(3), 437–44 (2016)
G. Sharmila, C. Muthukumaran, E. Sangeeth, H. Saraswathi, S. Soundarya, N. Manoj Kumar, Green fabrication, characterization of Pisonia alba leaf extract derived MgO nanoparticles and its biological applications. Nano-struct. Nano-obj. 20, 100380 (2019)
S. Sureshkumar, J. Devagnana Roopan, A. Sivaraj, K. Devi, B. Senthilkumar, Pharmacognosy of Achyranthes asperalinn: a review. ARJLS 1 (2015)
A. Habtamu, Y. Mekonnen, Evaluation of the antibacterial activities of leaf extracts of Achyranthus aspera. Afr. J. Bacteriol. Res. 9(2), 9–14 (2017)
W. Shibeshi, Μ.E. Makonnen, A. Debella, L. Zerihun, Phytochemical, contraceptive efficacy and safety evaluations of the methanolic leaves extract of Achyranthes asperain rats. Pharmacology. 3, 217–224 (2006)
P.R. Subbarayana, M. Sarkarb, S. Impellizzeric, F. Raymoc, B.L. Lokeshward, P. Kumare, R.P. Agarwala, B. Ardalan, Anti-proliferative and anti-cancer properties of Achyranthes aspera: specific inhibitory activity against pancreatic cancer cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 131, 78–82 (2010)
Y. He, S. Ingudam, S. Reed, A. Gehring, T.P. Strobaugh, P. Irwin, Study on the mechanism of antibacterial action of magnesium oxide nanoparticles against foodborne pathogens. J Nanobiotechnol. 14, 54 (2016)
J. Suresh, G. Pradheesh, V. Alexramani, M. Sundrarajan, S.I. Hong, green synthesis and characterization of hexagonal shaped MgO nanoparticles using insulin plant (Costus pictus d. Don) leave extract and Its antimicrobial as well as anticancer activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 29, 1685–169 (2018)
L. Peia, W. Yinb, J. Wanga, J. Chena, C. Fana, Q. Zhang, Low temperature synthesis of magnesium oxide and spinel powders by a sol-gel process. Mater. Res. 13, 339–343 (2010)
F. Al-Hazmi, F. Alnowaiser, A.A. Al-Ghamdi, A.A. Al-Ghamdi, M.M. Aly, R.M. Al-Tuwirqi, F. El-Tantawy, A new large—scale synthesis of magnesium oxide nanowires: structural and antibacterial properties. Superlattices Microstruct. 52, 200–209 (2012)
S.T. Fardood, A. Ramazani, S.W. Joo, Eco-friendly synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using arabic gum. J. Appl. Chem. 12, 8–15 (2018)
R. Coelhoa, P. Araujo, S. Quadros, F. Sousaa, Monteiro, Antibacterial bone substitute of hydroxyapatite and magnesium oxide to prevent dental and orthopaedic infections. Mater. Sci. Eng. 97, 529–538 (2019)
B. Das, S. Moumita, S. Ghosh, M.I. Khan, D. Indira, R. Jayabalan, S.K. Tripathy, A. Mishra, P. Balasubramanian, Biosynthesis of magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoflakes by using leaf extract of Bauhinia purpurea and evaluation of its antibacterial property against Staphylococcus aureus. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 1(91), 436–44 (2018)
P.K. Elumalai, K. Kaleena, A. Ashok, M. Suresh, Hemavathi, Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Achyranthes aspera and its larvicidal activity against three major mosquito vectors. Eng. Agric. Environ. Food 9, 1–8 (2016)
K. Karthik, S. Dhanuskodi, C. Gobinath, S. Prabukumar, S. Sivaramakrishnan, Fabrication of MgO nanostructures and its efficient photocatalytic, antibacterial and anticancer performance. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 190, 8–20 (2019)
Y.Y. Abdallah, S.O. Ogunyemi, A. Abdelazez, M. Zhang, X. Hong, E. Ibrahim, A. Hossain, H. Fouad, B. Li, J. Chen, The green synthesis of mgo nano-flowers using Rosmarinus officinalis l. (rosemary) and the antibacterial activities against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae. Biomed Res. Int. 8, 5620989 (2019)
N. John Sushma, D. Prathyusha, G. Swathi, T. Madhavi, B. Deva Prasad Raju, K. Mallikarjuna, Hak-Sung Kim, Facile approach to synthesize magnesium oxide nanoparticles by using Clitoria ternatea—characterization and in vitro antioxidant studies, Appl Nanosci. 6, 437–444 (2016)
J. Jeevanandam, Y.S. Chan, M.K. Danquah, Effect of ph variations on morphological transformation of biosynthesized mgo nanoparticles, particulate science and technology. Particul. Sci. Technol.0272–6351 (2019)
G. Sharma, R. Soni, N.D. Jasuja, Phytoassisted synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles with Swertia chirayaita. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 11, 471–477 (2017)
K. Ramanujam, M. Sundrarajan, Antibacterial effects of biosynthesized MgO nanoparticles using ethanolic fruit extract of Emblica officinalis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 141, 296–300 (2014)
K. Jhansi, N. Jayarambabu, K. Paul Reddy, N. Manohar Reddy, R. Padma Suvarna, K. Venkateswara Rao, V. Ramesh Kumar, V. Rajendar, Biosynthesis of MgO nanoparticles using mushroom extract: effect on peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seed germination. Biotechnique 7, 263 (2017)
J. Sackey, A.K.H. Bashir, A.E. Ameh, M. Nkosi, C. Kaonga, M. Maaza, Date pits extracts assisted synthesis of magnesium oxides nanoparticles and its application towards the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 32, 2767–2776 (2020)
H.A. Maishera, F.A. Kuta, J.O. Tijani, N.U. Adabara, A.S. Adedeji, J.D. Bala, Biosynthesis and antibacterial potential of Tectona grandismediated magnesium oxide nanorods. J. Bio-Sci. 27, 109–120 (2019)
P.D. Shankar, S. Shobana, I. Karuppusamy, A. Pugazhendhi, V.S. Ramkumar, S. Arvindnarayan, G. Kumar, A review on the biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles (gold and silver) using bio-components of microalgae: formation mechanism and applications. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 95, 28–44 (2016)
S. Pavithra, B. Mohana, M. Mani, R. Jayavel, S. Kumaresan, Physicochemical and morphological properties of Achyranthes aspera mediated CuO nanoparticles for inhibiting cellular adhesion. J. Clust. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01796-6
L. Kumari, W. Li, C. Vannoy, R. Leblanc, D. Wang, Synthesis, characterization and optical properties of Mg (OH)2 micro-/nanostructure and its conversion to MgO. Ceram. Int. 35, 3355–3364 (2009)
K.G. Chandrappa, T.V. Venkatesha, B.M. Praveen, B.S. Shylesha, Generation of nanostructured MgO particles by solution phase method. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 5, 13–18 (2015)
J.M. Yousef, E.N. Danial, In vitro antibacterial activity and minimum inhibitory concentration of zinc oxide and nano-particle zinc oxide against pathogenic strains. J. Health Sci. 2(4), 38–42 (2012)
L. Cai, J. Chen, Z. Liu, H. Wang, H. Yang, W. Ding, Magnesium oxide nanoparticles: effective agricultural antibacterial agent against Ralstonia solanacearum. Front. Microbiol. 9, 790 (2018)
K. Krishnamoorthy, G. Manivannan, S. Jae Kim, Kadarkaraithangam Jeyasubramanian, M. Premanathan, Antibacterial activity of mgo nanoparticles based on lipid peroxidation by oxygen vacancy. J Nanoparticle Res. 14, 1063 (2012)
X. Zhang, R. Zhou, P. Liu, L. Fu, X. Lan, G. Gong, Improvement of the antibacterial activity of nanocrystalline zinc oxide by doping Mg (II) Or Sb (III). Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 8(5), 1087–1098 (2011)
U.T. Khatoon, G.N. Rao, M.K. Mohan, A. Ramanaviciene, A. Ramanavicius, J. Environ. 6(5), 5837–5844 (2018)
U.T. Khatoon, G.N. Rao, M.K. Mohan, A. Ramanaviciene, A. Ramanavicius, Antibacterial and antifungal activity of silver nanospheres synthesized by tri-sodium citrate assisted chemical approach. Vacuum 146, 259–265 (2017)
L. Umaralikhan, M. Jamal Mohamed Jaffar, Green synthesis of MgO nanoparticles and it antibacterial activity. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. 42, 477–485 (2018)
Y. Abdallah, S. O. Ogunyemi, A. Abdelazez, M. Zhang, X. Hong, E. Ibrahim, A. Hossain, H. Fouad, B. Li, J. Chen, The Green Synthesis of MgO Nano-Flowers Using Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Rosemary) and the Antibacterial Activities against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. BioMed Res. Int. 5620989 (2019).
R. Rajeswari, H. Gurumallesh Prabu, Synthesis characterization, antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of ZnO nanorods on reduced graphene oxide. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 28, 679–693 (2017)
O. Azizian-Shermeh, A. A. Jalali-Nezhad, M. Taherizadeh, A. Qasemi, Facile, Low-Cost and Rapid Phytosynthesis of Stable and Eco-friendly Silver Nanoparticles Using Boerhavia elegans (Choisy) and Study of Their Antimicrobial Activities. J Inorg Organomet Polym. 1 – 13 (2020).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Crystal Growth Centre, Anna University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India for enabling laboratory facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavithra, S., Mohana, B., Mani, M. et al. Bioengineered 2D Ultrathin Sharp-Edged MgO Nanosheets Using Achyranthes aspera Leaf Extract for Antimicrobial Applications. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 1120–1133 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01772-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01772-7