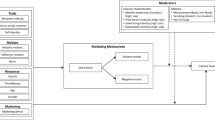
Abstract
When it comes to health(-risk) behaviors, researchers are apt to consider how to change behaviors from a top-down approach (i.e., using the conscious, reflective, deliberate system) even though much of human behavior is determined by bottom-up processes (i.e., the nonconscious, reflexive, impulsive system). Given that researchers have proposed that interventions that target nonconscious processes underlying health(-risk) behaviors may prove to be more effective than interventions that target conscious processes, we argue that understanding the ways in which mimicking and modeling affect health(-risk) behaviors is a critical—albeit largely unexplored—domain. In this paper, we review existing evidence that people mimic and model a broad range of health(-risk) behaviors: specifically, the cigarette smoking, alcohol drinking, (un)healthy eating, and physical activity of others. We then discuss the neural and psychological mechanisms underlying these effects. Next, we outline moderators: specifically, we discuss when mimicking and modeling are more likely to occur, who is more likely to mimic and model, as well as who is more likely to be mimicked and modeled. Finally, we consider how mimicry and modeling could be used to leverage healthy behavioral change.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Mimicry is a not as micro-level of a process as synchrony, which involves enacting the exact same behavior at the exact same time. In contrast to mimicry, synchrony is often studied at the level of milliseconds.
References
Adams, M. A., Hovell, M. F., Irvin, V., Sallis, J. F., Coleman, K. J., & Liles, S. (2006). Promoting stair use by modeling: An experimental application of the behavioral ecological model. American Journal of Health Promotion,21(2), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.4278/0890-1171-21.2.101.
Addessi, E., Galloway, A. T., Visalberghi, E., & Birch, L. L. (2005). Specific social influences on the acceptance of novel foods in 2–5-year-old children. Appetite,45(3), 264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2005.07.007.
Antonuccio, D. O., & Lichtenstein, E. (1980). Peer modeling influences on smoking behavior of heavy and light smokers. Addictive Behaviors,5, 299–306.
Bandura, A. (1989). Social cognitive theory. In R. Vasta (Ed.), Annals of child development (Vol. 6, pp. 1–60). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Bandura, A. (2005). The evolution of social cognitive theory. In K. G. Smith & M. A. Hitt (Eds.), Great minds in management (pp. 9–35). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Bauer, U. E., Briss, P. A., Goodman, R. A., & Bowman, B. A. (2014). Prevention of chronic disease in the 21st century: Elimination of the leading preventable causes of premature death and disability in the USA. The Lancet,384(9937), 45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60648-6.
Bevelander, K. E., Anschütz, D. J., Creemers, D. H. M., Kleinjan, M., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2013a). The role of explicit and implicit self-esteem in peer modeling of palatable food intake: A study on social media interaction among youngsters. PLoS ONE,8(8), e72481. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072481.
Bevelander, K. E., Anschütz, D. J., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2012). Social norms in food intake among normal weight and overweight children. Appetite,58(3), 864–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2012.02.003.
Bevelander, K. E., Lichtwarck-Aschoff, A., Anschütz, D. J., Hermans, R. C. J., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2013b). Imitation of snack food intake among normal-weight and overweight children. Frontiers in Psychology,4, 949. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00949.
Bevelander, K. E., Meiselman, H. L., Anschütz, D. J., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2013c). Television watching and the emotional impact on social modeling of food intake among children. Appetite,63, 70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2012.12.015.
Birch, L. L. (1980). Effects of peer models’ food choice and eating behaviors on preschoolers’ food preferences. Child Development,51(2), 489–496. https://doi.org/10.2307/1129283.
Brunner, T. A. (2010). How weight-related cues affect food intake in a modeling situation. Appetite,55(3), 507–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2010.08.018.
Brunner, T. A. (2012). Matching effects on eating. Individual differences do make a difference! Appetite,58(2), 429–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2011.12.003.
Caudill, B. D., & Kong, F. H. (2001). Social approval and facilitation in predicting modeling effects in alcohol consumption. Journal of Substance Abuse,13(4), 425–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-3289(01)00099-2.
Caudill, B. D., & Marlatt, G. A. (1975). Modeling influences in social drinking: An experimental analogue. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology,43(3), 405–415. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0076689.
Chartrand, T. L., & Bargh, J. A. (1999). The chameleon effect: The perception-behavior link and social interaction. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,76(6), 893–910.
Chartrand, T. L., & Lakin, J. L. (2013). The antecedents and consequences of human behavioral mimicry. Annual Review of Psychology,64, 285–308.
Chartrand, T. L., & van Baaren, R. B. (2009). Human mimicry. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology,41, 219–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2601(08)00405-X.
Cheng, C. M., & Chartrand, T. L. (2003). Self-monitoring without awareness: Using mimicry as a nonconscious affiliation strategy. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,85(6), 1170–1179. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.85.6.1170.
Chipperfield, B., & Vogel-Sprott, M. (1988). Family history of problem drinking among young male social drinkers: Modeling effects of alcohol consumption. Journal of Abnormal Psychology,97(4), 423–428. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsa.1987.48.430.
Christakis, N. A., & Fowler, J. H. (2007). The spread of obesity in a large social network over 32 years. New England Journal of Medicine,357(4), 370–379. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmsa066082.
Christakis, N., & Fowler, J. (2008). Quitting in drives: Collective dynamics of smoking behaviour in a large social network. New England Journal of Medicine,358(21), 2249–2258. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsa0706154.Quitting.
Christie, C. D., & Chen, F. S. (2018). Vegetarian or meat? Food choice modeling of main dishes occurs outside of awareness. Appetite,121, 50–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2017.10.036.
Cohen, D. A. (2008). Neurophysiological pathways to obesity: Below awareness and beyond individual control. Diabetes,57(7), 1768–1773. https://doi.org/10.2337/db08-0163.
Cohen-Cole, E., & Fletcher, J. M. (2008). Is obesity contagious? Social networks vs. environmental factors in the obesity epidemic. Journal of Health Economics,27(5), 1382–1387.
Collins, R. L., Parks, G. A., & Marlatt, G. A. (1985). Social determinants of alcohol consumption: The effects of social interaction and model status on the self-administration of alcohol. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology,53(2), 189–200.
Collins, R., & Quigley, B. (1999). The modeling of alcohol consumption: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Studies on Alcohol,60(1), 90–98. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsa.1999.60.90.
Conger, J. C., Conger, A. J., Costanzo, P. R., Wright, K. L., & Matter, J. A. (1980). The effect of social cues on the eating behavior of obese and normal subjects. Journal of Personality,48(2), 258–271. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.1980.tb00832.x.
Cooper, A. M., Waterhouse, G. J., & Sobell, M. B. (1979). Influence of gender on drinking in a modeling situation. Journal of Studies on Alcohol,40(7), 562–570. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsa.1979.40.562.
Cruwys, T., Bevelander, K. E., & Hermans, R. C. J. (2015). Social modeling of eating: A review of when and why social influence affects food intake and choice. Appetite,86(1), 3–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2014.08.035.
Cullum, J., O’Grady, M. A., & Tennen, H. (2011). Affiliation goals and health behaviors. Social and Personality Psychology Compass,5(10), 694–705. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-9004.2011.00376.x.
Dallas, R., Field, M., Jones, A., Christiansen, P., Rose, A., & Robinson, E. (2014). Influenced but unaware: Social influence on alcohol drinking among social acquaintances. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research,38(5), 1448–1453. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12375.
David, S. P., Munafò, M. R., Johansen-Berg, H., Smith, S. M., Rogers, R. D., Matthews, P. M., et al. (2005). Ventral striatum/nucleus accumbens activation to smoking-related cues in smokers and nonsmokers: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Biological Psychiatry,58(6), 488–494. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20328.Object.
de Luca, R. V., & Spigelman, M. N. (1979). Effects of models on food intake of obese and non-obese female college students. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science,11(2), 124–129.
de Wit, H., & Sayette, M. (2018). Considering the context: Social factors in responses to drugs in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl),235(4), 935–945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4854-3.
Dericco, D. A., & Garlington, W. K. (1977). The effect of modeling and disclosure of experimenter’s intent on drinking rate of college students. Addictive Behaviors,2(2–3), 135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4603(77)90031-4.
DeWall, C. N., & Pond, R. S. (2011). Loneliness and smoking: The costs of the desire to reconnect. Self and Identity,10(3), 375–385. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298868.2010.524404.
Dickter, C. L., Kieffaber, P. D., Kittel, J. A., & Forestell, C. A. (2013). Mu suppression as an indicator of activation of the perceptual–motor system by smoking-related cues in smokers. Psychophysiology,50(7), 664–670. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.12044.
Dimoff, J. D., & Sayette, M. A. (2017). The case for investigating social context in laboratory studies of smoking. Addiction,112(3), 388–395. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.13503.The.
Duffy, K. A., & Chartrand, T. L. (2015). The extravert advantage: How and when extraverts build rapport with other people. Psychological Science,26(11), 1795–1802. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797615600890.
Duffy, K. A., Harris, L. T., Chartrand, T. L., & Stanton, S. J. (2017). Women recovering from social rejection: The effect of the person and the situation on a hormonal mechanism of affiliation. Psychoneuroendocrinology,76, 174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.11.017.
Exline, J. J., Zell, A. L., Bratslavsky, E., Hamilton, M., & Swenson, A. (2012). People-pleasing through eating: Sociotropy predicts greater eating in response to perceived social pressure. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology,31(2), 169–193. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.2012.31.2.169.
Field, M., Mogg, K., & Bradley, B. P. (2006). Automaticity of smoking behaviour: The relationship between dual-task performance, daily cigarette intake and subjective nicotine effects. Journal of Psychopharmacology,20(6), 799–805. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881106063997.
Fillmore, M. T., Marczinski, C. A., & Bowman, A. M. (2005). Acute tolerance to alcohol effects on inhibitory and activational mechanisms of behavioral control. Journal of Studies on Alcohol,66(5), 663–672. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsa.2005.66.663.
Fletcher, A., Bonell, C., & Sorhaindo, A. (2011). You are what your friends eat: Systematic review of social network analyses of young people’s eating behaviours and bodyweight. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health,65(6), 548–555. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2010.113936.
Florack, A., Palcu, J., & Friese, M. (2013). The moderating role of regulatory focus on the social modeling of food intake. Appetite,69, 114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2013.05.012.
Frieden, T. R., Jaffe, H. W., Cono, J., Richards, C. L., Iademarco, M. F., Kent, C. K., et al. (2014). CDC National Health Report: Leading causes of morbidity and mortality and associated behavioral risk and protective factors—United States, 2005–2013 (Vol. 63).
Fugitt, J. L., & Ham, L. S. (2018). Beer for “brohood”: A laboratory simulation of masculinity confirmation through alcohol use behaviors in men. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors,32(3), 358–364. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000351.
Gallese, V., Fadiga, L., Fogassi, L., & Rizzolatti, G. (1996). Action recognition in the premotor cortex. Brain,119, 593–609.
Gallois, C., Ogay, T., & Giles, H. (2005). Communication accommodation theory: A look back and a look ahead. In W. B. Gudykunst (Ed.), Theorizing about intercultural communication (pp. 121–148). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781405186407.wbiecc067.
Gibbons, F. X., Houlihan, A. E., & Gerrard, M. (2009). Reason and reaction: The utility of a dual-focus, dual-processing perspective on promotion and prevention of adolescent health risk behaviour. British Journal of Health Psychology,14(2), 231–248. https://doi.org/10.1348/135910708X376640.
Giles, H. (Ed.). (2016). Communication accommodation theory: Negotiating personal relationships and social identities across contexts. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Glad, W., & Adesso, V. J. (1976). The relative importance of socially induced tension and behavioral contagion for smoking behavior. Journal of Abnormal Psychology,85(1), 119–121. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.85.1.119.
Goeders, N. E. (2003). The impact of stress on addiction. European Neuropsychopharmacology,13(6), 435–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2003.08.004.
Goldberg, R. M., Cutter, H. S. G., Kumler, M. L., & Hussey, R. W. (1982). Beer consumption as an interaction of motives for drinking and videotape-modeled drinking behavior. Journal of Studies on Alcohol,43(3), 289–300.
Goldman, S. J., Herman, C. P., & Polivy, J. (1991). Is the effect of a social model on eating attenuated by hunger? Appetite,17(2), 129–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/0195-6663(91)90068-4.
Greenhalgh, J., Dowey, A. J., Horne, P. J., Lowe, C. F., Griffiths, J. H., & Whitaker, C. J. (2009). Positive- and negative peer modelling effects on young children’s consumption of novel blue foods. Appetite,52(3), 646–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2009.02.016.
Guarino, M., Fridrich, P., & Sitton, S. (1994). Male and female conformity in eating behavior. Psychological Reports,75, 603–609.
Hagger, M. S. (2016). Non-conscious processes and dual-process theories in health psychology. Health Psychology Review,10(4), 375–380. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437199.2016.1244647.
Hallam, J., Boswell, R. G., DeVito, E. E., & Kober, H. (2016). Gender-related differences in food craving and obesity. Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine,89(2), 161–173.
Hamlin, J. K., & Wynn, K. (2012). Who knows what’s good to eat? Infants fail to match the food preferences of antisocial others. Cognitive Development,27, 227–239.
Harakeh, Z., Engels, R., Van Baaren, R. B., & Scholte, R. (2007). Imitation of cigarette smoking: An experimental study on smoking in a naturalistic setting. Drug and Alcohol Dependence,86(2–3), 199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.06.006.
Harakeh, Z., & Vollebergh, W. A. M. (2011). Actions speak louder than words: An experiment on the impact of peers discouraging young adult smoking. European Addiction Research,17(6), 316–320. https://doi.org/10.1159/000330318.
Harakeh, Z., & Vollebergh, W. A. M. (2012a). Internet chameleons: An experimental study on imitating smoking peers through digital interaction. Nicotine & Tobacco Research,14(3), 323–328. https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/ntr217.
Harakeh, Z., & Vollebergh, W. A. M. (2012b). The impact of active and passive peer influence on young adult smoking: An experimental study. Drug and Alcohol Dependence,121(3), 220–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.08.029.
Harakeh, Z., & Vollebergh, W. A. M. (2013). Young adult smoking in peer groups: An experimental observational study. Nicotine & Tobacco Research,15(3), 656–661. https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/nts183.
Harper, L. V., & Sanders, K. M. (1975). The effect of adults’ eating on young children’s acceptance of unfamiliar foods. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology,20(2), 206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0965(75)90098-3.
Hendricks, R. D., Sobell, M. B., & Cooper, A. M. (1978). Social influences on human ethanol consumption in an analogue situation. Addictive Behaviors,3(3–4), 253–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4603(78)90026-6.
Hendy, H. M. (2002). Effectiveness of trained peer models to encourage food acceptance in preschool children. Appetite,39(3), 217–225. https://doi.org/10.1006/appe.2002.0510.
Hendy, H. M., & Raudenbush, B. (2000). Effectiveness of teacher modeling to encourage food acceptance in preschool children. Appetite,34(1), 61–76. https://doi.org/10.1006/appe.1999.0286.
Herman, C. P., Koenig-Nobert, S., Peterson, J. B., & Polivy, J. (2005). Matching effects on eating: Do individual differences make a difference? Appetite,45, 108–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2011.12.003.
Herman, C. P., Roth, D. A., & Polivy, J. (2003). Effects of the presence of others on food intake: A normative interpretation. Psychological Bulletin,129(6), 873–886. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.129.6.873.
Hermans, R. C., Engels, R. C., Larsen, J. K., & Herman, C. P. (2009a). Modeling of palatable food intake. The influence of quality of social interaction. Appetite,52(3), 801–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2009.03.008.
Hermans, R. C. J., Herman, C. P., Larsen, J. K., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2010a). Social modeling effects on snack intake among young men. The role of hunger. Appetite,54(2), 378–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2010.01.006.
Hermans, R. C. J., Herman, C. P., Larsen, J. K., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2010b). Social modeling effects on young women’s breakfast intake. Journal of the American Dietetic Association,110(12), 1901–1905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2010.09.007.
Hermans, R. C. J., Larsen, J. K., Herman, C. P., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2008). Modeling of palatable food intake in female young adults. Effects of perceived body size. Appetite,51(3), 512–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2008.03.016.
Hermans, R. C., Larsen, J. K., Herman, C. P., & Engels, R. C. (2009b). Effects of social modeling on young women’s nutrient-dense food intake. Appetite,53(1), 135–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2009.05.004.
Hermans, R. C. J., Larsen, J. K., Lochbuehler, K., Nederkoorn, C., Herman, C. P., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2012a). The power of social influence over food intake: Examining the effects of attentional bias and impulsivity. British Journal of Nutrition,109(3), 572–580. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007114512001390.
Hermans, R. C. J., Lichtwarck-Aschoff, A., Bevelander, K. E., Herman, C. P., Larsen, J. K., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2012b). Mimicry of food intake: The dynamic interplay between eating companions. PLoS ONE,7(2), e31027. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031027.
Hermans, R. C., Salvy, S.-J., Larsen, J. K., & Engels, R. C. (2012c). Examining the effects of remote-video confederates on young women’s food intake. Eating Behaviors,13(3), 246–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2012.03.008.
Herrmann, A., Rossberg, N., Huber, F., Landwehr, J. R., & Henkel, S. (2011). The impact of mimicry on sales—Evidence from field and lab experiments. Journal of Economic Psychology,32(3), 502–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2011.03.017.
Hoek, H. W., & Van Hoeken, D. (2003). Review of the prevalence and incidence of eating disorders. International Journal of Eating Disorders,34(4), 383–396. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.10222.
Hofmann, W., Friese, M., & Wiers, R. W. (2008). Impulsive versus reflective influences on health behavior: A theoretical framework and empirical review. Health Psychology Review,2(2), 111–137. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437190802617668.
Hollands, G. J., Marteau, T. M., & Fletcher, P. C. (2016). Non-conscious processes in changing health-related behaviour: A conceptual analysis and framework. Health Psychology Review,10(4), 381–394. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437199.2015.1138093.
Johnston, L. (2002). Behavioral mimicry and stigmatization. Social Cognition,20(1), 18–35. https://doi.org/10.1521/soco.20.1.18.20944.
Kaisari, P., & Higgs, S. (2015). Social modelling of food intake. The role of familiarity of the dining partners and food type. Appetite,86, 19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2014.09.020.
Kniskern, J., Biglan, A., Lichtenstein, E., Ary, D., & Bavry, J. (1983). Peer modeling effects in the smoking behavior of teenagers. Addictive Behaviors,8, 129–132.
Koordeman, R., Kuntsche, E., Anschutz, D. J., van Baaren, R. B., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2011). Do we act upon what we see? Direct effects of alcohol cues in movies on young adults’ alcohol drinking. Alcohol and Alcoholism,46(4), 393–398. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agr028.
Kremers, S. P., de Bruijn, G.-J., Visscher, T. L., van Mechelen, W., de Vries, N. K., & Brug, J. (2006). Environmental influences on energy balance-related behaviors: A dual-process view. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity,3(9), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-3-9.
Kulesza, W., Dolinski, D., Migon, M., Rizulla, A., Gamian-Wilk, M., & Grzyb, T. (2017). The use of mimicry to improve evaluation of unsought beverages. Food Quality and Preference,62, 137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2017.06.004.
Lakin, J. L., & Chartrand, T. (2003). Using nonconscious behavioral mimicry to create affiliation and rapport. Psychological Science,14(4), 334–339.
Lakin, J. L., Chartrand, T. L., & Arkin, R. M. (2008). I am too just like you: Nonconscious mimicry as an automatic behavioral response to social exclusion. Psychological Science,19(8), 816–822.
Larsen, H., Engels, R. C. M. E., Granic, I., & Huizink, A. C. (2013a). Does stress increase imitation of drinking behavior? An experimental study in a (semi-)naturalistic context. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research,37(3), 477–483. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01942.x.
Larsen, H., Engels, R. C. M. E., Granic, I., & Overbeek, G. (2009). An experimental study on imitation of alcohol consumption in same-sex dyads. Alcohol and Alcoholism,44(3), 250–255. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agp002.
Larsen, H., Engels, R. C. M. E., Souren, P. M., Granic, I., & Overbeek, G. (2010a). Peer influence in a micro-perspective: Imitation of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages. Addictive Behaviors,35(1), 49–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2009.08.002.
Larsen, H., Engels, R. C. M. E., Wiers, R. W., Granic, I., & Spijkerman, R. (2012a). Implicit and explicit alcohol cognitions and observed alcohol consumption: Three studies in (semi)naturalistic drinking settings. Addiction,107(8), 1420–1428. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2012.03805.x.
Larsen, H., Lichtwarck-Aschoff, A., Kuntsche, E., Granic, I., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2013b). Drinking in a micro-perspective: The role of engagement in imitation of sips of alcoholic beverages. Journal of Experimental Psychopathology,4(3), 226–238. https://doi.org/10.5127/jep.027312.
Larsen, H., Overbeek, G., Granic, I., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2010b). Imitation of alcohol consumption in same-sex and other-sex dyads. Alcohol and Alcoholism,45(6), 557–562. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agq053.
Larsen, H., Overbeek, G., Granic, I., & Engels, R. C. (2012b). The strong effect of other people’s drinking: Two experimental observational studies in a real bar. American Journal on Addictions,21(2), 168–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1521-0391.2011.00200.x.
Lied, E., & Marlatt, G. (1979). Modeling as a determinant of alcohol consumption: Effect of subject sex and prior drinking history. Addictive Behaviors,4, 47–54.
Lochbuehler, K., Peters, M., Scholte, R. H. J., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2010). Effects of smoking cues in movies on immediate smoking behavior. Nicotine & Tobacco Research,12(9), 913–918. https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/ntq115.
Marteau, T. M., Hollands, G. J., & Fletcher, P. C. (2012). Changing human behavior to prevent disease: The importance of targeting automatic processes. Science,337, 1492–1495.
Martin, A., Fischer-Lokou, J., & Guéguen, N. (2016). Impact of verbal mimicry on children’s fruit consumption. Food Quality and Preference,49, 100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2015.11.006.
McFerran, B., Dahl, D. W., Fitzsimons, G. J., & Morales, A. C. (2010). I’ll have what she’s having: Effects of social influence and body type on the food choices of others. Journal of Consumer Research,36(6), 915–929. https://doi.org/10.1086/644611.
McGeown, L., & Davis, R. (2018). Social modeling of eating mediated by mirror neuron activity: A causal model moderated by frontal asymmetry and BMI. Behavioural Brain Research,338, 66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.10.009.
Meader, N., King, K., Moe-Byrne, T., Wright, K., Graham, H., Petticrew, M., et al. (2016). A systematic review on the clustering and co-occurrence of multiple risk behaviours. BMC Public Health,16(1), 657. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-3373-6.
Mokdad, A. H., Marks, J. S., Stroup, D. F., & Gerberding, J. L. (2004). Actual causes of death in the United States, 2000. Journal of the American Medical Association,291(10), 1238–1245. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.291.10.1238.
Nisbett, R. E., & Storms, M. D. (1974). Cognitive and social determinants of food intake. In H. London & R. E. Nisbett (Eds.), Thought and feeling: Cognitive alteration of feeling state (pp. 190–208). Oxford: Aldine.
Peterson, J. B., Morey, J., & Higgins, D. M. (2005). You drink, I drink: Alcohol consumption, social context and personality. Individual Differences Research,3(1), 50–58.
Pliner, P., & Mann, N. (2004). Influence of social norms and palatability on amount consumed and food choice. Appetite,42(2), 227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2003.12.001.
Pliner, P., & Salvy, S.-J. (2006). Food neophobia in humans. In R. Shepherd & M. Raats (Eds.), The psychology of food choice (pp. 75–92). Wallingford: CABI.
Polivy, J., Herman, C. P., Younger, J. C., & Erskine, B. (1979). Effects of a model on eating behavior: The induction of a restrained eating style. Journal of Personality,47(1), 100–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.1979.tb00617.x.
Rizzolatti, G., & Craighero, L. (2004). The mirror-neuron system. Annual Review of Neuroscience,27, 169–192. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2009.41.
Rizzolatti, G., Fogassi, L., & Gallese, V. (2001). Neurophysiological mechanisms underlying the understanding and imitation of action. Nature Neuroscience,2, 661–670. https://doi.org/10.1038/35090060.
Robinson, E., Blissett, J., & Higgs, S. (2013). Social influences on eating: Implications for nutritional interventions. Nutrition Research Reviews,26(2), 166–176. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954422413000127.
Robinson, E., & Higgs, S. (2013). Food choices in the presence of “healthy” and “unhealthy” eating partners. British Journal of Nutrition,109(4), 765–771. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114512002000.
Robinson, E., Oldham, M., Sharps, M., Cunliffe, A., Scott, J., Clark, E., et al. (2016). Social imitation of alcohol consumption and ingratiation motives in young adults. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors,30(4), 442–449. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000150.
Robinson, E., Tobias, T., Shaw, L., Freeman, E., & Higgs, S. (2011). Social matching of food intake and the need for social acceptance. Appetite,56(3), 747–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2011.03.001.
Romero, N. D., Epstein, L. H., & Salvy, S.-J. (2009). Peer modeling influences girls’ snack intake. Journal of the American Dietetic Association,109(1), 133–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2008.10.005.
Rosenquist, J., Murabito, J., Fowler, J., & Christakis, N. (2010). The spread of alcohol consumption behavior in a large social network. Annals of Internal Medicine,152(7), 426–433. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-152-7-201004060-00007.
Rosenthal, B., & Marx, R. D. (1979). Modeling influences on the eating behavior of successful and unsuccessful dieters and untreated normal weight individuals. Addictive Behaviors,4(3), 215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4603(79)90030-3.
Rosenthal, B., & McSweeney, F. K. (1979). Modeling influences on eating behavior. Addictive Behaviors,4(3), 205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4603(79)90029-7.
Salvy, S.-J., Howard, M., Read, M., & Mele, E. (2009). The presence of friends increases food intake in youth. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,90(2), 282–287. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.27658.
Salvy, S.-J., Jarrin, D., Paluch, R., Irfan, N., & Pliner, P. (2007a). Effects of social influence on eating in couples, friends and strangers. Appetite,49(1), 92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2006.12.004.
Salvy, S.-J., Kieffer, E., & Epstein, L. H. (2008a). Effects of social context on overweight and normal-weight children’s food selection. Eating Behaviors,9(2), 190–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2007.08.001.
Salvy, S.-J., Romero, N., Paluch, R., & Epstein, L. H. (2007b). Peer influence on pre-adolescent girls’ snack intake: Effects of weight status. Appetite,49(1), 177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2007.01.011.
Salvy, S.-J., Vartanian, L. R., Coelho, J. S., Jarrin, D., & Pliner, P. P. (2008b). The role of familiarity on modeling of eating and food consumption in children. Appetite,50(2–3), 514–518. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4002.BONE.
Sayette, M. A., Creswell, K. G., Dimoff, J. D., Fairbairn, C. E., Cohn, J. F., Heckman, B. W., et al. (2012). Alcohol and group formation: A multimodal investigation of the effects of alcohol on emotion and social bonding. Psychological Science,23(8), 869–878. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797611435134.
Sharps, M., Higgs, S., Blissett, J., Nouwen, A., Chechlacz, M., Allen, H., et al. (2015). Examining evidence for behavioural mimicry of parental eating by adolescent females: An observational study. Appetite,89(1), 56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2015.01.015.
Sheeran, P., Gollwitzer, P. M., & Bargh, J. A. (2013). Nonconscious processes and health. Health Psychology,32(5), 460–473. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029203.
Shiffman, S., & Rathbun, S. L. (2011). Point process analyses of variations in smoking rate by setting, mood, gender, and dependence. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors,25(3), 501–510. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0022178.
Shimizu, M., Johnson, K., & Wansink, B. (2014). In good company: The effect of an eating companion’s appearance on food intake. Appetite,83, 263–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2014.09.004.
Sinha, R. (2001). How does stress increase risk of drug abuse and relapse? Psychopharmacology (Berl),158(4), 343–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100917.
Sonnby-Borgström, M. (2002). Automatic mimicry reactions as related to differences in emotional empathy. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology,43, 433–443. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9450.t01-1-00312.
Spanos, S., Vartanian, L. R., Herman, C. P., & Polivy, J. (2014). Failure to report social influences on food intake: Lack of awareness or motivated denial? Health Psychology,33(12), 1487–1494. https://doi.org/10.1037/hea0000008.
Stel, M., & van Koningsbruggen, G. M. (2015). Healthy food consumption in young women. The influence of others’ eating behavior and body weight appearance. Appetite,90, 240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2015.03.016.
Tang, D. W., Fellows, L. K., Small, D. M., & Dagher, A. (2012). Food and drug cues activate similar brain regions: A meta-analysis of functional MRI studies. Physiology & Behavior,106(3), 317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.03.009.
Tanner, R. J., Ferraro, R., Chartrand, T. L., Bettman, J. R., & Van Baaren, R. (2008). Of chameleons and consumption: The impact of mimicry on choice and preferences. Journal of Consumer Research,34(6), 754–766. https://doi.org/10.1086/522322.
Uhart, M., & Wand, G. S. (2009). Stress, alcohol, and drug interaction: An update of human research. Addiction Biology,14(1), 43–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1369-1600.2008.00131.x.Stress.
Vartanian, L. R., Herman, C. P., & Polivy, J. (2007). Consumption stereotypes and impression management: How you are what you eat. Appetite,48(3), 265–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2006.10.008.
Vartanian, L. R., Herman, C. P., & Wansink, B. (2008). Are we aware of the external factors that influence our food intake? Health Psychology,27(5), 533–538. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-6133.27.5.533.
Vartanian, L. R., Sokol, N., Herman, C. P., & Polivy, J. (2013). Social models provide a norm of appropriate food intake for young women. PLoS ONE,8(11), e79268. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079268.
Vartanian, L. R., Spanos, S., Herman, C. P., & Polivy, J. (2015). Modeling of food intake: A meta-analytic review. Social Influence,10(3), 119–136.
Vollstädt-Klein, S., Loeber, S., Kirsch, M., Bach, P., Richter, A., Bühler, M., et al. (2011). Effects of cue-exposure treatment on neural cue reactivity in alcohol dependence: A randomized trial. Biological Psychiatry,69(11), 1060–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.12.016.
Wagner, D. D., Dal Cin, S., Sargent, J. D., Kelley, W. M., & Heatherton, T. F. (2011). Spontaneous action representation in smokers when watching movie characters smoke. Journal of Neuroscience,31(3), 894–898. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.5174-10.2011.
Webb, O. J., Eves, F. F., & Smith, L. (2011). Investigating behavioural mimicry in the context of stair/escalator choice. British Journal of Health Psychology,16(2), 373–385. https://doi.org/10.1348/135910710X510395.
Williams, A., Giles, H., Coupland, N., Dalby, M., & Manasse, H. (1990). The communicative contexts of elderly social support and health: A theoretical model. Health Communications,2(3), 123–143.
Wilsnack, R. W., Wilsnack, S. C., Kristjanson, A. F., Vogeltanz-Holm, N. D., & Gmel, G. (2009). Gender and alcohol consumption: Patterns from the multinational GENACIS project. Addiction,104(9), 1487–1500. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02696.x.GENDER.
Zin, N., Baharin, H., & Rosli, A. (2015). Can auditory icons Induce food intake mimicry? In Proceedings of the 5th international conference on computing and informatics (pp. 194–199). Retrieved from https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/e919/152de1ad1da5d01c2072c16370560ecababe.pdf.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duffy, K.A., Green, P.A. & Chartrand, T.L. Mimicry and Modeling of Health(-Risk) Behaviors: How Others Impact Our Health(-Risk) Behaviors Without Our Awareness. J Nonverbal Behav 44, 5–40 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10919-019-00318-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10919-019-00318-x